Category: Left politics
April 28th, 2017 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
In the May 2017 run-off between Emmanuel Macron and Marine Le Pen, the defeated first-round candidate Jean-Luc Mélenchon refused to endorse the liberal Macron over the neo-fascist Le Pen. Many of Mélenchon’s leftist supporters did the same, arguing positively for abstention.

Jean-Luc Mélenchon
The abstainers argued widely that Macron is a “neoliberal” and the voters faced a choice between the dictatorship of the market or a fascist president.
This failure to perceive any advantage of a pro-market liberal over the racist and neo-fascist authoritarian nationalism of Le Pen’s National Front, is a symptom of a deep ideological sickness that has endured for decades on the French Left.
The political degeneration of the French Left, which even exceeds that of its Corbynista counterpart in Britain, would be the subject of another blog. My purpose here is to focus on the abuse of the term “neoliberalism” and how this corrupted and overly-widened word has poisoned political discourse.
I also wish to show how some “neoliberals”, who do not include Macron, and whom I shall attempt to characterise more precisely than the n-word will allow, do indeed have connections with genuine fascism.
After the erosion of credibility in classical socialism, particularly after its failed experiments in the twentieth century, it must be understood that our sole alternative to the rising nationalisms of Le Pen, Trump, Putin, Xi, Erdoğan and others is a modern and democratic version of liberalism. Whatever his flaws, Macron fits into the latter category.
The degeneration of the “neoliberalism” label
The widespread use of the word “neoliberal” to describe anyone accepting a significant role for private property or markets has made the word so imprecise that it has become useless and beyond reform.
 Even the foremost historians of “the neoliberal project” have acknowledged the problem. Philip Mirowski and Dieter Plehwe wrote:
Even the foremost historians of “the neoliberal project” have acknowledged the problem. Philip Mirowski and Dieter Plehwe wrote:
“We can sympathize with the impatience for those who use the term ‘neoliberalism’ as a blanket swearword for everything they despise, or a brainless synonym for modern capitalism.”
Colin Talbot pointed out that “neoliberalism” has become “a term of abuse” to be used against “any type of pro-market reform or political position that recognizes markets may – in the right circumstances – be a good thing”. Consequently, everyone “from moderate social democrats to the most lurid free-marketeers gets lumped together under a convenient ‘neoliberal’ label.”
In a superb survey of its usage since the 1980s, Rajesh Venugopal concluded that “neoliberalism has become a deeply problematic and incoherent term that has multiple and contradictory meanings, and thus has diminished analytical value.”
Some may wish to retain the “neoliberal” label, to apply it to those free marketeers who attempt to shrink radically the size of the state, to privatise anything that walks, advocate economic austerity and deregulate the financial sector. This would certainly separate neoliberalism from the genuine liberalism of John A. Hobson, William Beveridge or John Maynard Keynes.
But I think that things are too far gone to allow any useful redefinition of the “neoliberal” label to succeed. It is perhaps best abandoned. Instead I wish to focus on a particular strain of so-called “neoliberalism”. This allows us to concentrate on some key issues.
Ludwig von Mises and fascism
Ludwig von Mises (1881-1973) and Friedrich Hayek (1899-1992) were key figures in the so-called Austrian school of economics. Among their major achievements were their contributions to the “socialist calculation debate” where they showed the practical and epistemic limitations of any system of national planning based on comprehensive public ownership.

Ludwig von Mises
While sharing with liberals the support for a market economy based on private ownership, von Mises and Hayek departed from both classical liberalism (of John Stuart Mill, for example) and from twentieth-century liberalism (of John A. Hobson, John Dewey and John Maynard Keynes, for example), in some important respects.
In a book originally published in 1927, Ludwig von Mises praised fascism as “an emergency makeshift” that “has, for the moment, saved European civilization”. This statement cannot be excused, despite the facts that it was in a book that was otherwise devoted to the promotion of classical liberal values, and that von Mises was a Jew who eventually had to flee the Nazis.
From 1932 to 1934 von Mises continued as an economic adviser in Austria, even to the “Austro-fascist” or “clerical fascist” government of Chancellor Engelbert Dollfuss, who assumed dictatorial powers, closed down parliament, smashed the trade unions, and banned several political parties. This does not mean that von Mises was a fascist, but other economists would have drawn the line at advising them.
Friedrich Hayek and the dictatorship of Augusto Pinochet

Friedrich Hayek
The idea that temporary dictatorships, even if murderous, might sometimes be necessary rubbed off onto von Mises’ student, Friedrich Hayek. Hayek argued that democracy, while desirable, can be temporarily dispensable, particularly in defence of private property.
Augusto Pinochet may have saved private property rights in Chile. But he imposed a vicious dictatorship that tortured an estimated thirty thousand civilians and murdered over three thousand.
The right to life, and freedom from torture, are existentially more basic, and hence even more important, than the right to property. Hayek visited Pinochet’s Chile and he failed to condemn these atrocious abuses of human rights. Hayek’s silence over abuses of basic human rights cannot be excused by his age: he was still publishing major books in the 1970s.
The twentieth century teaches us that Marxist socialism crushes human rights and leads to dictatorship. While opposing Communism, von Mises and Hayek (temporarily) tolerated some dictatorships and their removal of some basic human rights, including the rights of habeas corpus and to live without torture.
While earlier liberals had emphasized human rights, private property rights and democracy, in their reaction against socialism, von Mises and Hayek seemed to elevate private property rights over everything else. But private property rights require the protection of all actual or potential owners from torture or extermination. Basic human rights and democracy are vital, as well as the right to private property.
The Mont Pèlerin Society
The ideas of Mises and Hayek were prominent in the Mont Pèlerin Society, founded in Switzerland in 1947. The society accommodated a variety of views, including mainstream liberals plus some members who had collaborated with Nazism in the 1933-1945 period.
 The Mont Pèlerin Society was dominated by economists. No less than eight winners of the Nobel Prize in economics have been its members.
The Mont Pèlerin Society was dominated by economists. No less than eight winners of the Nobel Prize in economics have been its members.
The influence of economists is evident in the draft statement of aims of the Society. It opened with these words:
“Individual freedom can be preserved only in a society in which an effective competitive market is the main agency for the direction of economic activity. Only the decentralization of control through private property in the means of production can prevent those concentrations of power which threaten individual freedom.”
Agoraphobics (i.e. fearers of markets) such as George Monbiot and Naomi Klein will probably disagree, but there is a vital truth in this quotation.
The trouble is that it is also a half-truth. Private property and markets are necessary but insufficient to guarantee liberty, as countless market-based totalitarian regimes, from Putin’s Russia to Pinochet’s Chile, will testify. The Mont Pèlerin statement should have made this clear. Instead it gave licence to a view that only private property and markets matter.

Margaret Thatcher and Augusto Pinochet
Hence Mont Pèlerin fans, including UK Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher and US President Ronald Reagan, supported dictatorships and opposed sanctions against South African Apartheid.
In 1999, Thatcher even thanked the former dictator Pinochet for “bringing democracy to Chile”. Clearly, while addressing someone who in 1973 overthrew a democratically-elected government, she invested the term “democracy” with an esoteric, Thatcherite meaning. In truth, Pinochet was a torturer and an assassin.
Vital differences between liberalism and Mont Pèlerin neoliberalism
Even with this brief account we can see some wide, clear water between mainstream liberals such as Macron and Mont Pèlerin “neoliberals” such as Hayek. Unlike those “neoliberals”, modern liberals uphold the following five points:
-
While markets and private property are essential, they are not sufficient to guarantee human rights and liberty. Vigilance and debate, within a democratic system with a free press, are necessary as well.
-
Dictatorships, would-be dictators and all abuses of human rights must all be condemned, in market-based as well as in centrally-planned societies.
-
-
Because the owners of capital and labour do not, and cannot, meet on a level playing field, some legally-limited trade-union activity is warranted, along with reasonable employment rights and other protections.1
-
While early liberalism was born in an era of small-scale producers, modern industrial capitalism bestows an economic (alongside a moral) need for organized mass education, social security and healthcare, along with regulations and bureaucracies to ensure that markets worked effectively and consumers are protected.
If these liberal principles were understood, along with Macron’s support for them, abstention in the May 2017 French presidential elections would be impossible.
28 April 2017
Minor edits 1, 4 May – thanks to Pedra Pereira Hors.
|
My forthcoming book elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost
To be published by University of Chicago Press in December 2017
|
Endnote
-
Note that Macron (like his Socialist Party predecessor François Hollande) wants to reform the blundering and counter-productive French system of employment law, rather than to abolish all employment rights, which must at least conform to standards within the European Union.
References
Caldwell, Bruce J. and Montes, Leonidas (2015) ‘Friedrich Hayek and his Visits to Chile’, Review of Austrian Economics, 28(3), pp. 261-309.
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2016) ‘Some Limitations of the Socialist Calculation Debate’, Schmollers Jarhbuch, 136, pp. 1-26.
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2017) Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, forthcoming).
Mirowski, Philip and Plehwe, Dieter (eds) (2015) The Road from Mont Pèlerin: The Making of the Neoliberal Thought Collective, paperback edition (Cambridge MA: Harvard University Press). (Quote from p. xvii.)
Mises, Ludwig von (1985) Liberalism in the Classic Tradition. Translated by Ralph Raico from the German edition of 1927 (Irvington, NY: Foundation for Economic Education). (See pages 47 and 51.)
Posted in Democracy, George Monbiot, Karl Marx, Left politics, Liberalism, Ludwig von Mises, Markets, Naomi Klein, Politics, Private enterprise, Property, Right politics, Socialism
April 17th, 2017 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
“Bliss was that dawn to be alive.” With Labour’s landslide victory under Tony Blair, the general election of 1st May 1997 ended eighteen years of Tory rule.
The new government set out to implement a series of major reforms, including establishing devolved assemblies in Scotland and Wales, setting a statutory minimum wage, and injecting much-needed money into the education system and the NHS.
After winning two further elections with large majorities – in 2001 and 2005 – Labour’s period of office came to an end on 5th May 2010, when the Conservatives became the biggest party in Parliament. The Liberal Democrats made the mistake of entering into a coalition with the Tories, and paid the price when they lost most of their MPs in 2015.
So began a period of Tory rule that now seems that it could last for decades. But the Tories rule with the support of less than 50 per cent of the voters. If Blair had implemented electoral reform, then what might have happened instead?
Ending “division among the radicals”
Until the day of polling in May 1997, when the scale of his majority became clear, Tony Blair had considered a coalition with the Liberal Democrats after the election, He had negotiated with Paddy Ashdown (the leader of the Liberal Democrats) with that possibility in mind. But once Blair’s overwhelming victory was apparent, a coalition with the Liberal Democrats seemed unnecessary.
 But Blair still wanted to cooperate with the Liberal Democrats on several issues, including on electoral reform. He insisted that the two parties were natural allies, and they should not have gone their separate ways a hundred years earlier. In his first speech to a Labour conference after his landslide election victory, Blair declared:
But Blair still wanted to cooperate with the Liberal Democrats on several issues, including on electoral reform. He insisted that the two parties were natural allies, and they should not have gone their separate ways a hundred years earlier. In his first speech to a Labour conference after his landslide election victory, Blair declared:
“my heroes aren’t just Ernie Bevin, Nye Bevan and Attlee. They are also Keynes, Beveridge, Lloyd George. Division among radicals almost one hundred years ago resulted in a 20th century dominated by Conservatives. I want the 21st century to be the century of the radicals.”
By “division among the radicals” Blair referred to the 1900 decision to set up a party in parliament independent of the Liberals. Blair wished to reverse that mistake and install an enduring radical majority.
Labour’s 1997 promise of electoral reform
Blair wanted Labour and the Liberal Democrats to work together for progressive change, and, if possible, to exclude permanently the Tories from government, at least until they were forced to modernise and to abandon their reactionary, inward-looking nationalism.
“We are committed to a referendum on the voting system for the House of Commons. An independent commission on voting systems will be appointed early to recommend a proportional alternative to the first-past-the-post system.”
After the election, Blair continued his secret talks with Ashdown on co-operation between their two parties, including on the issue of electoral reform.
But what voting system should be chosen?
One problem was that the two parties found it difficult to agree on what “a proportional alternative” might mean. But a possible compromise emerged with a top-up system called “AV+”.
In addition, under AV+, each voter would get a second vote to elect a regional-level representative from a list of candidates for each party. An additional group of MPs would be elected via this route. This “top up” would ensure greater proportionality in Parliament.
Some people dislike AV+ because it creates two types of MP, with not all of them being responsible for a manageable constituency. In addition, AV+ does not satisfy purists who want a more proportional system.
Division of Labour
But the biggest problem with Blair’s strategy for long-term reform was Labour itself.
 While leading figures in his Cabinet such as Robin Cook, Mo Mowlam, Clare Short and Peter Mandelson supported electoral reform, Blair faced the implacable opposition of Chancellor Gordon Brown, Deputy Prime Minister and Secretary of State John Prescott, Home Secretary Jack Straw, numerous trade union leaders and an energetic campaign against proportional representation from Labour’s ranks.
While leading figures in his Cabinet such as Robin Cook, Mo Mowlam, Clare Short and Peter Mandelson supported electoral reform, Blair faced the implacable opposition of Chancellor Gordon Brown, Deputy Prime Minister and Secretary of State John Prescott, Home Secretary Jack Straw, numerous trade union leaders and an energetic campaign against proportional representation from Labour’s ranks.
Reasons for this opposition to electoral reform within Labour were numerous. But perhaps the most enduring argument was that Labour saw itself as a party committed to radical change in favour of working people, which was bound to meet fierce opposition from rich vested interests and the reactionary press.
 I can speak with a little authority here, because this was once my own major objection to proportional representation (PR). As loyal and active Labour party members, Peter Hain and I published a booklet in 1982 entitled Proportional Misrepresentation?
I can speak with a little authority here, because this was once my own major objection to proportional representation (PR). As loyal and active Labour party members, Peter Hain and I published a booklet in 1982 entitled Proportional Misrepresentation?
We argued that PR would favour parties of the centre, against parties like Labour who represented working people and were committed to radical change. The advantage of the existing system was that Labour could gain power and show piecemeal and in practice how socialist measures could work.
Although we were against PR, Peter and I argued for a change to the alternative vote (AV), without a top-up element. A few years’ later, Peter suggested that we develop our pamphlet into a book.
Thatcher in power
But this was after six years of Margaret Thatcher in power. Her Tory Party had won an overall majorities in 1979 and 1983, in both cases with less than 44 per cent of the vote. After 1983 I came to the view that Labour could not win the next election and the Tories could be power for about 15 years.1
 Just as the existing electoral system might be used by a left party for radical reform, it was being used by a newly-radicalised Tory party to divide the country, to undermine the welfare state and to attack the rights of working people.
Just as the existing electoral system might be used by a left party for radical reform, it was being used by a newly-radicalised Tory party to divide the country, to undermine the welfare state and to attack the rights of working people.
I had developed serious doubts about our 1982 arguments. So I declined Peter’s kind offer and he published the book in 1986 under his own name, fully acknowledging our previous joint arguments.
Others developed concerns similar to mine, especially as the years passed and the Tories remained in power with minority support. All this gave the impetus for Blair and others to push for PR in Labour’s 1997 manifesto.
But elements of Labour’s class-based tribalism remained strong, as did commitment to an ever-vague promise of something called “socialism” that only a majority Labour government could deliver. Hence Labour internally remained deeply divided on this issue, as it does to this day.
The Jenkins Commission
In December 1997, in line with the manifesto commitment, Blair set up a parliamentary commission under Lord Roy Jenkins, the former Labour minister and then Liberal Democrat peer. The Jenkins Commission would recommend which particular proportional system should be put before voters in a referendum.
 The Jenkins Commission reported in September 1998 and suggested the alternative vote top-up (AV+) system. Blair immediately faced intense opposition, from within his own Cabinet, from a large number of Labour MPs, from a large section of the Labour Party in the country, and from several trade unions.
The Jenkins Commission reported in September 1998 and suggested the alternative vote top-up (AV+) system. Blair immediately faced intense opposition, from within his own Cabinet, from a large number of Labour MPs, from a large section of the Labour Party in the country, and from several trade unions.
In 1997 Labour came to power with 43 per cent of the vote but won 63 per cent of the parliamentary seats. Any significant move toward greater proportionality would have deprived one hundred or more Labour MPs of their seats. Over one hundred turkeys would have to have voted for Christmas. The political barriers to this reform seemed unsurmountable. The recommendations of the Jenkins Commission were kicked into the long grass.
Several other attempts were taken to revive the project of electoral reform under the 1997-2010 Labour Government. Labour promised a review of the voting system in its 2001 manifesto. In 2003, talks were held between Labour and the Liberal Democrats on electoral reform.

But by 2010, under the new premiership of Gordon Brown, Labour retreated from its earlier promise of moving toward proportionality. Instead, Brown promised a referendum on the alternative vote (AV) without any top-up element. The Jenkins Commission had previously taken the view that such a minor change would not merit a referendum.
In fact, a referendum on AV was held in 2011, under the coalition government. The proposal was defeated by a large majority. This demonstrated the problem of convincing the public of the merit if a more complex system, which cannot be explained easily in one or two sentences. I raise this issue later below.
An alternative future
First we consider what might have happened if the more-proportional system of AV+ had been introduced sometime between 1997 and 2010.
In the 2010 election Tories got 36 per cent of the vote, Labour got 29 per cent and the Liberal Democrats 23 per cent. Under the existing voting system they got 306 seats, 258 seats, and 57 seats respectively. Under a more proportional system they would have got something like 255 seats, 204 seats and 162 seats respectively
Under the existing electoral system, a 2010 coalition between Labour and the Liberal Democrats would have had 315 seats, which is well short of an overall majority in a parliament of 650 seats. It would have been a minority coalition government, or other parties would have had to been involved. This was a significant obstacle, which played a part in scuppering any 2010 deal between Labour and the Liberal Democrats.
 But if a more proportional system had been in place in 2010, then a coalition between Labour and the Liberal Democrats would have had something like 366 seats, which would have been a clear overall majority. The Tories could have been kept out of power.
But if a more proportional system had been in place in 2010, then a coalition between Labour and the Liberal Democrats would have had something like 366 seats, which would have been a clear overall majority. The Tories could have been kept out of power.
Furthermore, Labour would have been obliged to cooperate with a centrist party, giving weight and prestige to its more moderate wing. Sure enough, there would have been protest on the left, led by a Jeremy Corbyn or a John McDonnell, but they would have probably been kept away from Labour’s levers of power.
As the years followed, all sorts of alternative scenarios might have then unfolded. But a referendum on Brexit would have been unlikely, or it would have taken place under conditions more favourable to the Remain campaign.
In short, if the electoral system had been changed in this way before 2010, then we would not be in this mess that we are now. We could still be on the road to a progressive future, rather than fighting a desperate battle against intolerant bigots and nationalists, who would drive the UK economy off a cliff to satisfy an anti-immigration sentiment fed by years of economic failure.
Winning the battle for electoral reform
Electoral reform is highly unlikely under a Tory government and hence the first objective must be to remove the Conservatives from power. This will require a progressive alliance of Labour, Liberal Democrats and Greens, which at present does not seem feasible. Also the Tories might remain in power for some time.
 But a tiny consolation of this dismal entrapment is the time it gives us to debate the best system, which would offer something closer to proportionality, and would have a chance of convincing the electorate.
But a tiny consolation of this dismal entrapment is the time it gives us to debate the best system, which would offer something closer to proportionality, and would have a chance of convincing the electorate.
Some kind of top-up system based on 400-500 single-member constituencies, topped up with a further 100-200 MPs elected from party lists, seems the best way forward. It is a possible compromise that the parties involved can accept, and it is understandable by the public.
But I have now come to the view that the use of AV to elect the MPs for the single-member constituencies is both intrinsically flawed and difficult to explain to the electorate. A better and easier-to-explain alternative exists.
There were several reasons why the AV referendum was lost in 2011, including the fact that many prominent figures in the Labour Party openly opposed it. Another was the complexity of AV itself. As Tom Clark wrote in the Guardian:
“Leaflets from the electoral commission, which were designed to explain what the reform would mean to every household with meticulous neutrality, ended up making AV look horrendously complex. The blurb summed up first-past-the-post in just three sentences, while describing AV with an excessively complex example election, which required three diagrams and text that spilled over four pages.”
A further problem is that AV itself, even if it can be explained to the public, has serious intrinsic flaws.
Why AV is flawed
The alternative vote (AV) is widely criticised by experts on voting systems. We are concerned with systems designed to elect one person, from a list of candidates, to a single position or seat.
Consider an example of a mayoral election with three candidates Ms Left, Ms Centre and Ms Right. Both Ms Left and Ms Right are pretty extreme, and the electorate is polarised. An AV systems is employed and the candidates get the following first-preference votes: Left 33 per cent, Centre 31 per cent and Right 36 per cent. Under the AV system Ms Centre would be eliminated and her second preferences would be allocated to Left or Right. One of the more extreme candidates would win, in a run-off between Left and Right.

Nicolas de Condorcet
But imagine a local newspaper had run an extensive poll which showed that if there had been a run-off between Centre and Right, then Centre would have won. And if there had been a run-off between Centre and Left, then Centre again would have won. In other words, a majority in all cases preferred Ms Centre to any of the extremes.
Technically this is known as a Condorcet winner – a person who would win all two-candidate elections against each of the other candidates in turn.2 A serious problem with AV is that it can often eliminate a Condorcet winner. More generally, a major problem with AV is that it can often militate against strong and popular compromise candidates.
Why Approval Voting is better than AV
If there were (say) four candidates for a parliamentary seat, then the electors may vote (with crosses rather than numbers) for zero, one, two, three or four of the candidates. The votes for each candidate are added up, and the candidate with the highest number of votes is elected. Simple.
Of course, an elector voting for none or four of the candidates in this case would have no effect on the result, except he or she would be helping to give an overall indication of the overall level of approval (or lack of it) for each candidate.
As well as its technical superiority, a huge advantage of approval voting is that it is much easier to explain and to understand.
My proposal is for an approval voting system for single-member constituencies, plus a party-list top-up in regional units, to move closer to proportionality. I propose Approval+.
High stakes
Rising above the technical details, a lot is at stake here. If a more proportional system had been introduced in 1997-2010 then we could have avoided the disastrous prospect of decades of Tory rule, elected each time on 40 per cent or less of the vote.
When asked, the UK public support a more proportional system. A 2015 poll showed that 57 per cent of the public agreed with the principle that “the number of seats a party gets should broadly reflect its proportion of the total votes cast” – compared to only 9 per cent who disagreed.
We need to think about the best and most persuasive system of electoral reform, and set about the task of building a progressive alliance to implement it.
17 April 2017
Minor edits – 18 April, 1, 13, 14 May, 6 June, 14 July, 12 August, 3 September 2017
Footnotes
1. I turned out to be too optimistic: the Tories were in power for 18 years. Using a statistical analysis, I developed my sceptical 1980s view of Labour’s chances while I was on the ruling council of the Labour Coordinating Committee. My assessment was unpopular among budding, ambitious Labour politicians.
2. Nicolas de Condorcet (1743-1794) was a French revolutionary, mathematician, advocate of female suffrage and friend of Thomas Paine.
3. This is a very useful but long video. To cut straight to Approval Voting, the first 36 minutes may be skipped.
References
Hain, Peter and Hodgson, Geoff (1982) Proportional Misrepresentation? (London and Nottingham: Tribune and Institute for Workers Control).
Hain, Peter (1986) Proportional Misrepresentation: The Case against PR in Britain (Guildford: Wildwood House).
Posted in Brexit, Jeremy Corbyn, Labour Party, Left politics, Liberalism, Tony Blair, Tony Blair, Uncategorized
March 26th, 2017 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
A quiz
Where are these quotes found?
“If a man has sexual relations with a man as one does with a woman, both of them have done what is detestable. They are to be put to death; their blood will be on their own heads.”
“If a man takes a wife … [and] did not find proof of her virginity. … If … the charge is true and no proof of the young woman’s virginity can be found, she shall be brought to the door of her father’s house and there the men of her town shall stone her to death.”
“When you go out to battle against your enemies, and the … God delivers them into your hands and you take them away captive, and see among the captives a beautiful woman, and have a desire for her and would take her as a wife for yourself, then you shall bring her home to your house, and she shall shave her head and trim her nails.”
“If two men, a man and his countryman, are struggling together, and the wife of one comes near to deliver her husband from the hand of the one who is striking him, and puts out her hand and seizes his genitals, then you shall cut off her hand; you shall not show pity.”
“If you hear in one of your cities … anyone saying that some worthless men have gone out from among you and have seduced the inhabitants of their city, saying, ‘Let us go and serve other gods’ … then you shall investigate and search out and inquire thoroughly. If it is true … you shall surely strike the inhabitants of that city with the edge of the sword, utterly destroying it and all that is in it …”
“A woman must learn in quietness and full submissiveness. I do not permit a woman to teach or exercise authority over a man; she is to remain quiet.”
All six quotes are from the Bible: the sixth is from its New Testament (see, respectively, Leviticus 20:13, Deuteronomy 22:21, Deuteronomy 21:11, Deuteronomy 25:12, Deuteronomy 13:12-15, Timothy 2:1). None of these quotes is from the Qur’an.
During March 2017 on Twitter I asked people to identify the source of each quote. In each case a minority (of between 7 and 25 per cent) guessed (wrongly) that the quote might be from the Qur’an. A majority identified the correct source in the case of the first, second and fifth quotes only.
The source of each quote can be easily discovered via Google. Maybe some people checked online before voting. In which case the unaided errors are likely to be larger.
Addressing this quiz, I wish to make two points. The first concerns equitable treatment of religious texts. The second concerns the possibilities of reform in different religions. The second point is more complex than the first.
Anti-Muslim prejudice
It is quite rare to find people quoting statements like the above from the Bible. But herein lies a contradiction. Muslims are often judged by their religious texts, but the same standards are less widely applied to Christians.
Sadly, in these dangerous times, there is a rising tide of anti-Muslim prejudice. To fuel this, some quote such inequitable or punitive statements from the Qur’an or Hadith, some chilling in their medieval intolerance. People should be aware of all the important messages in the Qur’an. But they should also be aware that the Bible is equally discriminatory and punitive.
Neither does the New Testament absolve Christianity. The religious laws in the Old Testament were not overturned by the New. Jesus himself is reported as saying: “Think not that I am come to destroy the law, or the prophets: I am not come to destroy, but to fulfil. … Till heaven and earth pass, one jot or one tittle shall in no wise pass from the law, till all be fulfilled” (Matthew 5:17-18). St Paul in Colossians (3:18) and in Ephesians (5:22-24) instructed women to submit to the commands and desires of their husbands.
Anti-Muslim bigots want to stop Islam but they do not want to offend Christians. Yet Christianity too has been responsible for a great deal of discrimination around the world. Its ancient punitive laws are no better than those found in Islam. Many Christians have moved on, to preach love and charity. But my initial point here concerns the texts themselves.
The intention here is not to let Islam off the hook. Quotes can be found in Islam’s Qur’an or Hadith that are discriminatory or brutally punitive.
If anti-Muslim bigots were really concerned about some aspects of Islamic religious law, then they should show the same concern about backward statements in the Bible, which are supported by some fundamentalist Christians. All religions have problems – not just Islam.
To defeat the hard right we have to acknowledge that there are popular fears about Islam, albeit often ungrounded in fact. Simply decrying such worries as racist, especially in the wake of terrorist attacks by alleged Muslims, helps to amplify the right-populist fear that elites are covering up the truth. While vigorously defending the universal right of peaceful worship, we should be able discuss the flaws in any religion.
Religion and law
Some problems with religion are bigger than others. These concern not simply the written word itself, but how it is interpreted and the extent to which it is followed. Here there are important differences between major religions.
This leads me to my second point deriving from the quiz above. This point requires an examination of the institutional nature of a religion and its relation to law.
For most (sadly not all) Christians and Jews today, the Old Testament is no longer regarded as supreme law. It does not overturn state laws. Believers are not generally obliged by their religion to punish those that break its rules. Believers agree to accept the authority of democratic states, even if they contradict their religion.
Crucially, despite sharing its Abrahamic roots with Judaism and Christianity, Islam currently sustains a different relationship between law and society. Those that miss-label criticism of Islam as “racism” inadvertently and inappropriately shift attention onto ethnic or racial characteristics, thus ignoring the social rules and norms that religions infuse into cultures.
We need to consider how a religion works, at the level of the promulgation and practical enforcement of its social rules.
The evolution of Christianity
Christianity became the dominant religion in the West when, in the fourth century AD, the Roman Emperor Constantine favoured it, and suppressed other religions. Established as the official religion of the Roman and Byzantine empires, it came to dominate the elites of medieval Europe and spread via colonialism to other continents. Although some were willing converts, many other ordinary people were obliged to become Christian because their rulers hitched onto that faith. It was largely a top-down process, often imposed by higher authorities.
In Christian Europe most ordinary people were denied access to the Biblical texts until the Reformation. In England the Bible was not widely available in English until the seventeenth century, at a time when a large majority of the population were illiterate. The Bible was used selectively and deviously by those in power, to maintain the authority of the state and of the nobility. They did not devolve matters of judgement or punishment to ordinary people.
The chronic disadvantage of the ruling-class monopoly of access to religious texts in Christian Europe was the suppression and ignorance of the population. But the top-down imposition of Christianity did allow for more flexibility. Official doctrine could shift as new circumstances and interests emerged.
When mass education belatedly spread in Europe in the late nineteenth century, its peoples were already entering a more secular and enlightened age.
The adaptability of Judaism
Even before the destruction of Jerusalem by the Romans in 70 AD, the Jews were dispersed throughout the Roman Empire. Catastrophic destruction in their homeland in Judea led to a further diaspora. The Jews were always in a minority in the places that they were tolerated. They retained their religion and customs, but otherwise adapted as much as possible to local laws and traditions.
For example, laws that required them to kill apostates (Deuteronomy 13:6-10) were eventually abandoned in deference to the laws in their host country. Adaptation was the necessary (but sadly sometimes insufficient) price for their survival.
Dispersed from their homeland, the Jews had to survive as minorities within other states. While keeping their religion, they otherwise adapted to local laws and customs.
Enforcement mechanisms in Islam
By contrast to Christianity, Islam has remained to a large degree a devolved system, with rules enforced by religious conversion and the dedication of its adherents. It offers powerful incentives for conversion and strong disincentives against apostasy.
Islamic scriptures provide a complex legal system governing the spheres of work and civil society, as well as of the family. The enforcement of these rules relies primarily on religious adherence and devotion, with less reliance on legal authority buttressed by the state.
Islamic religious and legal rules developed in communities where states were often weak and societies were fragmented into tribes and clans. Although Islamic legal texts decree that rulers have the duty to enforce laws, many of these laws are derived from religious sources and believers also have an obligation to enforce them.
Islam spread over a vast territory, encompassing many different languages and ethnicities. It did not rely on a strong, centralized, state apparatus. The shared, engrained, cultural dedication to religious rules made a smaller state possible.
Consequently, many legal rules in Islam are enforced bottom-up, by the authority of God as devolved to believers, rather than top-down by the authority of courts or governments.
Islam’s problems with modernisation
Despite its enormous cultural and scholastic achievements, especially from the eight to the thirteenth centuries, Islam turned out to be less adaptable than Christianity or Judaism. It relied on educated local observance from the bottom up. Within a state it was typically the religion of the majority rather than a minority.
Although there was scope for different interpretations, the Islamic fusion of law with religion created a largely conservative system of belief. In addition, the devolution of rights of legal judgment and punishment to individual believers contrasts with legal norms in the modern West, where citizens are prohibited from taking the law into their own hands.
A key problem with Islam is that many of its adherents have not yet modernized and accepted the practical supremacy of secular law. Backward cultural practices, often transmitted from less-developed countries with weak legal systems, have survived among Muslims, and are sustained by the religious customs of immigrant communities. Many Muslims do not accept the authority of secular law and democratic government above that of their religion. Many Muslims live in, or originate from, underdeveloped countries that have not experienced an equivalent of the Enlightenment.
Although the overwhelming majority of Muslim immigrants in developed countries comply with the law and shun violence, some still put religion above law and above democracy. Within this group there are some violent extremists.
This problem stems from the religiously-motivated, devolved mechanisms of reactionary rule-enforcement and punishment within Islam. We should recognize this problem, as well as the hugely valuable, past, present and potential contributions of Islamic culture to Western democracies.
The Muslim reformers
We should support the efforts of those Muslims that are trying to reform and modernise Islam, just as Christians and Jews have largely accepted the authority of secular law. We should not simply oppose all criticism of Islam, for fear that it might offend or cause division. Instead, we should add our voice to the modernisers, in their struggle against fundamentalists and conservatives.
The reformers have issued a Declaration defending gender equality, freedom of speech and freedom of religion, stating that they are for “secular governance” and “against political movements in the name of religion.” They have called for the separation of “mosque and state”, so that law rests on secular rather than religious authority. This is the route towards a tolerant and inclusive society, within a framework of universal human rights, democracy and secular law.
Accordingly, we can accept multiculturalism if it means recognition of cultural diversity, but we cannot accept multi-legalism. Diverse peoples must live together, but within a single framework of law, under a democratic political system.
Conclusion
Unreformed and discriminatory versions of Islamic law represent a problem for any society that is based on Enlightenment principles, and which requires obedience to laws that are enacted by the state. It creates major difficulties for integration and assimilation.
We must, of course, protect the freedoms of Muslims and others to worship, to express themselves, and to obtain a livelihood. Cultural and religious diversity can greatly enrich a modern nation, but only if the state legal system and over-arching secular values remain healthy and intact. Such a diverse society requires a just legal system and strong secular values, not least to protect the human rights of members of minority religions or ethnicities.
The strident but imprecise rhetoric of “Islamophobia” – advanced among others by politicians trying to capture the votes of Muslims in Western democracies – has blocked serious discussion of the merits and demerits of Islamic institutions. It can undermine careful and scholarly attempts by Muslims and others to identify where these institutions are in need of reform.
It cannot be repeated often enough that informed criticism of some Islamic rules or practices is not equivalent to bigotry toward Muslims. Racism, and persecution of Muslims, are serious problems and should be vigilantly opposed. But the option to criticise Islam, Christianity or any other set of beliefs, is an important human right, and it should be protected.
26 March 2017
Minor edits – 5 June 2017
|
This book elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost
Published by University of Chicago Press in January 2018
|
Posted in Assimilation, Christianity, Democracy, Immigration, Islam, Judaism, Left politics, Liberalism, Politics, Religion
February 21st, 2017 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
Despite her previous opposition to Brexit, Prime Minister Theresa May tells us that the UK must quit the European Union because it is “the will of the people”. Despite aligning himself in the Remain campaign during the referendum, opposition leader Jeremy Corbyn says that we must pursue Brexit because it is “the will of the people”. Many Labour MPs, who are critical of Corbyn and believe that leaving the EU will be a disaster, voted to start the exit process, without any guarantees or conditions, because it is “the will of the people”.
This is now the dreadful state of our democracy. On crucial matters such as immigration and Brexit, we are governed by tabloid headlines, opinion polls and lie-infested referendums. The “will of the people” has become the catch-phrase of the cowering, lazy or unprincipled politician. No longer driven by truth or principle, many of them knowingly connive in disaster because it is regarded as the peoples’ will.
Where can following “the will of the people” lead?
Polls show that the use of torture has sometimes, even recently, received majority support from the US public. President Donald Trump was elected after expressing a desire to re-introduce torture. Torture is “the will of the American people” – as some might put it.
But the use of torture has been against the Eighth Amendment to the United States Constitution since 1791. The very role of a constitution is to help protect rights and freedoms, even if “the will of the people”, or of a deviant President or Prime Minister, would take them away. One of the limits to democracy is that it should not be able to overturn our human rights.
 Dictators and populists are fond of referendums because they deploy “the will of the people” against constitutional safeguards. Hitler held a referendum in 1933, to garner mass support to withdraw from the League of Nations. In 1934 he held another referendum, which endorsed his bid for supreme power in Germany. Yet another referendum in 1936 ratified Hitler’s military occupation of the Rhineland and his one-party state. A fourth referendum in 1938 approved Hitler’s annexation of Austria. All propositions in these plebiscites received huge majorities.
Dictators and populists are fond of referendums because they deploy “the will of the people” against constitutional safeguards. Hitler held a referendum in 1933, to garner mass support to withdraw from the League of Nations. In 1934 he held another referendum, which endorsed his bid for supreme power in Germany. Yet another referendum in 1936 ratified Hitler’s military occupation of the Rhineland and his one-party state. A fourth referendum in 1938 approved Hitler’s annexation of Austria. All propositions in these plebiscites received huge majorities.
The death penalty
In recent polls in the USA, 60 per cent of the adult population supported the death penalty for murder, despite 64 per cent also believing that it does not lower the murder rate and 59 per cent believing that innocent people had been wrongly executed in the previous five years.
 In the UK in 1983, around 75 per cent of people were in favour of the death penalty. Although recent polls show a lower level of support, it is still close to 50 per cent.
In the UK in 1983, around 75 per cent of people were in favour of the death penalty. Although recent polls show a lower level of support, it is still close to 50 per cent.
Imagine that we had a referendum to re-introduce the death penalty in the UK. Thanks to some reactionary newspapers, it is possible that the proposal would gain majority support. But that does not justify its re-introduction, even if it was “the will of the people”. The morality of a law cannot be decided by popular vote.
Should homosexual acts be legal?
In some states of the USA there were laws prohibiting sodomy (between same-sex or different-sex couples) until 2003. As recently as 2004, the number of people polled in the USA who thought that homosexual acts should be illegal exceeded the number who thought they should be legal.
 By these measures, according to “the will of the people” homosexual acts should not have been made legal in 2003 or 2004.
By these measures, according to “the will of the people” homosexual acts should not have been made legal in 2003 or 2004.
But opinions change. This is another major problem with being governed by “the will of the people”.
After 2004, support in the USA for the legality of homosexual acts rose steadily. By 2016, the number supporting legality exceeded the contrary view by 40 per cent.
in the UK, as recently as 1998, 50 per cent of respondents in a poll thought that homosexual acts were “always” or “mostly” wrong, compared with 31 per cent saying they were “rarely” or never wrong.
Since then, opinion has switched, largely because leading politicians in the Tory as well as other major parties (with the notable exception of UKIP) have countered a sizeable segment of public opinion and underlined gay rights as a matter of principle.
By 2012, only 28 per cent of respondents in the UK thought that homosexual acts were “always” or “mostly” wrong, compared with 57 per cent saying they were “rarely” or never wrong. The will of the people can change.
The “will of the people” can be wrong or immoral
Whatever the “will of the people”, homosexual acts are either morally admissible or immoral. Moral principles are not determined by referendums or opinion polls.
 Instead, they must be the subject of ongoing, informed debate, guided by the need to minimise harm, alongside “an egalitarian conception of the good, focusing on equal opportunities for a worthwhile life” (as Philip Kitcher puts in his important book on The Ethical Project).
Instead, they must be the subject of ongoing, informed debate, guided by the need to minimise harm, alongside “an egalitarian conception of the good, focusing on equal opportunities for a worthwhile life” (as Philip Kitcher puts in his important book on The Ethical Project).
Consider another illustration. In 1984, 49 per cent of the UK public agreed “a man’s job is to earn money; a woman’s job is to look after the home and family”. But by 2012, only 13 per cent subscribed to this view.
Considerations of equal rights and equality of opportunity militate against such gendered attitudes and the discrimination that they sustain. While there is much more to be done, arguments have been won, opinions have changed and progress has been made. People can be persuaded that their previous opinions were wrong.
The need for experts
Just as votes cannot establish what is moral or immoral, they cannot determine what is scientifically valid and what is not. A majority of Americans would disregard claims concerning human-induced climate change. For many Americans, they are all part of a “hoax” to promote more intervention by the Federal Government.
Democratic votes cannot establish the veracity of scientific claims. Science proceeds through detailed scrutiny of claims by experts in a specialist field and a dialogue of different expert views. It thus creates an evolving consensus over what truths have been established and what research must be prioritised for further investigation.
 In the case of climate change, there is a strong consensus that human activity is leading to global warming. Albeit imperfect, this is the best indication we have of scientific truth. It is not the opinion of the general public, most of whom do not understand climate science.
In the case of climate change, there is a strong consensus that human activity is leading to global warming. Albeit imperfect, this is the best indication we have of scientific truth. It is not the opinion of the general public, most of whom do not understand climate science.
Another common fallacy, perpetrated by people who do not understand economics, is that we should treat the budgeting problems of a national economy in the same way that we treat our individual or household budgets. This is the “every housewife knows” economics of Margaret Thatcher and her ilk.
This mistaken view ignores the capacity of many sovereign states to issue money and sustain deficits: unlike individuals or firms, such states cannot go bankrupt. It ignores the fact that what may be true for an individual may not be true in the aggregate, as Keynesians and others have pointed out for decades.
Many economists (possibly most economists in the UK) accept this Keynesian argument. But it is difficult to get the point across to the general public, so that they elect governments that pursue austerity policies, which reduce aggregate demand and economic growth, leading to increased debt.
The role of democracy
If the behaviour of most British MPs over Brexit were taken as a guide, there would be no role for MPs at all. They blindly follow “the will of the people”, even when they know that it will lead to adverse economic and political outcomes.
 If this were a valid guiding rule, then MPs would be redundant. They could be replaced by online opinion polls on every question. The public would be invited to vote over every piece of legislation and “the will of the people” could be upheld.
If this were a valid guiding rule, then MPs would be redundant. They could be replaced by online opinion polls on every question. The public would be invited to vote over every piece of legislation and “the will of the people” could be upheld.
Before long we might be putting immigrants in sealed trains to remote or foreign destinations, and publicly flogging delinquents to teach them a lesson.
Democracy is vital not because it provides a means of implementing “the will of the people” on any specific proposal. The primary purpose of democracy is to legitimate government. It replaces unacceptable claims that rulers are legitimised by the “will of God” or by their family lineage.
There is a strong case for improving our democratic institutions, and the functioning of democracy itself. There are also forceful arguments for increasing participation in some local and workplace decisions, where we are intimately affected and have local knowledge. But there are severe practical and moral limits to the extension of democracy over all our affairs.
At least at the national level, in any large and complex socio-economic system, democracy must involve representatives rather than delegates. Representatives must be given some autonomy to seek expert advice and make judgments on complex issues. Extensive participatory democracy in such circumstances is both unfeasible and undesirable.
Members of Parliament receive a mandate from their electorates to represent their interests. Representing interests does not mean polling opinions: that is the lazy and irresponsible option. Instead it is a matter of exercising informed judgment. It is a question of deliberation and interpretation, involving the use of expert advice. We know that MPs often get things wrong. That is why their constituents have the opportunity to remove them at the next election.
The reactionary media are not solely to blame
The reactionary media and their malign influence on public opinion are not the sole cause of the current political malaise in Britain and the USA. Among others, one can blame the intellectually-lazy part of the Left, which trots out the mantra of “democratic control” whenever it sees a policy problem.
One can also blame the majority of economists, who have abandoned all moral considerations save for utility maximisation (or mere “satisfaction”) by “rational fools” (the term used by Nobel Laureate Amartya Sen).
Hence it is not just the reactionary media that are to blame. Many political activists have been intellectually lazy for too long. We need an enhanced and better-informed conversation concerning rights, morality and practical institutional design.
Armed with this knowledge, we need to hold our representatives to account, and expose the laziness and lack of principle of those who blindly follow “the will of the people”. If they see themselves as nothing more than unintelligent voting machines, then they should give up their positions to others, who would be guided by moral principles and offer greater dedication to the true interests of the people that they are supposed to serve.
21 February 2017
Minor edits – 28 February, 7 March, 4 May
|
This book elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost
Published by University of Chicago Press in January 2018
|
Bibliography
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2017) Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, forthcoming).
Kitcher, Philip (1993) The Advancement of Science: Science without Legend, Objectivity without Illusions (Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press).
Kitcher, Philip (2011) The Ethical Project (Cambridge MA: Harvard University Press).
Sen, Amartya K. (1977) ‘Rational Fools: A Critique of the Behavioral Foundations of Economic Theory’, Philosophy and Public Affairs, 6(4), pp. 317-44.
Posted in Brexit, Democracy, Left politics, Liberalism, Nationalization, Property, Uncategorized
January 28th, 2017 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
The political earthquakes of 2016 are probably the beginning of a series of major ruptures in world politics. Donald Trump was elected in the USA, Britons voted for Brexit, Turkey lurched toward dictatorship, Brazil ejected a democratically-elected president, Russia extended its global influence, and China tightened internal security while building military bases in the South China Sea.
From America to Asia, authoritarian nationalism is on the march. The future of old alliances is cast in doubt, raising a renewed spectre of global war.
These seismic changes should prompt us to reconsider our priorities. Is ‘neoliberalism’ – whatever that means – our main enemy? Or is it rising authoritarianism and nationalism instead?
We have been here before, albeit with much less dangerous military weapons. The rival imperialisms of the nineteenth century led to the First World War. Collapsing imperial dynasties triggered revolution in Central and Eastern Europe. Communists successfully seized power in Russia in 1917. Post-war political and economic turbulence led to the triumph of fascism in Italy, Germany and Spain. Imperial Japan invaded nationalist China.
I am not suggesting that history will repeat itself in the same way. But it is important to understand how the tectonic plates of political change affected the way we understand and map political positions, and the way in which we prioritise political issues.
The thirty-year squeeze (1918-1948)
Europe suffered economic depression for much of the interwar period. The financial crash of 1929 exacerbated the crisis and led to a collapse of world trade. Liberal defenders of the market economy were put on the defensive: capitalism seemed at the end of its tether.

Beatrice & Sidney Webb
Meanwhile, some intellectuals from the USA and Britain – including Labour stalwarts George Bernard Shaw and Sidney and Beatrice Webb – visited the Soviet Union brought back glowing accounts of an expanding economy and a joyful population. (The Soviet propagandists explained away disasters such as the Ukranian Famine as resulting from sabotage by rich peasants or foreign agents.)
With the crisis of capitalism, the rise of fascism and the apparent success of Soviet Russia, many British and American radicals became Communists or fellow travellers. For them, liberalism and the defence of the market economy seemed a weak or unviable option.
The choice seemed to be between two forms of authoritarian government: much better the one that proclaimed equality and opposed racism. (But in reality, the Stalin regime promoted antisemitism, genocide against several other ethnic minorities, and dramatic internal inequalities of power.)

Stalin, Roosevelt and Churchill in 1941
The alliance between Russia and the West in the Second World War smothered criticism of what was really going on within Stalin’s regime. But, with the beginning of the Cold War in 1948, socialists were forced to make a choice between either supporting an antagonistic and undemocratic foreign power, or aligning with the USA and its allied democracies.
Labour under Clement Attlee aligned with the West. But rose-tinted visions of Soviet Russia or (from 1949) Mao’s China lived on among he Left.
In major European democracies, the thirty years between the end of the First World War and the start of the Cold War had seen liberalism squeezed, between socialism on the one hand, and reactionary authoritarianism on the other.
‘American imperialism’ and the rise of neoliberalism
Things were different in the USA, which polarised between forms of Republican conservatism and Democratic liberalism. But rising tensions in the Cold War, and the eruption of the Vietnam War in the 1960s, made American-style liberalism less attractive for the global Left.
 Marxist-led national liberation movements in Cuba, Indochina and elsewhere kept the collectivist vision alive for the Left around the world. Liberalism was see as the fake ideology of American imperialism and the global bourgeoisie.
Marxist-led national liberation movements in Cuba, Indochina and elsewhere kept the collectivist vision alive for the Left around the world. Liberalism was see as the fake ideology of American imperialism and the global bourgeoisie.
Some have argued that neoliberalism was reborn in the 1970s, when conservatives such as Ronald Reagan and Margaret Thatcher adopted a vision of expanding markets and a contracting state. Although the Left could never agree on what ‘neoliberalism’ meant, they mostly agreed that it was the main enemy.
Much of the Left, throughout the world, had never got rid of its agoraphobia – its fear of markets. Private enterprise and market forces were always and everywhere seen as the problem. Liberals, who defended private property and markets as well as human rights, were mocked as the bourgeois enemy.
Our brave new world
But the global tectonic plates are now shifting abruptly, in an erupting national and international crisis, as big as anything since 1948.
Nationalist leaders strut around the world stage. They stock up their nuclear and conventional arsenals and jostle for geopolitical advantage.
Torture is endorsed. Journalists are threatened or imprisoned. Scientific findings on climate change are denied. Intellectuals and experts are ridiculed. Ignorance and dogma are celebrated. Truth is swamped by lies. Legislation protecting workers and the poor is undone. Minorities are attacked and made scapegoats. Racism is given licence. People suffer discrimination on the basis of their religious or other beliefs. Democratic systems are damaged. Judges and lawyers are treated as traitors. The rule of law is undermined.
In this dangerous new world, it matters less whether that railway is nationalised or whether water distribution is in public ownership. Forms of ownership are always secondary to the actual provision and distribution of vital goods and services. But when our rights and liberties can no longer be taken for granted, questions over forms of ownership move even further down the ranking of priorities.
The ubiquitous, trivialising idea that the Left is defined in terms of public provision, and Right as private provision, is historically recent and a gross reversal of their original meanings. It is also a polarisation of lesser relevance in this world of rising authoritarian nationalism.
Our fundamental rights, our liberty, and the rule of law are now increasingly threatened. Their defence becomes the great struggle of our time.
This lesson is hardest for Americans and Britons, who were spared domestically from the jackboots of twentieth-century despotism. Struggles for British and American national liberty are beyond living memory. We have grown fat and lazy on the fruits of the liberal order. We have taken for granted its institutions and underestimated their fragility. We must repair our vigilance.
The liberal opportunity
For 100 years, for the reasons given above, liberalism has been marginalised. Now is its opportunity – indeed its urgent necessity.
Unlike our grandparents in the crisis-ridden 1930s, we have seen the socialist experiments of the twentieth century and counted their cost at 90 million lives. History and social science have more to teach us. If we wish to learn, we can know more about how markets work. We can understand the informational, organisational and other impediments to comprehensive national planning. We can appreciate why countervailing politico-economic power, based on a strong private sector, are necessary to buttress democracy and resist authoritarianism. The twentieth century has taught us these lessons.
The old Marxist mantra of bourgeoisie versus proletariat is also ungrounded in reality. Instead we have a highly fragmented working class, much of it enduringly aligned with authoritarianism and nationalism. Marxism relies on a quasi-religious and nonsensical belief that the working class – whatever it actually believes or strives for – carries our human destiny.
Class struggle has mattered, but it has never been the main motor of history. What have mattered more have been struggles for power, by individuals, dynasties, nations, religions or ideological movements.

The Storming of the Bastille in 1789
Liberalism was one of those movements. Based on the imperatives of equality and liberty, it matured in the Enlightenment.
Liberalism rose up in the English Civil War of the 1640s, in the American Revolution of the 1770s, and in the French Revolution of 1789, in titanic struggles against despotism and oppression.
Now, once again, liberalism is centre stage, as the enemy of authoritarian nationalism.
The liberal rainbow
Its allies are not those who pander to authoritarianism by eroding civil liberties, or do the spadework of the nationalist Right by making immigration (rather than assimilation) a foremost problem. The prime allies of liberalism are all those who defend liberty and human rights. But therein lies a concern, which must be discussed.
From the beginning, liberalism has harboured different views on the role of the state and of the degree of state intervention required in the economy and society. On the one hand there are liberals – sometimes called libertarians – who wish to minimise the role of the state.

Thomas Paine
John Maynard Keynes – another great liberal – argued that state regulation of financial markets and counter-cyclical expenditures are necessary to stabilise the capitalist system. Keynes showed that economic austerity is a flawed doctrine. Government deficits are best reduced by growth: budget cuts can contract the entire economy and make the problem worse.
There is a spectrum of views between individualist and social-democratic liberalism, but all liberals are united in their defence of individual liberty, human rights and political democracy. The diverse colouring of this rainbow does not diminish its united opposition to the dark intolerance and division that is exacerbated by authoritarian nationalism.
The struggle for liberty and equality has always been vital. But many twentieth-century radicals were diverted by the delusions of socialism. The renewed rise of authoritarianism has shown us again that liberalism is the vital political movement of the modern age.
28 January 2017
Minor edits: 29 January, 1, 16 May 2017
|
This book by G. M. Hodgson elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost
Published by University of Chicago Press in January 2018
|
Bibliography
Allett, John (1981) New Liberalism: The Political Economy of J. A. Hobson (Toronto: University of Toronto Press).
Beveridge, William (1944) Full Employment in a Free Society (London: Constable).
Clarke, Peter (1978) Liberals and Social Democrats (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press).
Claeys, Gregory (1989) Thomas Paine: Social and Political Thought (London and New York: Routledge).
Courtois, Stéphane, Werth, Nicolas, Panné, Jean-Louis, Packowski, Andrzej, Bartošek, and Margolin, Jean-Louis (1999) The Black Book of Communism: Crimes, Terror, Repression (Cambridge MA: Harvard University Press).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2015) Conceptualizing Capitalism: Institutions, Evolution, Future (Chicago: University of Chicago Press).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2017) Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, forthcoming).
Keane, John (1995) Tom Paine: A Political Life (London: Bloomsbury).
Keynes, John Maynard (1936) The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money (London: Macmillan).
McCloskey, Deirdre Nansen (2017) ‘Nationalism and Socialism Are Very Bad Ideas: But liberalism is a good one’, Reason.Com, February. http://reason.com/archives/2017/01/26/three-big-ideas
Monbiot, George (2016) ‘Neoliberalism – the ideology at the root of all our problems’, The Guardian, 15 April. https://www.theguardian.com/books/2016/apr/15/neoliberalism-ideology-problem-george-monbiot.
Townshend, Jules (1990) J. A. Hobson (Manchester: Manchester University Press).
Venugopal, Rajesh (2015) ‘Neoliberalism as a Concept’, Economy and Society, 44(2), pp. 165-87. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/03085147.2015.1013356.
Posted in Brexit, Common ownership, Democracy, Donald Trump, Immigration, Karl Marx, Labour Party, Left politics, Liberalism, Markets, Nationalization, Politics, Populism, Private enterprise, Right politics, Socialism
January 5th, 2017 by geoffhodgson1946

“Worth reading to show how Liberals have played their part in the development of much of Labour’s social and economic policies over the years” John Rogan
Geoffrey M. Hodgson
Labour did not win a majority in the 2017 general election. A future majority Labour government seems less likely than a progressive alliance of Labour with other parties.
But as Neal Lawson put it: “Labour’s tribalists, including its leader it seems, simply cannot stand the idea of working with others.” Furthermore, Britain’s unfair electoral system means that, even with 20 per cent of the vote in the new constituency boundaries, Labour could retain about 150 MPs, while the Liberal Democrats would be likely to get less than 50 MPs with the same share of the overall vote.
Labour’s tribalism and self-interest could transform it into a rump party of purists in permanent opposition, rather than as a serious engine of political power that can tackle the pressing problems of poverty, inequality, poor education, declining health services and global warming.
Labour has depended on Liberalism
My purpose here is to argue that such insularity is historically ungrounded. Furthermore, while Liberals too have their sins – from support of the First Word War to endorsement of Tory austerity in 2010-2015 – the very vitality and survival of the Labour Party has been largely due to Liberals and liberalism. Strange but true.
“Nonsense,” you might say: “Labour was built on the trade unions and the organised working class.” True. But what made strong trade unionism possible?

William Ewart Gladstone
Trade unions were made legal in the UK for the first time in 1871, under the Liberal Prime Minister William Ewart Gladstone. Gladstone also introduced the Representation of the People Act 1884, which extended the right to vote from roughly 28 per cent (in 1867) to about 60 per cent of adult males.
Liberals also introduced the Education Act of 1870, which established schooling for all children between the ages of 5 and 12 in England and Wales. (It was already instituted in Scotland.) This widened literacy and political awareness.
Liberalism in the nineteenth century made possible the widespread development of trade unionism and the election of working class members of parliament. Many of these reforms were prompted by the expansion of the industrial working class and fears of riot or revolution. The Lib-Lab dialectic has run both ways.
Gladstone was an individualistic Liberal, advocating low taxes and a minimal state. But from the origins of liberalism in the Enlightenment, there have co-existed welfarist, cooperative and redistributive strains within liberalism.

Thomas Paine
These include the proposals by Tom Paine (1737-1809) for welfare provision and redistributive wealth taxes. John Stuart Mill (1806-1883) supported taxes on unearned income, inheritance taxes, trade unions, worker cooperatives, participatory democracy, votes for women as well as men, and care for the natural environment. Thomas Henry Green (1836-1882) argued that the state should protect the social, political and economic environments in which individuals could freely develop. Liberalism has always fostered notions of social obligation beyond narrow self-interest.
As the male franchise was widened, Liberals recruited working-class candidates, including those financially maintained by trade unions. The first Lib-Lab candidate stood in the Southwark by-election of 1870. The Lib-Labs represented working class interests but remained within the Liberal Party.
But as socialist ideas became more widespread, some working-class leaders began to move away from the Liberals. The Independent Labour Party was formed in 1893 and it put up its own candidates in the 1895 general election. The ILP was involved in the formation of the Labour Representation Committee in 1900, which was renamed the Labour Party in 1906. This was the great schism between Labour and Liberalism.
Liberalism, solidarity and welfare
Gladstone’s resignation in 1894 was partly prompted by his opposition to the proposal by his Liberal chancellor Sir William Harcourt to introduce death duties – a substantial tax on property. These events dramatized the tension between individualist and redistributive-welfarist strands within liberalism. Even after Gladstone’s departure, the Liberal Party remained internally divided on these issues, and it suffered a cataclysmic defeat in the 1895 general election.
Liberals were also divided on the question of Irish home rule, imperialism and war. A faction of “Liberal Unionists” broke away to form their own party in 1886: they entered a coalition with the Tories in 1900 and later fused with them.
But this period also saw the rise of a “new” or “modern” liberalism in both Britain and the United States. It stressed the importance of economic equality, a welfare state and judicious state intervention in a market economy. A key British intellectual involved in this revival was John Atkinson Hobson (1858-1940).

John A Hobson
Frustrated by the Liberal Party divisions of the 1880s and 1890s, Hobson had been in favour of the formation of a new party, but by 1901 he was calling for an alliance between labour representatives such as Keir Hardie and “progressive” Liberals. But Hardie eventually came to the conclusion that his Independent Labour Party had “nothing in common” with the Liberals.
A revived Liberal Party won a huge election victory in 1906, and Hobson returned to working within its ranks. After the 1910 general election the Liberal Party did not have a majority and formed a coalition with 42 Labour Party MPs who had been elected. The Liberal Henry Campbell-Bannerman was Prime Minister until 1908, followed by Herbert Asquith, who was in power until 1916.
Aware of the need to retain and extend support among the working class, the 1906-1914 Liberal-led governments executed a series of major reforms and laid the foundations of the British welfare state. These reforms included the introduction of a state pension, compulsory health insurance, unemployment and sickness pay, an extension of free secondary education, and a reform of the House of Lords. As Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1908 to 1915, David Lloyd George was a key figure in the introduction of many of these reforms.
Liberal decline and Labour gain
Subsequently, the Liberal Party suffered a rapid decline. In his classic diagnosis, George Dangerfield put this down to the crises over Ireland, where the Liberals were unable to prevent violence and revolt, to the rise of the labour movement and industrial militancy, and to votes for women, over which the Liberal Party fatally hesitated. During the war, the Liberal government antagonised progressive support by introducing illiberal measures including conscription and restrictions on freedom of speech.

David Lloyd George
The Liberal Party split again in 1916, when a wing led by Lloyd George entered a coalition with the Conservatives. The presence of the new and vigorous Labour Party on the Left gave a new home to disenchanted Liberals. Hobson quit the Liberal party in 1916, later to dally with Labour. But he always advocated a mixed economy and insisted on the virtues of market competition and extensive private ownership.
The much-diminished Liberal group in Parliament propped up the minority Labour governments in 1924 and 1929.
The Liberal share of the vote slumped, falling as low as 10 per cent in 1931. In the interwar period, liberalism was ground down by the rising, opposed totalitarianisms of Communism and fascism. It had to wait to the 1970s to begin a long, slow and punctuated revival.
The Labour Party was built on the twin pillars of socialist ideology and strong trade unionism. It rose from 21 per cent of the vote in 1918 to 48 per cent of the vote in 1945.
But these pillars are inadequate. Trade unionism is important for the defence of worker’s rights and as a counterbalance to powerful corporate interests. But trade unionism does not a government build. It lacks the hegemonic capacity to unite diverse sectional interests in a fractured and class-divided society.
At the outset, Labour’s socialism offered no defence of a private sector or of private property. From 1918 to 1995, Labour’s Clause Four offered common but not private or mixed ownership.

Clement Attlee
In 1937, eight years before he became Prime Minister, Clement Attlee wrote of the “evils” of capitalism: their “cause is the private ownership of the means of life; the remedy is public ownership.” Attlee approvingly quoted the words of Bertrand Russell: “Socialism means the common ownership of land and capital together with a democratic form of government. … It involves the abolition of all unearned wealth and of all private control over the means of livelihood of the workers.”
It was possible to advance such views at the time, without much loss of popular appeal. The full horrors of Stalin’s Soviet Union were initially unappreciated and then masked by the Soviet alliance with Western powers in the Second World War. The unprecedented famines and other brutalities of Mao Zedong were yet to come.
Liberalism defined Labour in power
After 1945, the position of many leading Labour Party members began to shift. The realities of gaining and holding on to power – as a majority party for the first time – dramatized the political and practical unfeasibility of abolishing all private enterprise. Some nationalization was achieved, but a large private sector remained. Then the outbreak of the Cold War in 1948 impelled everyone to make a choice between capitalism and democracy on the one hand, and state ownership and totalitarianism on the other.
The twin pillars of trade unionism and Clause Four socialism could not, and never will, sustain Labour in power. Labour nationalized several industries, but hardly more than the Liberal Hobson had proposed as early as 1909.
The greatest achievement of the 1945-1951 Labour government was its massive development of the welfare state, upon the foundations laid down by the Liberals in 1906-1914. In this second round, Liberals still played a major role.
Beveridge, Keynes and social democracy

William Beveridge
William Beveridge (1879-1963) was originally close to the Fabians but, against the prevailing current, he moved toward the Liberals, and was briefly a Liberal MP from 1944-1945. His wartime Beveridge Report (1942) became the foundation Labour’s post-1945 welfare state.
Impelled by a strong vision of social justice, Beveridge proposed a system of universal national insurance, conferring benefits to people who were sick, unemployed, retired or widowed. He argued that this system would provide a minimum standard of living “below which no one should be allowed to fall”. His proposals were developed in conjunction with the plan for a National Health Service, as developed by the Ministry of Health.

John Maynard Keynes
Near-full employment was pivotal to his system of social welfare. He expanded on this in his 1944 book Full Employment in a Free Society. In developing this goal, Beveridge relied explicitly on the policy approach developed by another great Liberal – John Maynard Keynes. Keynes was instrumental in instating full employment a major policy goal. In his General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money he provided the theoretical underpinnings of this policy.
Much of the success of the 1945-51 Labour government depended on Liberal ideas. The bland mantra of common ownership provided neither a theoretical rationale nor a practical grounding for detailed policy.
When the Labour government tackled the problems of poverty, inequality and unrealised human potential within actually existing capitalism, they turned to Liberal thinkers such as Hobson, Keynes and Beveridge, who had grappled with the policy issues for years.
Insofar as Labour became a social-democratic rather than a genuinely socialist party, it has done so by borrowing ideas from liberals. (Socialism today is too-often taken to mean almost anything, but it was originally defined by Robert Owen as the abolition of private property.)
Labour after 1951
The graph of Labour’s share of the vote shows a long decline from its peak in 1951 to the disastrous result in 1983. The Labour governments of 1964-1970 and 1974-1979 had seen major reforms under the premiership of Harold Wilson. From 1974 to 1979 there was a pact between the Liberals in Parliament and the Labour Government.
But the Labour pillar of trade unionism begat the strike wave in the so-called 1978-1979 Winter of Discontent, and Labour’s Clause Four mantra still hung around its neck.
These enhanced the conditions for the victory of Margaret Thatcher in the 1979 general election. With an inadequately-developed alternative ideology sustaining a mixed economy, Labour fell back on its founding twin pillars and lurched the Left. The result was the disaster of 1983 and Labour’s lowest share of the vote since 1918.
When Neil Kinnock became Labour leader in 1983 he pulled the party back from the brink. It took a further 14 years for Labour to recover sufficiently to win a general election.
The coalition that never was
Until the day of polling in May 1997, when the scale of his majority became clear, Tony Blair considered a coalition with the Liberal Democrats after the election, and negotiated with Paddy Ashdown on that possibility. In his first speech to a Labour conference after his landslide election victory, Blair declared:
“my heroes aren’t just Ernie Bevin, Nye Bevan and Attlee. They are also Keynes, Beveridge, Lloyd George. Division among radicals almost one hundred years ago resulted in a 20th century dominated by Conservatives. I want the 21st century to be the century of the radicals.”

Tony Blair
Blair of course referred to the 1900 decision to set up a party in parliament independent of the Liberals, to represent working people. Blair’s election victory was impelled by shift toward liberalism and an explicit rejection of classical socialism. He tackled the twin pillars of trade unionism and common ownership, upon which Labour was founded.
The opportunity of another coalition emerged after Labour’s loss of an overall majority in 2010. But instead, the Liberal Democrats turned to the Tories and formed a coalition with them. One reason for this choice was that the Liberal Democrats under Nick Clegg had abandoned their Keynesian heritage and accepted a strategy of economic austerity. This mistake cost the Liberal Democrats dearly in the 2015 election.
When Labour suffered a second successive defeat in 2015 it moved again to the Left, ending in 2015 and 2016 with the election and re-election of a hard leftist with little experience in government and a preference for slogans over both theoretical argument and practical details.
Around sixty percent of the membership voted for Jeremy Corbyn on these occasions, showing that Labour had retained its 1918 roots. This has created the conditions for a similar return to Labour’s 1918 share of the vote.
Conclusion: history in reverse
The Labour Party was founded in an era of mass industrial trade unionism and increasing ideological support for socialism, as classically defined. Both of these forces have been gravely weakened and are in dramatic decline. Traditional trade unionism has not simply been undermined by the anti-union legislation by Conservative governments. Trade unions face vastly transformed workplaces with a much more fragmented workforce, often engaged in tasks that require detailed experience and specialist skills. To survive, their role must be transformed.
But the unions have been slow to adapt to this new reality and have declined in strength. Where some disruptive power has been retained – such as on some parts of the railway system – they hasten the demise of their jobs and their replacement by robots.
The ideological appeal of classical socialism has been fatally undermined by the practical experiments in Russia, China, North Korea, Cambodia, Cuba, Venezuela and elsewhere. These experiments have without exception undermined human rights and have led to an estimated total of 90 million deaths.

Jeremy Corbyn
From 1945 Labour was unable to rely on the twin pillars of trade unionism and socialism but it retained them nevertheless. Corbyn makes them central once again, but his anachronistic strategy is doomed to failure.
Labour’s problems are exacerbated by internal divisions over immigration, Brexit, defence and NATO (in a time of increasing international tension and insecurity). The Liberal Democrats alone speak for the 48 per cent that voted to remain in the European Union.
5 January 2017
Edited 6-8, 14 January, 1 July
|
My forthcoming book elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost
To be published by University of Chicago Press in November 2017
|
References
Allett, John (1981) New Liberalism: The Political Economy of J. A. Hobson (Toronto: University of Toronto Press).
Attlee, Clement R. (1937) The Labour Party in Perspective (London: Gollancz).
Beveridge, William (1944) Full Employment in a Free Society (London: Constable).
Clarke, Peter (1978) Liberals and Social Democrats (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press).
Dangerfield, George (1935) The Strange Death of Liberal England (London: Constable).
Harrop, Andrew (2017) ‘Stuck: How Labour is too weak to win, and too strong to die’, 3 January (London: Fabian Society). http://www.fabians.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Stuck-Fabian-Society-analysis-paper.pdf
Hobson, John A. (1909) The Crisis of Liberalism: New Issues of Democracy (London: King).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2017) Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, forthcoming).
Keynes, John Maynard (1936) The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money (London: Macmillan).
Lawson, Neil (2017) “Labour’s poll woes show why we need to do a deal with rival parties”, Labour List, 4 January. http://labourlist.org/2017/01/neal-lawson-labours-poll-woes-show-why-we-need-to-do-a-deal-with-rival-parties/
Townshend, Jules (1990) J. A. Hobson (Manchester: Manchester University Press).
Posted in Common ownership, Jeremy Corbyn, Labour Party, Left politics, Liberalism, Politics, Socialism, Tony Blair, Tony Blair
December 6th, 2016 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
Racist nationalism has returned from the fringes to mainstream politics. In 2016 it played a major role in the Brexit vote in the UK, in the election of Donald Trump in the US, in the presidential election in Austria, and in developments in many other countries.
Racism and other forms of discrimination, including by gender or belief, must be defeated. The Left has played a major role in countering racism, and it should be give due credit for that. But in some other respects the Left on this issue is weak and misguided.
Some things we cannot talk about – but we must
Some things have become difficult to discuss. I once tweeted the (obviously true) statement that “Islam is religion, not a race”. A fellow tweeter immediately assumed that I was some kind of bigot and responded “ugh!”
In this reactive climate it has become difficult to raise concerns about (say) Sharia law without being branded racist or right-wing. Discussion ends. But the fact that rightist bigots – such as Nigel Farage and Geert Wilders – go on about Sharia law does not mean that we cannot discuss it.
 Of course, Muslims and others suffer significant discrimination, in Britain and elsewhere. In recent months, Trump has been responsible for major anti-Muslim outbursts and has whipped up violent anti-Muslim sentiment in the US.
Of course, Muslims and others suffer significant discrimination, in Britain and elsewhere. In recent months, Trump has been responsible for major anti-Muslim outbursts and has whipped up violent anti-Muslim sentiment in the US.
We must defend the full human rights of everyone, including members of all faiths. But this does not mean that we must refrain from criticising religious doctrines.
On the contrary, our failure to discuss these issues has favoured conservatives over reformers within these religions, has allowed religious extremism to ferment, and has repeatedly played into the hands of the reactionary and extremist Right.
I explain here where and how the Left has got things wrong in this area. I concentrate mostly on the moderate Left. The sins of many on the Far Left are much worse, including their support for fanatical, religious, “anti-Imperialist”, extremists in Palestine, Iran and elsewhere.
The election of Trump is a wake-up call. We need to find more effective ways to counter racism and other forms of discrimination. We need to find ways to make multi-religious and multi-ethnic communities more inclusive and cohesive.
Immigration – beyond the numbers game
The recent massive increases of immigration into Europe and elsewhere are a fact. But at least as far as the UK is concerned, it has been shown that the economic benefits of immigration are positive.
 But much of the political debate is about immigrant numbers. The Tories ignore the economic evidence and start a Dutch auction of targets, to stem numbers. A large part of the Labour Party, facing a seepage of its working class support to UKIP, moves in a similar direction.
But much of the political debate is about immigrant numbers. The Tories ignore the economic evidence and start a Dutch auction of targets, to stem numbers. A large part of the Labour Party, facing a seepage of its working class support to UKIP, moves in a similar direction.
Of course, mass immigration becomes a problem when there are not enough school places, health services are severely stretched, housing is limited and inadequate, and the transport infrastructure groans from decades of under-investment.
Labour is internally divided between those that want to restrict immigration, and the leadership around Jeremy Corbyn who propose no restrictions at all. With some notable exceptions, what is missing is a discussion prioritising assimilation.
The Casey Review

Louise Casey
The recently-published, government-commissioned report by Louise Casey suggests that “the tough questions on social integration are being ducked”. Casey and her team found evidence that black and minority ethnic groups are still suffering from discrimination and disadvantage and responses by government and others are inadequate. While she found some evidence of integration, in other areas the outcomes were different:
“In some council wards, as many as 85% of the population come from a single minority background, and most of these high minority concentrations are deprived Pakistani or Bangladeshi heritage communities.”
These concentrated enclaves are more difficult to assimilate and create particular problems for women:
“this sense of retreat and retrenchment can sometimes go hand in hand with deeply regressive religious and cultural practices, especially when it comes to women. These practices are preventing women from playing a full part in society, contrary to our common British values, institutions and indeed, in some cases, our laws. … I’ve met far too many women suffering the effects of misogyny and domestic abuse, women being subjugated by their husbands and extended families. Often, the victims are foreign-born brides brought to Britain via arranged marriages. They have poor English, little education, low confidence, and are reliant on their husbands for their income and immigration status. They don’t know about their rights, or how to access support, and struggle to prepare their children effectively for school.”
Casey argued that fears of being labelled “racist” have prevented society from challenging sexist, misogynistic and patriarchal behaviour in some minority communities. Her report cites claims that some Sharia councils had supported the values of extremists, condoned wife-beating, ignored marital rape and allowed forced marriages.
Her report concluded with a rallying cry:
“The problem has not been a lack of knowledge but a failure of collective, consistent and persistent will to do something about it or give it the priority it deserves at both a national and local level.”
But to “do something about it” requires a clearer understanding of the problems involved and what kind of policies are needed to deal with them. Some people have criticised Casey’s empirical claims and more research is clearly required.
Multiculturalism
As several authors have pointed out, multiculturalism is an ambiguous concept. In one sense, at least, it is unobjectionable. All civilisations have drawn and benefitted from cultural variety. Western countries today benefit enormously from the influx of ideas, skills, fashions, cuisines and experiences that successive waves of immigration have brought. This has been true for millennia. It is no less true today.
Institutions are the stuff of society: institutions are systems of social rules. Some rules – concerning dress and fashion for example – can change profoundly without social collapse.
Other institutions – particularly in law and politics – are the outcomes of centuries of experience, deliberation and experimentation. We cannot put these in a culture-mixing food blender without tearing apart the fabric of society and wrecking social cohesion and solidarity.
Much discourse about multiculturalism ignores these differences in types of rules and institutions. Everything is placed under the vague and overly-capacious category of “culture”, assuming everything can be mixed at will. This soup-making, food-blender approach is dangerous and misconceived.
Cultural relativism
Some parts of the Left have embraced normative cultural relativism. This is the view that one person’s morality is as good as any other. It is said that there is no “objective” or “correct” morality. No overriding importance is given to democracy or to the United Nations Declaration of Universal Human Rights. Other cultures have different codes and priorities: let them be.
According to this view, asking people from other cultures to adopt our over-arching laws and values is seen as a manifestation of “oppression” or “Western imperialism”. We have to be very careful not to jump to the conclusion that Western moral values are superior. But that does not mean that we should reach no judgmental conclusion at all.

Germaine Greer
For example, in her 1999 book The Whole Woman, the self-declared “Marxist” and iconic feminist Germaine Greer asked us to refrain from criticising female genital mutilation, on the grounds that it would impose our cultural values on others.
In his excellent book What’s Left? Nick Cohen gives some further examples of highly misguided cultural relativism, including attempts by feminists and leftists to defend the Indian practice of burning widows alive after the deaths of their husbands.
Analytically, this kind of cultural relativism has major flaws. First, it falls down in dealing with changing attitudes through time in one country. A cultural relativist, time travelling back to 1800, could raise no objection to slavery, or to the lack of women’s rights. If one morality is as good as any other, then there can be no moral force for change.
Second, it is internally inconsistent. Cultural relativism denies that our values are valid or suitable for other cultures. Why should this normative claim (that we should not impose our normative values on other cultures) be adopted by others in different cultures? By the logic of cultural relativism, thinkers in other cultures are not obliged to be cultural relativists. The whole argument is self-defeating.
Third, cultural relativism degrades the role of morality, by treating it as a matter of individual preference. The whole point about morality is that it transcends individual preferences. Moral claims (be they right or wrong) are universal. Humans have developed systems of morality to provide us with rules that help social cohesion while simultaneously protecting individual rights and liberties.
Reticence to act – condemnation of action
As well as the benefits of cultural enrichment, mass immigration has also brought problems of assimilation. In the UK there are large communities where many people do not speak English, or remain ignorant of prevailing laws and values that have evolved over centuries to keep our society together and to protect our interests.
Many of these immigrants had limited experience of any Western-style democracy and had an inadequate appreciation of universal human rights. Many came from rural areas in undeveloped countries, where the state was weak and social and business interactions were governed by custom and religion, based on ties of loyalty to family and clan.

Ann Cryer
Faced with this issue, many progressive politicians have adopted a stance of ultra-tolerance and inaction. Consider the question of language. Should immigrants be obliged to learn the language of their new country, so that they can understand its culture and its laws? Some other countries take this on board.
But such an assimilationist policy in the UK was highly controversial as late as 2001. In that year, the Labour MP Ann Cryer bravely argued that many Muslims were held back economically and educationally by language difficulties. The problem was especially severe among Muslim women.
But she was faced with criticism and scorn from the Left. Shahid Malik, then a senior member of the Commission for Racial Equality and of the Labour Party National Executive Committee, and subsequently a Labour MP and government minister, responded to Cryer: “Her arguments are sinister and they have no basis in fact … she is doing the work of the extreme right wing.”
Promoting faith schools
Schooling must be central to any viable integration programme. Young people need to learn about the struggles for democracy, independence, rights and human emancipation, throughout the world. They should be free to discuss and evaluate all these things.
Such a broad education is less likely in a school that is linked to one particular religion. Instead it would be more viable in secular schools with pupils from multiple religions, classes and cultures. Broad-based secular education is even more vital in multi-cultural and multi-faith societies.
 After coming to power in 1997, Labour Prime Minister Tony Blair promoted a programme of expansion of faith schools. But a 2001 report commissioned by Bradford City Council concluded that its communities were becoming increasingly isolated along racial, cultural and religious lines, and that faith-segregated schools were fuelling the divisions.
After coming to power in 1997, Labour Prime Minister Tony Blair promoted a programme of expansion of faith schools. But a 2001 report commissioned by Bradford City Council concluded that its communities were becoming increasingly isolated along racial, cultural and religious lines, and that faith-segregated schools were fuelling the divisions.
In 2001 there were riots in Bradford, which spread to other northern cities. Yet in the same year the Labour Government proposed a large increase in the number of state schools run by religious organizations.
By 2002 there was a major public row, with accusations that some pupils were being taught creationism in and that homosexual acts are against God’s law. Campaigners for women’s rights expressed concern that conservative religious teachers were instructing young girls that women should take a secondary role in society.
Despite his previous opposition to Blair, in 2016 the Labour Leader Jeremy Corbyn expressed his support for faith schools. No major UK political party has dared to come out against them. They are being vigorously promoted by the current Conservative government.
Faith schools have hindered assimilation

David Bell
David Bell warned in a January 2005 speech to the Hansard Society – when he was Chief Inspector of Schools – that a traditional Islamic education did not equip Muslim children for living in modern Britain. He said: “I worry that many young people are being educated in faith-based schools, with little appreciation of their wider responsibilities and obligations to British society.” He continued:
“We must not allow our recognition of diversity to become apathy in the face of any challenge to our coherence as a nation … I would go further and say that an awareness of our common heritage as British citizens, equal under the law, should enable us to assert with confidence that we are intolerant of intolerance, illiberalism and attitudes and values that demean the place of certain sections of our community, be they women or people living in non-traditional relationships.”

Trevor Phillips
His comments were condemned as “irresponsible” and “derogatory” by some senior Muslims, but supported by Trevor Phillips, then chair of the Commission for Racial Equality.
In another lecture Bell said: “We can choose … whether we want to bring our diversity together in a single rainbow or whether we allow our differences to fester into separate cultures and separate communities.”
Phillips came to the conclusion that increasing self-segregation of British communities along ethnic and religious lines was a major threat to national integration and to Enlightenment values. Young people were being brought up with insufficient awareness of these values, in closed communities where extremism could fester.

David Miliband
Ken Livingstone, then Mayor of London, attacked Phillips for “pandering to the right”. During a televised discussion, the prominent Labour Minister David Miliband shook his head and described Phillips’s remarks about community segregation as “fatuous”.
Since then, Phillips’s concerns about social segregation in British communities have been vindicated by several experts, while other evidence indicates a small amount of progress. Even the most optimistic reading of the evidence suggests a serious and enduring problem.
On faith schools, the Casey report noted their role in institutionalising segregation:
“The Government had attempted to alter the segregation of pupils in faith schools by introducing admissions criteria for new faith-based Free Schools. But these did not seem to be having an impact on the diversity of minority faith schools … [their] admission policies do seem to play a role in reinforcing ethnic concentrations.”
But Casey did not take the final step. She wrote: “ending state support for all faith schools would be disproportionate”. But how serious do the problems have to become before it becomes proportionate?
Rather than relying on failed palliatives, state-funded faith schools should be phased out. Taxpayers should not subsidise religion: religion and the state should part company.
A recent poll found that an overwhelming majority of the British public opposed religious discrimination in faith school admissions. Making all faith schools non-discriminatory in terms of religion would be a big positive step.
Fostering extremism
Ed Husain was born and educated in Britain, where he obtained a Master’s Degree. He was drawn toward extreme versions of Islam and was persuaded that Western democracies are irredeemably corrupt and must be replaced by a theocracies based on Islamic law.
 After several years he renounced his former extremism, but retained his Islamic faith. In an interview he revealed the segregated life of his upbringing:
After several years he renounced his former extremism, but retained his Islamic faith. In an interview he revealed the segregated life of his upbringing:
“The result of 25 years of multiculturalism has not been multicultural communities. It has been mono-cultural communities. Islamic communities are segregated. Many Muslims want to live apart from mainstream British society; official government policy has helped them do so. I grew up without any white friends. My school was almost entirely Muslim. I had almost no direct experience of ‘British life’ or ‘British institutions’.” (Quoted in Cohen 2007, p. 378.)
British policy-makers have welcomed diversity. But they have defined needs and rights via the ethnic categories into which people were placed, using those divisions to shape public policy. The result has been a more fragmented society, which has nurtured extremism.
In the name of multi-culturalism, Britain has become a more divided society, where inclusive, universal, Enlightenment values are often side-lined or unknown. These communal enclaves, found in France and Belgium as well as Britain, have become hothouses for violent extremism.
Hassan Butt was born in Luton in England in 1980. In 2000 he travelled to Pakistan and worked for the Taliban and other jihadists against the West. Subsequently he renounced his anti-Western views.
Butt explained that “Islamic theology, unlike Christian theology, does not allow for the separation of the state and religion … [they] are considered to be one and the same.” Consequently, since there no righteous Islamic state is deemed to exist, the extremists have “declared war on the whole world”.
 Some on the Far Left disowned Butt for betraying the struggle against “Western imperialism”. He was also criticized by one member of the “Stop the War” movement, who is a leading supporter of the Muslim Brotherhood, for his “call to change the face of Islam” (Cohen 2007, pp. 371-2).
Some on the Far Left disowned Butt for betraying the struggle against “Western imperialism”. He was also criticized by one member of the “Stop the War” movement, who is a leading supporter of the Muslim Brotherhood, for his “call to change the face of Islam” (Cohen 2007, pp. 371-2).
Butt’s response was clear: “I believe that the issue of terrorism can be easily demystified if Muslims and non-Muslims start openly to discuss the ideas that fuel terrorism.” However, many on the Left, as well as the Right, are not helping this process.
British values?
Successive British Prime Ministers have reacted to the threat of Islamist extremism by calling for “British values”. After claims that some schools in Birmingham were promoting Islamist extremism, in 2014 the Conservative Prime Minister David Cameron outlined plans to put the promotion of “British values” at the heart of the national curriculum for schools. This is now official policy:
“Schools should promote the fundamental British values of democracy, the rule of law, individual liberty, and mutual respect and tolerance of those with different faiths and beliefs.”
 But the official government document outlining this policy mentions respect and tolerance for other races but fails to mention discrimination against women or gays. It rightly mentions the freedom to “choose and hold” any faith, but not the freedom to exit a religion without sanction. It mentions “individual liberty” only once, and fails to uphold freedom of non-violent expression, including when it may cause offence.
But the official government document outlining this policy mentions respect and tolerance for other races but fails to mention discrimination against women or gays. It rightly mentions the freedom to “choose and hold” any faith, but not the freedom to exit a religion without sanction. It mentions “individual liberty” only once, and fails to uphold freedom of non-violent expression, including when it may cause offence.
Are these omissions an accident, or are they designed not to offend a particular religious minority?
 Another problem here is not the values as such, but their nationalistic description as “British”. Democracy was not invented in Britain: Ancient Athens and Viking Iceland have much earlier precursors. The US and France have much earlier claims to the values of liberty and religious tolerance. Britain legally discriminated against Protestant nonconformists and Catholics until the nineteenth century, and it still bars any Catholic from becoming its sovereign.
Another problem here is not the values as such, but their nationalistic description as “British”. Democracy was not invented in Britain: Ancient Athens and Viking Iceland have much earlier precursors. The US and France have much earlier claims to the values of liberty and religious tolerance. Britain legally discriminated against Protestant nonconformists and Catholics until the nineteenth century, and it still bars any Catholic from becoming its sovereign.
Apart from being misleading and inaccurate, the label of “British values” would hardly be effective in preventing a young Muslim from being radicalised. On the contrary, the label can help bolster the misperception that Britain and the rest of the West are at war against Islam. This nationalistic labelling readily allows the distortion that “British values” are being promoted by the UK authorities in a global effort to counter Islam.
It would be more accurate and effective to label values such as democracy, the rule of law, individual liberty, and freedom of worship as “universal values” or “Enlightenment values”. They are not simply values that British residents and citizens should adopt. Other countries should promote these values too.
Islamophobia?
Polly Toynbee is a leading progressive, and vigilantly anti-racist, British journalist. Yet in 2004 she was proclaimed by the Islamic Human Rights Commission as the winner of their “Most Islamophobic Media Personality” award.

Polly Toynbee
In her words, she received this ridiculous appellation because she “had challenged the legitimacy of the idea of Islamophobia and warned of the danger to free speech of trying to make criticism of a religion a crime akin to racism.” She rightly noted that the “occasional note of reason from moderate Islamic groups is so weak it hardly makes itself heard”. She highlighted the difficulties involved in starting a serious dialogue on this issue.
The failure to distinguish racism from criticism of religion sadly remains widespread. Many on the Left have done excellent work since the 1970s in campaigning against racism, fascism and discrimination. But the frequent confusion of criticism of religion with racism has diverted their efforts.
It must be repeated that concerns about Islam as a belief system are not equivalent to bigotry toward Muslims. Racism and persecution of Muslims are serious problems and should be vigilantly opposed. But the option to criticise Islam, or any other belief system, is an important right, and it should be protected.
The term “Islamophobia” is partly to blame. Despite widespread usage, it is rarely defined and there is no consensus on its definition.
Does it literally mean fear of Islam? Or criticism of Islam? Or hatred of Islam? Or persecution of Muslims? Its intended meaning can range from scholarly criticism of Islamic doctrines to racist acts against ethnic groups who are Muslim. These are obviously very different. Yet they are all lumped together under the same label.
“Anti-Muslim prejudice” or “anti-Muslim discrimination” would be much better terms. They accurately describe this very real and sadly widespread problem.
Criticism of religion can be enlightening – indeed a part of Enlightenment (and British) values, from Voltaire to Bertrand Russell. We should also be free to criticise Sharia law, as we are free to criticise other laws.

Justin Welby
As Archbishop of Canterbury Justin Welby pointed out recently, there also needs to be a discussion about the doctrinal links between religion and extremism:
“This requires a move away from the argument that has become increasingly popular, which is to say that ISIS is nothing to do with Islam, or that Christian militia in the Central African Republic are nothing to do with Christianity, or Hindu nationalist persecution of Christians in South India is nothing to do with Hinduism.”
Extreme and draconian statements can be found in the Old Testament of the Bible as well as in the Qur’an. Believing that they are obeying the word of God, these texts have spurred violent religious extremists, as we are all sadly aware.
Nevertheless, many modern Christians, Jews and Muslims have accepted the power of state law over religious law. They obey the laws of their country. They do not kill homosexuals (Leviticus 20:13), or slay apostates (Deuteronomy 13:6-10), or stone to death a bride who is not a virgin (Deuteronomy 22:20-21), or rape non-Muslim women (Qur’an 23:1-6, 70:22-30), or make war on unbelievers (Qur’an 8:12, 9:5, 9:73, 9:123).
We must help this vital transition from regressive religious law, toward a recognition of modern secular law and democracy. But we do not do so by pretending it is not needed, or refusing to discuss it, or branding those that discuss it as “Islamophobic”.
Signs of hope
On a more positive note, the authors of the 2007 Policy Exchange Report argued for a change of approach. The government and others “should stop emphasising difference and engage with Muslims as citizens”.
Policies of “group rights or representation” for specific Islamic communities are likely to alienate other sections of the Muslim population further. These well-informed remarks went against much of the then-current local and national government policy.
The authors continued: “The exaggeration of Islamophobia does not make Muslims feel protected but instead reinforces feelings of victimisation and alienation.” They also called for “a broader intellectual debate in order to challenge the crude anti-Western, anti-British ideas that dominate cultural and intellectual life. This means allowing free speech and debate, even when it causes offence to some minority groups.”
We need to be honest. Extremist religions of all kinds can threaten liberal, democratic and Enlightenment values. Christianity in particular has been violently repressive and brutal. Some religious sects today are fanatical and intolerant.
These issues need to be openly discussed, in a civilised manner. They should not be swept under the carpet by those on the Regressive Left who act as if they do not understand the difference between race and religion, or would shut down critical discussion of a religion because it might be wrongly construed by others as an attack on a minority, or by other politicians of any stripe who are simply too scared to take the issue on.
In an immensely positive development, the “Muslim Reform Movement” was launched in 2015. In their inaugural statement they defended freedom of speech, gender equality, a secular state and the UN Declaration of Universal Human Rights. They noted explicitly that freedom of speech included the right to criticize Islam: “Ideas do not have rights. Human beings have rights.”
By contrast, the blanket and ill-defined leftist rhetoric of “Islamophobia” does not help those Muslims who are struggling to reform and modernise their religion. Instead, the more conservative leaders of Muslim communities protect their regressive and reactionary views behind its smokescreen. Modernising Muslims are thus impaired by an unwitting coalition of leftists and Muslim conservatives.
Responsibility lies on both sides. In a climate of open discussion, we all need to be vigilant against acts of hatred or violence against Muslims and other minorities.
Initiatives to preserve liberal values in a multi-faith and multi-ethnic world should be welcomed. In addition, the Left needs to re-establish its links with the Enlightenment and its project to separate church from state. Within any society, freedom of worship should be protected, as well as the freedom to criticise religion.
Inward-looking, unreforming, dogmatic religion is a major barrier to assimilation. The Left needs to learn that lesson, and to encourage open discussion of the issues involved.

6 December 2016
Edited 7th and 10th December 2016, with thanks to Andrew Ross. Further edit, 23 January 2017.
|
My forthcoming book elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost
To be published by University of Chicago Press in November 2017
|
References
Accord Coalition (2016) ‘Public overwhelmingly opposes religious discrimination in faith school admissions’, Accord, 2 November. http://accordcoalition.org.uk/2016/11/02/public-overwhelmingly-opposes-religious-discrimination-in-faith-school-admissions/
Asthana, Anushka and Nazia Parveen (2016) ‘Call for action to tackle growing ethnic segregation across UK’, The Gaurdian, 1 November. https://www.theguardian.com/society/2016/nov/01/call-for-action-to-tackle-growing-ethnic-segregation-across-uk
Asthana, Anushka and Peter Walker (2016) ‘Casey review raises alarm over social integration in the UK’, The Guardian, 5 December. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2016/dec/04/social-integration-louise-casey-uk-report-condemns-failings
BBC News (2001) ‘MP calls for English tests for immigrants’, 17 July. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/1436867.stm
Bell, David (2005) ‘Full Text of David Bell’s Speech’, The Guardian, 17 January. http://www.theguardian.com/education/2005/jan/17/faithschools.schools
Board of Deputies of British Jews (2016) ‘Board of Deputies statement on meeting with Leader of the Opposition Jeremy Corbyn’, 9 February. https://www.bod.org.uk/board-of-deputies-statement-on-meeting-with-leader-of-the-opposition-jeremy-corbyn/
Butt, Hassan (2007) ‘My plea to fellow Muslims: You must renounce terror’, The Observer, 1 July. http://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2007/jul/01/comment.religion1
Casey, Louise (2016) ‘The tough questions on social integration are being ducked’, The Observer, 4 December. https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2016/dec/04/tough-questions-social-integration-laws-values-every-person-britain
Cohen, Nick (2007) What’s Left? How the Left Lost its Way (London and New York: Harper).
Department of Education (2014) Promoting Fundamental British Values as Part of SMSC in Schools (London: Department of Education). https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/380595/SMSC_Guidance_Maintained_Schools.pdf
Department for Communities and Local Government (2016) The Casey Review: A review into opportunity and integration (London: Department for Communities and Local Government). https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/574565/The_Casey_Review.pdf
Dobson, Roger (2014) ‘British Muslims face Worst Job Discrimination of any Minority Group, According to Research’, The Independent, 30 November. http://www.independent.co.uk/news/uk/home-news/british-muslims-face-worst-job-discrimination-of-any-minority-group-9893211.html
Gillard, Derek (2007) Never Mind the Evidence: Blair’s Obsession with Faith Schools www.educationengland.org.uk/articles/26blairfaith.html
Greer, Germaine (1999) The Whole Woman (New York: Doubleday).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2017) Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, forthcoming).
Husain, Ed (2007) The Islamist: Why I Joined Radical Islam in Britain, What I Saw Inside, and Why I Left (London Allan Lane).
Hussain, Dilly (2015) ‘How “British Values” are used as a Smoke Screen for Anti-Muslim Government Policies’, Stop the War Coalition, 15 June. Formerly http://www.stopwar.org.uk/news/how-british-values-are-used-as-a-smokescreen-for-anti-muslim-government-policies. Now unavailable.
Kinnock, Stephen (2016) ‘How to build an inclusive and patriotic view of Britishness’, Labour List, 2 December. https://labourlist.org/2016/12/kinnock-how-to-build-an-inclusive-patriotic-and-confident-view-of-britishness/
Malik, Kenan (2005) ‘The Islamophobia Myth’, Prospect, February. http://www.kenanmalik.com/essays/prospect_islamophobia.html
Mirza, Munira, Senthilkumaran, Abi and Ja’far, Zein (2007) Living apart Together: British Muslims and the Paradox of Multiculturalism (London: Policy Exchange), https://policyexchange.org.uk/publication/living-apart-together-british-muslims-and-the-paradox-of-multiculturalism
Mortimer, Caroline (2016) ‘Justin Welby: It’s time to stop saying Isis has ‘nothing to do with Islam’”, The Independent, 19 November. http://www.independent.co.uk/news/people/isis-nothing-to-do-with-islam-justin-welby-archbishop-canterbury-religion-a7427096.html
National Secular Society (2015c) ‘Muslim Reform Movement Embraces Secularism and Universal Human Rights’, National Secular Society, 8 December. http://www.secularism.org.uk/news/2015/12/muslim-reform-movement-embraces-secularism-and-universal-human-rights
Portes, Jonathan (2012) ‘Inching towards integration?, National Institute of Economic and Social Research, 5 March. http://www.niesr.ac.uk/blog/inching-towards-integration#.WEglE01vicx
Sides, John (2015) ‘New research shows that French Muslims experience extraordinary discrimination in the job market’, The Washington Post, 23 November. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/monkey-cage/wp/2015/11/23/new-research-shows-that-french-muslims-experience-extraordinary-discrimination-in-the-job-market/
Toynbee, Polly (2004) ‘We Must be Free to Criticise without Being Called Racist’, The Guardian, 18 August. http://www.theguardian.com/world/2004/aug/18/religion.politics
Travis, Alan (2016) ‘Mass EU migration into Britain is actually good news for UK economy’, The Guardian, 18 February. https://www.theguardian.com/uk-news/2016/feb/18/mass-eu-migration-into-britain-is-actually-good-news-for-uk-economy
White, Michael (2015) ‘Trevor Phillips says the Unsayable about Race and Multiculturalism’, The Guardian, 16 March 2015. http://www.theguardian.com/uk-news/2015/mar/16/trevor-phillips-race-multiculturalism-blog
Posted in Assimilation, Christianity, Democracy, Donald Trump, Immigration, Islam, Judaism, Labour Party, Left politics, Liberalism, Populism, Religion, Right politics
November 18th, 2016 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
“One of the most important essays you will read in 2016” @Rokewood
What caused the election of Donald Trump? I am deeply dissatisfied by some of the quick answers to this question.
The leader of Her Majesty’s Opposition had an instant answer. Jeremy Corbyn blamed the left’s association “with the forces of globalisation during the Obama administration”. Instead, he insisted, we need to reject “that free market, economic thinking, which processed deindustrialisation in Britain”.

Naomi Klein
Others used different words on the same “free market” theme. Naomi Klein put it bluntly: “the force most responsible” for Trump’s success was “neoliberalism”. This worldview, “fully embodied by Hillary Clinton and her machine”, was “no match for Trump-style extremism.”
Trump won over US voters because: “Under neoliberal policies of deregulation, privatisation, austerity and corporate trade, their living standards have declined precipitously.”
The Guardian columnist George Monbiot followed with a historical piece, claiming that “the events that led to Donald Trump’s election started in England in 1975”, when Margaret Thatcher embraced the free-market “neoliberal” philosophy of Friedrich Hayek. This was a harbinger of the global rise of free-market thinking that allegedly wrought havoc in recent years.
Both Klein and Monbiot argue that Trump capitalised on the failure of other politicians to deal with the adverse effects of neoliberalism.
There is no doubt that the global expansion of capitalism in recent decades has been hugely disruptive, shifting millions of manufacturing jobs to East Asia. In the absence of adequate retraining and investment, it has led to declining opportunities for large swathes of the working population in North America and Europe.
Trump tapped into working class discontent. In important respects his policies are not neoliberal, by any reasonable definition of that term. In his campaign, Trump used anti-neoliberal, protectionist slogans such as high import tariffs and closed borders.

George Monbiot
But why did it take so long for people to react to “neoliberalism” and vote in this way? As Monbiot argued, the current so-called “neoliberalism” got under way in the 1970s. It accelerated after the beginning of economic reform in China in 1978 and after the fall of the Berlin Wall in1989. The whole world was then opened up for trade.
But while right-populist movements had emerged, they were then far from power. Tony Blair won a landslide election in 1997 and increased public spending on welfare, education and health. Three years after Blair had won a third election, the United States elected its first black President.
If neoliberalism and stagnant living standards had been around since the 1970s, then why did it take 40 years for a Trump-like demagogue to be elected? The political wind swung decisively to the right more recently, after the Great Crash of 2008.
But it is also difficult to explain Trump’s populist success as a targeted reaction to the financial crash. The removal of some banking regulations, by Bill Clinton in the US and Gordon Brown in the UK, did exacerbate the lending boom that led to the crash of 2008.
Yet, despite his protectionism, Trump offers still more deregulation. He is not targeting the bankers as part of the “elite”. On the contrary, he has pledged to repeal the Dodd-Frank Act, which was designed to curb some of the excesses of the financial sector. As Larry Elliott put it: “This looks curious for someone trying to surf a tidal wave of populist anger against the bankers.”
 Putting the blame on “neoliberalism” underestimates the way in which outsiders such as Trump and Farage have created populist movements that blame “the elite” and offer simplistic solutions, such as to “curb immigration”. Blaming “neoliberalism” underestimates the pernicious influences of racism and anti-Muslim prejudice. Simplistic economic explanations of Trump’s victory ignore much stronger evidence of other factors at work.
Putting the blame on “neoliberalism” underestimates the way in which outsiders such as Trump and Farage have created populist movements that blame “the elite” and offer simplistic solutions, such as to “curb immigration”. Blaming “neoliberalism” underestimates the pernicious influences of racism and anti-Muslim prejudice. Simplistic economic explanations of Trump’s victory ignore much stronger evidence of other factors at work.
The Pavlovian leftist response of blaming markets or “neoliberalism” for “all our problems” is far off the mark.
What is neoliberalism?
Monbiot is keen to identify “neoliberals” such as Hayek as the villains. According to Monbiot:
“Neoliberalism sees competition as the defining characteristic of human relations. … Tax and regulation should be minimised, public services should be privatised. The organisation of labour and collective bargaining by trade unions are portrayed as market distortions that impede the formation of a natural hierarchy of winners and losers. Inequality is recast as virtuous: a reward for utility and a generator of wealth, which trickles down to enrich everyone.”
I shall pass over the many flaws in the essay from which the above passage is quoted. Monbiot conflates the different views of Ludwig von Mises, Friedrich Hayek and Milton Friedman, and he is inaccurate on several details. Note also that Monbiot does not highlight deregulation of the financial sector in this passage.
After taking on board Monbiot’s definition of neoliberalism, let us consider the extent to which it has been achieved in the real world.
Has neoliberalism been achieved in practice?
Monbiot described how in the 1970s “elements of neoliberalism, especially its prescriptions for monetary policy, were adopted by Jimmy Carter’s administration in the US and Jim Callaghan’s government in Britain.” He is unclear on the details, but presumably in part he refers to Callaghan’s embrace of monetarist ideas from 1976 to 1979.

Milton Friedman
Monetarism, incidentally, is not obviously the same as neoliberalism. While monetarists such as Friedman were free-marketeers, monetarism’s central claim is that the main cause of inflation is the rise in the money supply – a thesis that (as Friedman himself recognised) could also apply to a planned economy. Indeed, this central monetarist tenet was adopted by some Marxist economists.
“After Margaret Thatcher and Ronald Reagan took power, the rest of the [neoliberal] package soon followed: massive tax cuts for the rich, the crushing of trade unions, deregulation, privatisation, outsourcing and competition in public services.”
He is right. Albeit to different degrees in different countries, these things happened.
But go back to Monbiot’s checklist definition of neoliberalism, as quoted above. He saw neoliberalism as minimising “tax” not simply “tax cuts for the rich”. Has this happened?

Ronald Reagan & Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Thatcher reduced taxation for the rich. But the overall tax burden (all taxes as a percentage of GDP) rose during her period of office. This figure fell in the 1990s and has fluctuated from 1997 in a range between 35 per cent and 38 per cent of GDP. The UK austerity governments since 2010 have not reduced the overall tax take significantly.
Similarly, Ronald Reagan began by cutting income taxes for the rich, but ended his eight-year term of office with a Federal percentage tax take almost identical to that of his predecessor Jimmy Carter, and slightly above the average for the entire 1970-2009 period.
The “neoliberal” mission of massive overall tax cuts was not achieved under Thatcher or Reagan, or under subsequent administrations. Put in a longer historical perspective, taxation and public spending in the UK and USA today are much higher than they were before the Second World War.
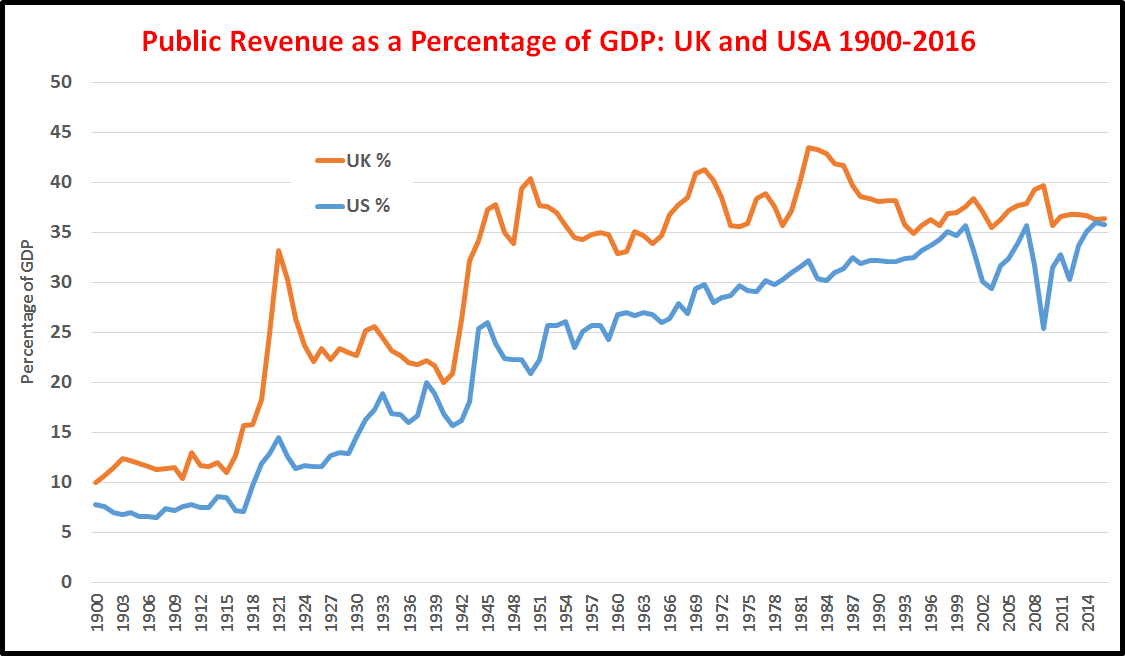
The above figure shows the tax revenues, from national, state and local government combined, for the UK and the USA from 1900 to 2016. The alleged era of “neoliberalism” from the 1970s has not been associated with declining tax revenues. If anything, the “neoliberal” era of a minimal state was pre 1914, not post-1975.
What is characteristic of fiscal policy in the UK and USA is not the alleged “neoliberal” overall reduction of taxation but a lightening of taxation on the rich, and a failure to redistribute sufficiently, in the face of widening inequality.
Klein is probably right to suggest: “A good chunk of Trump’s support could be peeled away if there were a genuine redistributive agenda on the table.” But she, with Corbyn and Monbiot, are wrong to chime in with the crude anti-market mantras that have disabled the Left for 180 years. In building a redistributive agenda we must look to Thomas Paine, rather than Robert Owen or Karl Marx.
Privatisation: against dogma
By contrast, Monbiot’s other point, about growing privatisation since the 1970s, has been borne out by the evidence. In the UK, USA and much of the world there has been massive privatisation and outsourcing of public services.
 Unlike any false claim that “neoliberalism” has reduced overall taxes, the increase of privatisation is manifest. In addition, it has sometimes led to deleterious consequences including lower pay for workers and a reduced quality of services.
Unlike any false claim that “neoliberalism” has reduced overall taxes, the increase of privatisation is manifest. In addition, it has sometimes led to deleterious consequences including lower pay for workers and a reduced quality of services.
But Corbyn and Monbiot speak and write as if privatisation is necessarily bad – always and everywhere it is seen as a negative policy. This doctrinaire stance simply inverts the claim of the crudest free marketeers, who claim that state provision is always bad and that private provision is always good. The Corbyn-Monbiot stance simply turns this upside-down. It is equally dogmatic. It is based on ideology, not evidence.
Regarding markets as always bad, amounts to agoraphobia or fear of markets (from the Greek words agora for market, and phobia for fear). This is an inversion of the kratophobia of the free-marketeers – a fear of government or of the state.
Instead of these ideologically-driven, simplistic positions, it is necessary to be more pragmatic. Some privatisations work. Others do not. Some state provision is effective. Some is wasteful and inefficient. We need to look at individual cases to understand why.
There are many case studies to look at and they are too wide-ranging to be reviewed here. A good start would be to look at an important early article on privatisation by John Goodman and Gary Loveman in the Harvard Business Review. They wrote:
“the issue is not simply whether ownership is private or public. Rather, the key question is under what conditions will managers be more likely to act in the public’s interest … managerial accountability to the public’s interest is what counts most, not the form of ownership.”
Goodman and Loveman argued that profits and the public interest overlap best when the privatised organisation is in a competitive market. Competition from other companies can discipline managerial behaviour. Consequently, there is little point in privatisation if competition is lacking.
Subsequent research has shown that other factors are involved as well. Instead of being driven by dogma, we need to be pragmatic and experimental, taking account of research.

Jeremy Corbyn
You may respond that Corbyn is pragmatic, because he has declared that he is in favour of a mixed economy: he accepts a private as well as a public sector. But notice the imbalance in his presentations. He treats public provision as ideal, and the private sector as an expedient to be tolerated, at least for a while.
Corbyn says he accepts a mixed economy, but he has offered has no defence of private sector. His “mixed economy” could be a stopping point on the road to a fully-socialist planned economy, where private enterprise is pushed to the side-lines.
Declining public provision?
 Ken Loach’s moving film, I, Daniel Blake, portrays the heart-breaking human consequences of the UK Conservative government’s shredding of the welfare safety net for the poor. Attempts to reduce public spending in many countries have led to millions of human tragedies like this.
Ken Loach’s moving film, I, Daniel Blake, portrays the heart-breaking human consequences of the UK Conservative government’s shredding of the welfare safety net for the poor. Attempts to reduce public spending in many countries have led to millions of human tragedies like this.
Doctrinaire austerity policies – which fail in their own terms because they depress economic demand for goods and services and create more unemployment – have been adopted by many governments and imposed by the European Union.
 All this is real, and tragic. Millions have suffered because of such misguided policies. But we should not jump to the conclusion that “neoliberalism” has been successful in moving toward a minimal economic role for the state.
All this is real, and tragic. Millions have suffered because of such misguided policies. But we should not jump to the conclusion that “neoliberalism” has been successful in moving toward a minimal economic role for the state.
In my book Conceptualizing Capitalism I examined differences and changes in public social spending in different developed countries from 1980 to 2005, using OECD data. The principal components of public social spending include health services, old age benefits, unemployment benefits, incapacity-related benefits, family support, active labour market public programs, and housing benefits.
Amounts of public spending as percentages of GDP (in 1980 and 2005) are shown below.
|
1980 |
2005 |
change |
| Australia |
10.3 |
16.5 |
+6.2 |
| Austria |
22.4 |
27.1 |
+4.7 |
| Belgium |
23.5 |
26.5 |
+3.0 |
| Canada |
13.7 |
16.9 |
+3.2 |
| Denmark |
24.8 |
27.7 |
+2.9 |
| Finland |
18.1 |
26.2 |
+8.1 |
| France |
20.8 |
30.1 |
+9.3 |
| Germany |
22.1 |
27.3 |
+5.2 |
| Italy |
18.0 |
24.9 |
+6.9 |
| Japan |
10.2 |
18.5 |
+8.3 |
| Netherlands |
24.8 |
20.7 |
–4.1 |
| Norway |
16.9 |
21.6 |
+4.7 |
| Portugal |
9.9 |
23.0 |
+13.1 |
| Spain |
15.5 |
21.1 |
+5.6 |
| Sweden |
27.1 |
29.1 |
+2.0 |
| Switzerland |
13.8 |
20.2 |
+6.4 |
| UK |
16.5 |
20.5 |
+4.0 |
| US |
13.2 |
16.0 |
+2.8 |
Public Social Spending as Percentage of GDP in Selected Countries
Most countries increased their public social spending, during a period when the ideology of privatization was resurgent. The Netherlands is an exception. Note that the increases in public social spending are not explained by rises in unemployment benefit, because generally this comprises a small proportion of public social spending.
Of course, it needs to be emphasised that there is an ideologically-driven agenda that has led to deep cuts in some welfare and has been gravely damaging for the poor. But we are far from re-entering the era of the minimal state.
Pursuing unicorns
Much of the hysteria against “neoliberalism” draws from the Left’s deep rooted antipathy to markets. Let’s briefly address this.
First, they may be alternatives to markets in modern, large-scale economic systems but they would greatly out-do the miseries inflicted on the fictional Daniel Blake and his millions of real-world counterparts.
Karl Marx
Every attempt to get rid of markets, since Robert Owen and Karl Marx proclaimed their redundancy in the nineteenth century, has led to famine, repression and the termination of democracy. Look to Stalin’s Russia, Mao’s China, Cambodia, Cuba and Venezuela. Twentieth-century Communism resulted in over 90 million deaths.
In the light of twentieth-century experience it would be worse than foolhardy to make yet another attempt to minimise markets, or as Klein oddly put it, “corporate trade”.
A better way is possible, but it involves taming and supplementing markets, not repressing them. It means regulating corporations, not casting them as sorcerers of evil. But sadly, agoraphobia still afflicts many on the left.
“It seems to me that the questions we urgently need to ask ourselves are these: is totalitarianism the only means of eliminating capitalism? If so, and if … we abhor totalitarianism, can we continue to call ourselves anti-capitalists? If there is no humane and democratic answer to the question of what a world without capitalism would look like, then should we not abandon the pursuit of unicorns, and concentrate on capturing and taming the beast whose den we already inhabit?”
Excellent. But since then he has gone down the rocky road of blaming “neoliberalism” for “all our problems”. Without defending some role for private property or markets, he thereby allies himself with the many leftists who now describe anyone defending private property or markets as “neoliberal”.
Has Monbiot now abandoned the idea of taming the capitalist beast? Does he wish to kill it instead?
In April 2016 he wrote: “Every invocation of Lord Keynes is an admission of failure.” So he junked the best macroeconomic theory we have for limiting some of the excesses of capitalism. His grounds for doing so were these:
“Keynesianism works by stimulating consumer demand to promote economic growth. Consumer demand and economic growth are the motors of environmental destruction.”

John Maynard Keynes
Wrong. “Consumer demand and economic growth” can destroy the planet, but only if that demand and growth relate to non-renewable material resources. Much demand and growth in modern economies is for services. Intangible assets now make up much of corporate wealth. For example, there are demands for information and education, and such services are added to GDP. There is no necessary reason why economic growth in a modern information-rich economy should ruin the planet. Keynes is still relevant.
Those that have pursued unicorns have imagined that it is possible to design a better system than capitalism. Monbiot says the same, declaring that for the Left
“the central task should be to develop an economic Apollo programme, a conscious attempt to design a new system, tailored to the demands of the 21st century.”
This puts him in full, unicorn-chasing mode. One of the biggest mistakes by early socialists was to ignore the massive complexity of modern economic systems and attempt to “design a new system” at the behest of some utopian dreamer.
Instead, what is required is careful, incremental, experimental change, retaining the flexibility and devolved autonomy afforded by widespread private property. This autonomy allows for multiple experiments and deeper learning from mistakes.
While state intervention is necessary, no complete or adequate overall “design” is possible, because of the way much knowledge is irretrievably dispersed throughout the economy. The economies of the twenty-first century are more knowledge-intensive than those before. Hence the possibilities of comprehensive central planning or “design” are even more limited.
Neoliberalism and economic man
“as modern psychology and neuroscience make abundantly clear – human beings, by comparison with any other animals, are both remarkably social and remarkably unselfish. The atomisation and self-interested behaviour neoliberalism promotes run counter to much of what comprises human nature.”
 The first sentence is valid and important. The second is simplistic. As I elaborate in my book From Pleasure Machines to Moral Communities, strong evidence from psychology, evolutionary biology and primatology shows that the picture of self-seeking “economic man”, which dominated mainstream economics until recently, is deeply flawed.
The first sentence is valid and important. The second is simplistic. As I elaborate in my book From Pleasure Machines to Moral Communities, strong evidence from psychology, evolutionary biology and primatology shows that the picture of self-seeking “economic man”, which dominated mainstream economics until recently, is deeply flawed.
But that does not mean that we can or should get rid of markets. Our capacities for cooperation evolved culturally and genetically because our ancestors hunted and foraged in groups, rarely numbering more than 200 individuals, for millions of years. Relying on emotions and facial expressions, we developed sophisticated social mechanisms to engender trust and cooperation, and to enforce social rules.
As larger-scale cities emerged about 14,000 years ago, these face-to-face mechanisms could no longer be relied upon exclusively to regulate social interactions. Institutions such as law, property and contract were developed to deal with these more impersonal, non-familial, transactions.
Every human civilisation that has developed has relied on property, trade and contracts. These require different enforcement mechanisms, but they too require measures of trust and moral obligation, as Adam Smith made clear in his Theory of Moral Sentiments. The idea that markets inevitably corrode away all social ties is mistaken.
Even the Soviet-style economies of the twentieth century relied on some private property and trade. They failed because state bureaucracy stifled autonomy and innovation. China grew rapidly when it expanded the private sector after 1978.
Of course, the spread of the market would be detrimental if it invaded all our social relations, attempting to put prices on love and friendship and reducing everything else to money transactions. But a system of private property provides a degree of autonomy that is required to maintain non-market interactions at home and at work. Successful corporations create islands of cooperation and teamwork within their organisational boundaries.
 Impersonal relations occur in bureaucracies as well as in markets. Large-scale systems of national planning also make much interaction impersonal. People become atomised; they become numbers, to be processed by bureaucrats and computers.
Impersonal relations occur in bureaucracies as well as in markets. Large-scale systems of national planning also make much interaction impersonal. People become atomised; they become numbers, to be processed by bureaucrats and computers.
The experience of centrally-planned economies in Russia, China and Eastern Europe shows that systems of state planning can be cesspits of human alienation and corruption, governed impersonally by disillusioned bureaucrats and corrupt state officials. I recommend the film The Lives of Others for a glimpse into that dark world.
Abandoning neoliberalism
I have written at further length elsewhere on the limits to markets. I accept Hayek’s explanation that comprehensive overall planning is dysfunctional. But I do not accept that everything should or can become a monetary transaction in its place.
Indeed, the growing use of information in a capitalist economy puts limits on the role of information as property. Furthermore, the very freedom of waged employees means that there are constraints on entering into contracts for future work. There are limited futures markets for labour. For such reasons, capitalism can never be a 100 per cent market system.
Hayek failed to acknowledge fully the limits to markets. Such free marketeers are the mirror-image of socialists who fail to acknowledge adequately that there are limits to common ownership. We have to transcend both agoraphobia and kratophobia.
Agoraphobics react adversely to any tolerance of markets. Hence economic interventionists such as Tony Blair, and supporters of public healthcare such as Hillary Clinton, have recently and frequently been accused of being neoliberals. This is misleading and absurd.
As Colin Talbot has pointed out, “neoliberalism” has become “a term of abuse” to be used against “any type of pro-market reform or political position that recognizes markets may – in the right circumstances – be a good thing”. Consequently, everyone “from moderate social democrats to the most lurid free-marketeers gets lumped together under a convenient ‘neoliberal’ label.”
In a brilliant survey of its usage since the 1980s, Rajesh Venugopal concluded that “neoliberalism has become a deeply problematic and incoherent term that has multiple and contradictory meanings, and thus has diminished analytical value.”
Some may wish to retain the “neoliberal” label, to apply it to those free marketeers who attempt to shrink radically the size of the state, and to privatise anything that walks. The definition could be further sharpened by adding advocacy of economic austerity. It could also could be sharpened by including deregulation of the financial sector.
 But such nuances have been lost in a global storm of “neoliberal” accusations. Klein and Monbiot have added some force and authority to this widening tempest.
But such nuances have been lost in a global storm of “neoliberal” accusations. Klein and Monbiot have added some force and authority to this widening tempest.
They do not confine their accusations to the likes of Hayek. Most seriously, they pointed the “neoliberal” finger at Hillary and Bill Clinton, as Corbyn made the “forces of globalisation” jibe at Barack Obama.
If it means anything, neoliberalism is an ideology and only partly a reality. Austerity and welfare cuts have wreaked havoc, but markets and private enterprise have lifted millions out of poverty. Agoraphobic accusations of “neoliberalism” miss the latter point.
“Neoliberalism” gave us Trump
We may ask: what part did the accusers of “neoliberalism” have to play in Trump’s victory? The constant tainting of Hillary Clinton as a “neoliberal” may have helped to persuade many Democratic supporters to stay at home. We know from the data that the below-par turnout by Democrats – especially by the young – was decisive in losing those swing states.
Tainting Hillary Clinton as a “neoliberal” could have played a part in clinching Trump’s success. If so, “neoliberalism” gave us Trump, but not in the way that Klein and Monbiot suggest.
18 November 2016
Minor edits – 19, 25, 30 November, 15, 28 December 2016
|
My forthcoming book elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost
To be published by University of Chicago Press in November 2017
|
Bibliography
BBC News (2016) ‘Jeremy Corbyn outlines Labour’s vision of a “new economics”’, 21 May. http://www.bbc.com/news/uk-politics-36351149.
Chantrill, Chrisopher (2016a) ‘UK Public Revenue’. http://www.ukpublicrevenue.co.uk/uk_national_revenue_analysis
Chantrill, Chrisopher (2016b) ‘US Government Revenue’. http://www.usgovernmentrevenue.com/revenue_history
Elgot, Jessica (2016) ‘Corbyn backs reduction of NATO presence along Russia’s borders’, The Guardian, 13 November. https://www.theguardian.com/politics/2016/nov/13/jeremy-corbyn-hints-at-reducing-nato-presence-russia-putin?CMP=share_btn_tw.
Elliott, Larry (2016) ‘Trump’s economic view is far from neoliberal, but it rides a populist wave’, The Guardian, 31 July. https://www.theguardian.com/business/2016/jul/31/trumps-economic-view-is-far-from-neoliberal-but-it-rides-a-populist-wave.
Goodman, John B. and Loveman, Gary W. (1991) ‘Does privatization serve the public interest?’ Harvard Business Review, November-December. https://hbr.org/1991/11/does-privatization-serve-the-public-interest.
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2013) From Pleasure Machines to Moral Communities: An Evolutionary Economics without Homo Economicus (Chicago: University of Chicago Press).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2015) Conceptualizing Capitalism: Institutions, Evolution, Future (Chicago: University of Chicago Press).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2017) Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, forthcoming).
Johnson, Christopher (1991) The Economy under Mrs Thatcher (Harmondsworth: Penguin).
Klein, Naomi (2016) ‘It was the Democrat’s embrace of neoliberalism that won it for Trump’, The Guardian, 9 November. https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2016/nov/09/rise-of-the-davos-class-sealed-americas-fate.
Monbiot, George (2003) ‘Rattling the Bars’, The Guardian, 18 November. See http://www.monbiot.com/2003/11/18/rattling-the-bars/.
Monbiot, George (2016a) ‘Neoliberalism – the ideology at the root of all our problems’, The Guardian, 15 April. https://www.theguardian.com/books/2016/apr/15/neoliberalism-ideology-problem-george-monbiot.
Monbiot, George (2016b) ‘Neoliberalism: the deep story that lies beneath Donald Trump’s triumph’, The Guardian, 14 November. https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2016/nov/14/neoliberalsim-donald-trump-george-monbiot.
O’Hara, Glen (2016) ‘Stop saying that Trumpism is about economics’, 15 November. http://publicpolicypast.blogspot.co.za/2016/11/stop-saying-that-trumpism-is-about.html.
Pagano, Ugo (2014) ‘The Crisis of Intellectual Monopoly Capitalism’, Cambridge Journal of Economics, 38(6), November, pp. 1409-29. http://cje.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2014/08/04/cje.beu025.
Sahadi, Jeanne (2010) ‘Taxes: What people forget about Reagan’, CNN Money, 12 September. http://money.cnn.com/2010/09/08/news/economy/reagan_years_taxes/.
Talbot, Colin (2016) ‘The myth of neoliberalism’, 31 August. https://colinrtalbot.wordpress.com/2016/08/31/the-myth-of-neoliberalism/.
Velasco, Andrès (2016) ‘The Real Roots of Populism’, Project Syndicate, 28 July. https://www.project-syndicate.org/commentary/real-roots-of-populism-by-andres-velasco-2016-07?backaction=
Venugopal, Rajesh (2015) ‘Neoliberalism as a Concept’, Economy and Society, 44(2), pp. 165-87. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/03085147.2015.1013356.
Posted in Common ownership, Donald Trump, George Monbiot, Jeremy Corbyn, Karl Marx, Left politics, Liberalism, Markets, Naomi Klein, Nationalization, Populism, Private enterprise, Right politics, Tony Blair, Uncategorized
September 16th, 2016 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
There are several different kinds of populism, emanating from both the left and right. But they have in common a view that some powerful minority group are clearly to blame for the ills suffered by a majority. As Julian Baggini put it, in his excellent article on Corbyn’s populism:
‘Populism is … a way of doing politics that has three key features. First, it has a disdain for elites and experts of all kinds, especially political ones. Second, it supposes that the purpose of politics is simply to put into action the will of the people, who are seen as homogenous and united in their goals. Third, it proposes straightforward, simple solutions to what are in fact complex problems.’
Rather than enter into a discussion over political problems and details, populists accuse those who fail to support them as collaborators of the exploiting elite. They believe that the elite is the main obstacle to progress, and solutions will appear once the elite is removed. They are suspicious of experts and dissenters. They are typically vague about their own objectives: their primary aim is to unite the bulk of the population behind a leader, against the elite.
The Great Crash of 2008 undermined confidence in existing elites. For this and other reasons, populism is now on the rise, in both Europe and the USA.
Populism on the Right
The campaign by UKIP to quit the European Union was populism incarnate. Its leader, Nigel Farage, complained frequently that the elites have gained too much power over hard-working ordinary people. Furthermore, elites at the national level had allegedly handed over power to unaccountable rulers in Europe, who have allowed mass immigration and robbed the UK of its sovereignty.
Because of his focus on a nationalist solution, and his identification of foreigners as a primary problem, Farage is an example of a right populist. By championing ‘ordinary British people’ against the establishment, and relying more on sentiment than on reasoned argument or expert advice, he is populist to the core.
 After his success in the Brexit referendum, Farage flew across the Atlantic to show his support for Donald Trump. At his August 2016 speech at a Donald Trump rally in Mississippi, Farage celebrated that Britain ‘chose not to be ruled by unelected old men in Brussels’. He drew parallels between the US and Britain, saying ordinary people everywhere had been ‘let down by government’. He was greeted by rapturous applause.
After his success in the Brexit referendum, Farage flew across the Atlantic to show his support for Donald Trump. At his August 2016 speech at a Donald Trump rally in Mississippi, Farage celebrated that Britain ‘chose not to be ruled by unelected old men in Brussels’. He drew parallels between the US and Britain, saying ordinary people everywhere had been ‘let down by government’. He was greeted by rapturous applause.
Trump’s rhetoric has much in common with that of Farage. Both blame immigrants for the problems in the country. Trump adds his rabid hostility to Muslims.
Corbynism as Left Populism
There are important differences between populists on the left and right. Left populists place less emphasis on the role of immigrants or foreigners: they are more inclusionary. Left populists also tend to favour greater state involvement in the economy. But elements of right populism can find their way into left movements, and vice versa.
 Jeremy Corbyn is very different from Nigel Farage and Donald Trump. Corbyn is neither a racist nor a misogynist (although he has shared political platforms with homophobes and anti-Semites). But Corbynism as a movement has strong populist features.
Jeremy Corbyn is very different from Nigel Farage and Donald Trump. Corbyn is neither a racist nor a misogynist (although he has shared political platforms with homophobes and anti-Semites). But Corbynism as a movement has strong populist features.
Other prominent examples of left populist movements include Syriza in Greece, Podemos in Spain and the ‘socialist’ regime established by the late President Hugo Chávez in Venezuela.
Labour has always been more pragmatic than ideological. Although Corbyn has some Marxist theoreticians close to him, including within his Momentum Praetorian Guard, he has relied much more on populist sentiment rather than Marxist theory.
The recent growth of left populism has been triggered by the crisis within social democracy, the disastrous invasion of Iraq in 2003, increasing economic inequality within leading economies, unaffordable housing, cuts in the welfare state and high rates of unemployment, especially among the young.
Corbynism vaguely promotes ‘socialism’, but there is no apparent agreement on what this means. There is a general suspicion of private enterprise, as well as a justified concern about the excessive power of some large corporations. When difficulties appear, public ownership is typically seen as the simple and obvious cure.
Like all populists, Corbyn rails against the elite. For him it is the rich minority and the large corporations. Like Farage, he identifies an elite that is bolstered by powerful friends abroad. But for Corbyn the most important foreign allies of the despised British elite are in Washington DC. With its anti-West foreign policy, Corbynism is Marxism-Leninism in populist clothing.
Corbynism Undermines Parliamentary Democracy
To public ownership is added the populist Corbynista slogans of ‘democratic control’ or ‘democratic management’ of enterprises. Without any detailed explanation of how this would work, it nevertheless reassures the left-populist followers that they, and not the elite, will somehow be in control. This left-populist slogan of ‘democratic control’ is seen as the obvious and straightforward way to ‘put into action the will of the people’.

Some extension of worker and community participation is desirable. But it cannot be a substitute for managerial discretion and leadership. Corbyn’s ultra-democracy is infeasible. When it threatens parliamentary democracy it is dangerous.
The Corbynistas want to shift power away from Parliament. They want MPs to follow ‘the will of the people’, which means, in practice, the implementation in Parliament of the resolutions of their local constituency parties. Inadequate heed is taken of the diverse views and interests of the electorate, and the need for expert deliberation and debate to make policy feasible and effective.
Instead of careful, empirically-grounded debate among diverse viewpoints, aimed at developing viable policies to deal with complex economic and political problems, Corbynistas are suspicious of dissent from their official line.
Any defence of markets or private ownership is worrying for them. It challenges their ‘obvious’, ‘democratic’ and simplistic solutions, and therefore must be opposed. Such dissent is branded ‘Blairite’ or ‘red Tory’ or ‘neoliberal’.
Instead of pluralism and extended debate, Corbynism treats the party resolution as the correct line, which all are instructed to follow. There is little appreciation of the complexity of modern politico-economic systems, and the consequent fallibility of all decision making.
Parliamentary institutions have evolved to deal with real-world complexities. They provide some mechanisms to challenge and scrutinise legislation. By moving from representative to delegate democracy, Corbynism would corrode the basic institutions of parliamentary democracy.
Any leader of any political party committed to working through parliament would resign when 80 per cent of his or her parliamentary representatives passed a vote of no confidence in his or her leadership. When this happened, Corbyn did not resign: his primary focus is not on parliament but on the populist ‘mass movement’ outside.
Totalitarian Dangers of Populism – The Example of Venezuela
The record of both left and right populism in power is abysmal. There is an important example of left populism in power, and it is close to Corbyn’s heart.
He has always had a romantic soft spot for Latin American revolutionaries. He wrote in 2011: ‘What the Cubans and … Che Guevara were preaching in the 1960s has an even greater resonance today’. This suggests that armed insurrection is appropriate, even in those Latin American countries that have become democracies.

Jeremy Corbyn and Hugo Chávez
In 1998, the Marxist politician Hugo Chávez was elected as President of Venezuela. Using the high oil revenues during 1999-2007, his government expanded access to food, housing, healthcare, and education, especially for the poor and the indigenous minorities.
Chávez nationalized key industries and created participatory Communal Councils. His ‘Chavista’ populism emphasised the ‘will of the people’, against the rich elite and their perceived allies in the United States.
Chávez created new ‘democratic’ institutions at the base to bolster his power. In 1999, the new Constitutional Assembly, filled with elected supporters of Chávez, drafted a new constitution that made censorship easier and granted the executive branch of government more power. The Constitutional Assembly extended the presidential term. It abolished the two houses of Congress. It also granted Chávez the power to legislate on citizen rights, to promote military officers and to oversee economic and financial matters.
In 2002 Chávez was briefly deposed in a coup, which may have had support from foreign agencies such as the CIA. The hostility of the US government to his regime was no secret. But Chávez was restored to power by the army and popular mobilisations.
Chávez seized control of the courts and the electoral authority, and suppressed much of the opposition media. He removed political checks and balances, seeing them as obstacles to his socialist revolution.

Hugo Chávez
Accordingly, the device of populist democracy was used to push the country in the direction of dictatorship. The high pre-Crash oil revenues were used to address some basic needs and to buy the support of the people. These supporters were then persuaded to approve increases in presidential powers, to protect the ‘socialist revolution’ against its enemies.
Chávez failed to diversify the economy and reduce its reliance on oil. He antagonised private investors. The economy was not robust enough to withstand the post-2008 oil price collapse. His government had become one of the most corrupt in the world. Serious shortages of food and medicine emerged. Chávez died of cancer in 2013 and was replaced as President by Nicolás Maduro.
But Corbyn’s enthusiasm for the regime was undiminished. As late as 2015, when Venezuela was in ever-deepening crisis, he remarked:
‘we celebrate, and it is a cause for celebration, the achievements of Venezuela, in jobs, in housing, in health, in education, but above all its role in the whole world … we recognise what they have achieved.’

Food Shortages in Venezuela
These gave him powers to intervene more heavily in companies and in the currency markets. Arbitrary detentions of dissidents became more common.
In July 2016 he used his executive powers to decree that citizens could be forced to work in the country’s fields for 60-day periods, which may be extended ‘if circumstances merit.’
Starvation became rife. In August 2016 a gang of hungry Venezuelans broke into a zoo and butchered a horse for its meat.
Populism in general, and the left populisms of Chávez, Maduro and Corbyn in particular, are profound threats to any enduring and viable democracy. Using Chávez as a prime example. Kurt Weyland wrote:
‘Determined and politically compelled to boost their personal predominance, populist leaders strive to weaken constitutional checks and balances and to subordinate independent agencies to their will. They undermine institutional protections against the abuse of power and seek political hegemony. Correspondingly, populist leaders treat opponents not as adversaries in a fair and equal competition, but as profound threats. Branding rivals “enemies of the people,” they seek all means to defeat and marginalize them. Turning politics into a struggle of “us against them,” populists undermine pluralism and bend or trample institutional safeguards.’

“There’s no food”
The tragic example of Venezuela is a warning to us all. Like Corbyn, Chávez started with a fairly modest economic programme, closer to social democracy than Marxist orthodoxy. But to bolster his power, Chávez extended state control. Maduro further undermined freedom of speech and put opponents in jail.
Because of a populist mistrust of liberal, pluralist institutions, Venezuela is lurching toward despotism. Currently it retains some semblance of democracy, but press freedom is limited and critical journalists are jailed. Since 2004, ‘defamation’ of the government, including ‘disrespect for the authorities’, has been a criminal offence.
Supporters of Chávez and Maduro blame the hostility of the US for Venezuela’s distress, just as it was blamed for economic problems in Cuba after its 1959 revolution. US belligerence made things worse. But the major cause of economic stagnation in both places is the hobbling of the private sector, and the unchecked concentration of excessive political, legal and economic power in the hands of the overbearing state.
Populism must be Defeated
Although it is unlikely that either UKIP or Corbyn’s Labour will ever win power, they can do serious damage to public debate and the functioning of a parliamentary democracy. In particular, by neutering Labour as a parliamentary force, the UK is deprived of an effective opposition to the Tory government.
 Consider the example of the EU referendum in June 2016. After the result, Corbyn took it for granted that Britain should leave the EU and immediately trigger Brexit, irrespective of the outcome of Britain’s negotiations on the terms of leaving. Like his fellow-populist Farage, Corbyn accepted that ‘the people had spoken’. For him, the expression of popular will was the end of the matter.
Consider the example of the EU referendum in June 2016. After the result, Corbyn took it for granted that Britain should leave the EU and immediately trigger Brexit, irrespective of the outcome of Britain’s negotiations on the terms of leaving. Like his fellow-populist Farage, Corbyn accepted that ‘the people had spoken’. For him, the expression of popular will was the end of the matter.
After the June 2016 vote to leave the EU, Britain is probably in its worse political crisis since the Second World War. It faces years of political and economic uncertainty, with no obvious resolution. In these circumstances, popular frustration and deprivation can feed populism. Left populism has its own dangers, and we know from history that left populists can shift to the right. In turn, right populism can feed fascism.
All populisms, including Corbynism, pose a serious threat to representative democracy. As Baggini put it:
‘Our tradition of representative democracy rests on a rejection of all three pillars of populism. It accepts that a well-run society needs specialists and full-time politicians whose judgments often carry more weight than those of voters who put them into power. It accepts that the “will of the people” is diverse and contradictory, and that the job of politics is to balance competing demands, not simply to obey them. It follows that there are few, if any, easy solutions and that anyone who promises them is a charlatan. Making the case for representative democracy therefore means telling the electorate it doesn’t always know best, a truism that populism has turned into an elitist heresy.’
Populists do not understand that political checks and balances, safeguarded by countervailing politico-economic power, are necessary to help protect democracy and liberty. With confidence in their ‘obvious’ solutions to complex problems, they treat criticism with disdain and close down reasonable discussion. All must ‘unite behind the leader’ who is revered for saving the masses from the enemy elite.
For these reasons Corbynism must be treated as a dangerous ideological threat to a liberal democracy, and not as an infantile, reversible outburst of ultra-leftism.
No-one has a feasible strategy to turn Labour back to its previous form. History offers no clear example of the internal undoing of populist fanaticism. It has always been defeated from outside. Labour is now irretrievable: there is no way of reversing the populist entrenchment within.
Corbyn’s Labour is a danger for the British political system as the Tories are for its economy and for its social fabric. Corbynism is a threat to liberal, pluralist democracy.
We need to build a progressive opposition to both Toryism and Corbynism. We need to defend liberal, pluralist democracy from the populisms of left and right. Building an alternative will take a generation, but we must start now.
16 September 2016
Minor edits: 17,18, 22 September 2016
Major edit: 18 June 2017

Bibliography
Bagehot (2016) ‘Why a “True Labour” splinter party could succeed where the SDP failed’, The Economist, 12 April. http://www.economist.com/blogs/bagehot/2016/08/labour-pains.
Baggini, Julian (2016) ‘Jeremy Corbyn is a great populist. But that’s no good for our democracy’, The Guardian, 30 July. https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2016/jul/25/jeremy-corbyn-populist-democracy-mps.
Borger, Julian (2016) ‘Venezuela’s worsening economic crisis’, The Guardian, 22 June. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2016/jun/22/venezuela-economic-crisis-guardian-briefing
Canning, Paul (2016) ‘Venezuela: The Left’s giant forgetting’. http://paulocanning.blogspot.co.uk/2016/09/venezuela-lefts-giant-forgetting.html
Corbyn, Jeremy (2011) ‘Foreword, to John A. Hobson, Imperialism: A Study’, facsimile reprint of 1902 edition (Nottingham: Spokesman).
Cunliffe, Rachel (2016) ‘Corbyn looks the other way as Venezuela self-destructs’, 18 January, http://capx.co/corbyn-looks-the-other-way-as-venezuela-self-destructs/.
Lawson, Neal (2016) ‘Social democracy without social democrats: how can the left recover?’ New Statesman. 12 May. http://www.newstatesman.com/politics/staggers/2016/05/social-democracy-without-social-democrats-how-can-left-recover.
Telesur (2015) ‘British MP Jeremy Corbyn speaks out for Venezuela’, 6 June. http://www.telesurtv.net/english/news/British-MP-Jeremy-Corbyn-Speaks-Out-For-Venezuela-20150605-0033.html.
Weyland, Kurt (2013) ‘The threat from the populist left’, Journal of Democracy, 24(3), pp. 18-32.
Wikipedia (2016) ‘Populism’. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Populism.
Posted in Democracy, Jeremy Corbyn, Labour Party, Left politics, Liberalism, Populism, Socialism, Uncategorized, Venezuela
August 16th, 2016 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
“This, from the always measured g. m. hodgson, shows Labour’s existential crisis in horrifying detail” – Susan Wilde
“The revolutionary road: excellent sober distillation of Marxism/Leninism/Trotskyism/socialism; rights v insurrection” – Rich Greenhill
“A very good summary of Labour and Trotskyism” – Gerry Hassan
“Another fantastic article!” – Lily Jayne Summers
John McDonnell, the Labour Shadow Chancellor, is an admirer of Trotsky. Corbyn once called upon the USSR to rehabilitate the Russian revolutionary.2
 Trotskyists are socialists who believe in the common ownership of the means of production. This goal was stated in Labour’s Clause Four from 1918 to 1995, so why shouldn’t Trotskyists be allowed to join Labour?
Trotskyists are socialists who believe in the common ownership of the means of production. This goal was stated in Labour’s Clause Four from 1918 to 1995, so why shouldn’t Trotskyists be allowed to join Labour?
Trotskyists differ from the devotees of Mao Zedong or Joseph Stalin. Trotskyists do not describe the murderous regimes of Mao’s China and the USSR as socialist. They promote themselves as anti-totalitarian, and they might seem much more democratic than other Marxists.
So why shouldn’t Trotskyists be allowed to join Labour?
The Parliamentary versus the Revolutionary Road
There is a prominent negative answer to this question. It raises profound differences of strategy. As Neil Kinnock (who did the party a great service by kicking out Militant in 1985) said in a speech to the Parliamentary Labour Party in July 2016:
‘In 1918 in the shadow of the Russian revolution [Labour members decided] … that they would not pursue the revolutionary road – it was a real choice in those days. They would pursue the parliamentary road to socialism.’
According to this view, Labour members and revolutionary Marxists share the same aim – socialism – but they differ on the method of getting there. Labour follows the parliamentary road; Marxists choose the revolutionary road.

Robert Owen
There are big problems with a part of this argument. Socialism was defined by Robert Owen and Karl Marx in terms of common ownership of the means of production and ‘the abolition of private property’.
But at least in practice since 1945, Labour has been less and less devoted to this goal. Finally, the goal of ‘common ownership’ was removed from Clause Four of the Labour Party Constitution in 1995.
Labour now says that it is a ‘democratic socialist’ party but defines this not in terms of common ownership. Instead there is a goal of social solidarity, believing ‘that by the strength of our common endeavour we achieve more than we achieve alone’, and in a society ‘in which power, wealth and opportunity are in the hands of the many not the few’.
Arguably, such a goal might be achievable in a reformed capitalism. But Trotskyists, like all Marxists, are emphatically against capitalism.
What Trotskyists and the post-1995 Labour Party Constitution mean by ‘socialism’ are very different. The divergences between Labour and Trotskyists concern different ends, as well as different means.
But Corbyn’s election as Leader by over 59 per cent of the membership in 2015 shows that the traditional definition and goal of socialism in the Labour Party is far from dead and buried. Under Corbyn’s leadership, Labour could return to its pre-1995 goals.

Tony Blair
Ironically, by getting rid of the traditional ‘common ownership’ version of socialism in 1995, but retaining the word ‘socialism’ in an attempt to invest it with a different meaning, Tony Blair provided legitimacy for any later attempt by classical socialists – including currently by Trotskyists and Corbynistas – to restore Labour to its original colours.
Within Labour today, because of this legacy, everyone from Trotskyists and Corbynistas at one extreme, through Owen Smith, Neil Kinnock and then on to Tony Blair at the other extreme, is obliged to call themselves a ‘socialist’. But there are massive silences and huge disagreements on its meaning.
Labour becomes less capable of discussing fundamental differences of goal, but clings onto the illusion of the fundamental goodness of something called ‘socialism’. Labour’s problem of entryism will never go away while the s-word continues to cast its spell. The word itself is an invitation for those who propose the common ownership of anything to join.
The Totalitarian Politics of Class Struggle
There are other fundamental problems with Marxism in general, and Trotskyism in particular. First, Marxism rejects the supreme values of the Enlightenment.
For example, Frederick Engels in Socialism: Utopian and Scientific, saw these Enlightenment values as ‘nothing more than the idealized kingdom of the bourgeoisie’ with its ‘bourgeois justice’, its ‘bourgeois equality before the law’ and ‘bourgeois property … proclaimed as one of the essential rights of man’.
 Marxists do not see the French Revolutionary principles of liberty, equality and fraternity as a potential achievement for all, but the rhetoric of the rising capitalist class in the class struggle against the old feudal order.
Marxists do not see the French Revolutionary principles of liberty, equality and fraternity as a potential achievement for all, but the rhetoric of the rising capitalist class in the class struggle against the old feudal order.
After playing their progressive historic role, Enlightenment ideas are seen as ‘bourgeois’ ideology, which now serves to repress the working class.
Marx saw socialism as the class destiny of the proletariat, which by overthrowing capitalism would emancipate humankind from inequality and exploitation. Socialism was not validated by an appeal to justice or rights. Instead it was grounded on ‘material’ and ‘economic’ developments within capitalism that were leading to growing internal crises and the rise of the proletariat.
Marx rejected all appeals to rights or justice. He bypassed the issues of morality and justice by focusing on the real social forces allegedly leading to socialism. But neither the driving forces of history nor the supposed destiny of a social class make this socialist future just, or morally right.
Karl Marx
By shelving the discourse on rights, in favour of the scientifically-clothed rhetoric of proletarian destiny, all versions of Marxism – including Trotskyism – are on the slippery slope toward totalitarianism.
When rights are no longer universal, and no-one has the protection of an independent legal system, the any action that is deemed ‘counter-revolutionary’ or ‘against the interests of the working class’ gives the accused no effective defence. The prosecutors monopolise the interpretation of guilt. Arbitrary punishment can follow.
The rights of critics and dissenters have to be protected, by their formal recognition and the autonomy of the judiciary. Unless this is done, any criticism can be crushed.
Trotsky was wrong: the roots of totalitarianism do not lie principally in the personalities of brutal, power-hungry individuals such as Stalin, but in Marxism itself. As Leszek Kolakowski suggested:
‘Marx’s anticipation of perfect unity of mankind and his mythology of the historically privileged proletarian consciousness … were responsible for his theory being eventually turned into an ideology of the totalitarian movement: not because he conceived of it in such terms, but because its basic values could hardly be materialized otherwise.’
Violence versus Parliament and Law
Laws get in the way of revolutionary struggle. Hence, along with their dilution of the notion of rights, Lenin proposed that all laws should be abolished.
 Writing in 1918, Lenin described the desired ‘dictatorship of the proletariat’ as ‘rule based directly upon force and unrestricted by any laws. The revolutionary dictatorship of the proletariat is rule won and maintained by the use of violence by the proletariat against the bourgeoisie, rule that is unrestricted by any laws.’ Trotsky supported Lenin in this and most other respects.
Writing in 1918, Lenin described the desired ‘dictatorship of the proletariat’ as ‘rule based directly upon force and unrestricted by any laws. The revolutionary dictatorship of the proletariat is rule won and maintained by the use of violence by the proletariat against the bourgeoisie, rule that is unrestricted by any laws.’ Trotsky supported Lenin in this and most other respects.
Consequently, a fundamental problem with Marxism is its failure to support the universality of human rights. Human rights apply to all, as in the majestic 1948 United Nations Declaration of Universal Human Rights.
Instead, Marxists see social advancement as a matter of ‘class struggle’ where one class must seize power and remove rights from another class. Lenin and Trotsky went one step further: they argued that this struggle for proletarian power must override the rule of law.
The Second Congress of the Communist International took place in Russia in 1920. Under the leadership of Lenin, one of its resolutions mentioned ‘bourgeois parliaments’ and declared:
‘The task of the proletariat consists in breaking up the bourgeois state machine, destroying it, and with it the parliamentary institutions, be they republican or constitutional monarchy.’
 Throughout his life, Trotsky defended the decisions of the first four congresses of the Communist International, which took place when Lenin was alive and before Stalin seized power.
Throughout his life, Trotsky defended the decisions of the first four congresses of the Communist International, which took place when Lenin was alive and before Stalin seized power.
Trotsky added his own idea of ‘permanent revolution’, involving civil war, even in a parliamentary democracy:
‘Socialist construction is conceivable only on the foundation of the class struggle, on a national and international scale. This struggle … must inevitably lead to explosions, that is, internally to civil wars and externally to revolutionary wars. Therein lies the permanent character of the socialist revolution as such, regardless of whether it is a backward country … or an old capitalist country which already has behind it a long epoch of democracy and parliamentarism.’
Conclusion: Hands Tied Behind their Backs
Those in Labour wanting to fight the battle against entryism have two hands tied behind their backs.
 First, by hanging on to the word ‘socialism’, after abandoning its original meaning, it is difficult to exclude those who are more genuinely socialist in the classical sense of common ownership. Labour’s obligatory (but now shallow) rhetoric of ‘socialism’ is a green light for socialist entryists of all kinds.
First, by hanging on to the word ‘socialism’, after abandoning its original meaning, it is difficult to exclude those who are more genuinely socialist in the classical sense of common ownership. Labour’s obligatory (but now shallow) rhetoric of ‘socialism’ is a green light for socialist entryists of all kinds.
Second, Labour has long-ago ditched the politics of class struggle, but it retains a notion of class partisanship in its very name. It was formed historically to represent the interests of the working class. It was built upon the trade union movement. Labour itself is a class party.
 Of course, Labour in practice has put aside the notion that it is speaking for one section of society only. But its name remains a problem, both for broadening its appeal and for barring the more energetic and extreme exponents of working class representation and power.
Of course, Labour in practice has put aside the notion that it is speaking for one section of society only. But its name remains a problem, both for broadening its appeal and for barring the more energetic and extreme exponents of working class representation and power.
Of course, to achieve its goals, Labour is pledged to working through parliament, rather than through revolution. This is a very important difference. Many Marxists are still devoted to insurrection. Labour clearly is not. With this one big foot it can kick back. But its two hands are tied.
Labour still has much outdated baggage to deal with. Even if it staves off Trotskyist entryism – which now seems unlikely, at least while Corbyn is Labour Leader – it still will have a number of big problems. It will need to find and package a new identity for itself, which is suitable for the twenty-first century.
Retaining an unconvincing redefinition of ‘socialism’ and calling itself ‘Labour’ will not do.
Labour needs to come to terms with the fact that both classical socialism and class politics are untenable. It has to put democratic and progressive Enlightenment values at its centre, and reconfigure itself for the challenges of the twenty-first century.
16 August 2016
Minor edits: 17-18 August 2016
Endnotes
- Note that I refrain in this article from estimating the scale or impact of Trotskyist entryism in the Labour Party. They are not central to my argument here. For evidence of both (and of Corbyn’s links with the IRA) see here. At least currently, entryists into Labour are probably few in number, but it is a well-established fact that a few determined people can influence many thousands.
- In 2010, McDonnell attended an event commemorating the 70th anniversary of Trotsky’s assassination and has praised the ‘importance’ of his ideas (Riley-Smith 2016a). In 1988 Corbyn demanded from Parliament that the USSR should ‘give complete rehabilitation to Leon Trotsky’ (Riley-Smith, 2016b). Nothing wrong with that, but its shows the way he leans and who he chooses as friends.
- Personal note: I was a critical and wobbly Trotskyist from 1968 to 1973. I re-joined the Labour Party in 1974 and left it in 2001. The photograph below shows me (not then a Trot) visiting Trotsky’s house in Mexico in 1981, where he was murdered in 1940. It is a moving and impressive place.

References
Crick, Michael (2016) Militant (London: Biteback Publishing), esp. pp. xvii–xviii.
Kolakowski, Leszek (1977) ‘Marxist Roots of Stalinism’, in Robert C. Tucker (ed.) (1977) Stalinism: Essays in Historical Interpretation (New York: Norton), pp. 283-98.
Lenin, Vladimir Ilyich (1967) Selected Works in Three Volumes (London: Lawrence and Wishart), esp. vol. 3, p. 49.
Marx, Karl and Engels, Frederick (1962) Selected Works in Two Volumes (London: Lawrence and Wishart), esp. vol. 2, p. 117.
New Park Publications (1977) The Second Congress of the Communist International, 2 vols (London: New Park), esp. vol. 2, p. 52.
Riley-Smith, Ben (2016a) ‘Labour Entryism Row: John McDonnell Attended Celebration of Leon Trotsky and Praised ‘Importance’ of his Ideas’, The Telegraph, 14 August. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2016/08/14/labour-entryism-row-john-mcdonnell-attended-celebration-of-leon/.
Riley-Smith, Ben (2016b) ‘Jeremy Corbyn Called for a “Complete Rehabilitation” of Leon Trotsky in Parliament’, The Telegraph, 16 August. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2016/08/15/jeremy-corbyn-called-for-complete-rehabilitation-of-leon-trotsky/
Sparrow, Andrew and Jones, Harrison (2016) ‘Secret Recording of Kinnock’s anti-Corbyn Speech to MPs – In Full’, The Guardian, 6 July. http://www.theguardian.com/politics/2016/jul/08/secret-recording-neil-kinnock-jeremy-corbyn-step-down-speech-to-mps-in-full.
Trotsky, Leon D. (1962) The Permanent Revolution and Results and Prospects (London: New Park), esp. ch. 10.
Watson, Tom (2016) ‘Tom Watson Sends Corbyn “Proof of Trotskyist Labour Infiltration”’, The Guardian, 10 August. http://www.theguardian.com/politics/2016/aug/10/tom-watson-sends-corbyn-proof-of-trotskyist-labour-infiltration
Posted in Common ownership, Democracy, Jeremy Corbyn, Labour Party, Left politics, Liberalism, Nationalization, Robert Owen, Socialism, Tony Benn, Tony Blair, Uncategorized


 Even the foremost historians of “the neoliberal project” have acknowledged the problem. Philip Mirowski and Dieter Plehwe wrote:
Even the foremost historians of “the neoliberal project” have acknowledged the problem. Philip Mirowski and Dieter Plehwe wrote:

 The Mont Pèlerin Society was dominated by economists. No less than eight winners of the Nobel Prize in economics have been its members.
The Mont Pèlerin Society was dominated by economists. No less than eight winners of the Nobel Prize in economics have been its members.

 But Blair still wanted to cooperate with the Liberal Democrats on several issues, including on electoral reform. He insisted that the two parties were natural allies, and they should not have gone their separate ways a hundred years earlier. In his first speech to a Labour conference after his landslide election victory,
But Blair still wanted to cooperate with the Liberal Democrats on several issues, including on electoral reform. He insisted that the two parties were natural allies, and they should not have gone their separate ways a hundred years earlier. In his first speech to a Labour conference after his landslide election victory,  While leading figures in his Cabinet such as Robin Cook, Mo Mowlam, Clare Short and Peter Mandelson supported electoral reform, Blair faced the implacable opposition of Chancellor Gordon Brown, Deputy Prime Minister and Secretary of State John Prescott, Home Secretary Jack Straw, numerous trade union leaders and an energetic campaign against proportional representation from Labour’s ranks.
While leading figures in his Cabinet such as Robin Cook, Mo Mowlam, Clare Short and Peter Mandelson supported electoral reform, Blair faced the implacable opposition of Chancellor Gordon Brown, Deputy Prime Minister and Secretary of State John Prescott, Home Secretary Jack Straw, numerous trade union leaders and an energetic campaign against proportional representation from Labour’s ranks. I can speak with a little authority here, because this was once my own major objection to proportional representation (PR). As loyal and active Labour party members, Peter Hain and I published a booklet in 1982 entitled Proportional Misrepresentation?
I can speak with a little authority here, because this was once my own major objection to proportional representation (PR). As loyal and active Labour party members, Peter Hain and I published a booklet in 1982 entitled Proportional Misrepresentation?  Just as the existing electoral system might be used by a left party for radical reform, it was being used by a newly-radicalised Tory party to divide the country, to undermine the welfare state and to attack the rights of working people.
Just as the existing electoral system might be used by a left party for radical reform, it was being used by a newly-radicalised Tory party to divide the country, to undermine the welfare state and to attack the rights of working people. The Jenkins Commission reported in September 1998 and suggested the alternative vote top-up (AV+) system. Blair immediately faced intense opposition, from within his own Cabinet, from a large number of Labour MPs, from a large section of the Labour Party in the country, and from several trade unions.
The Jenkins Commission reported in September 1998 and suggested the alternative vote top-up (AV+) system. Blair immediately faced intense opposition, from within his own Cabinet, from a large number of Labour MPs, from a large section of the Labour Party in the country, and from several trade unions.
 But if a more proportional system had been in place in 2010, then a coalition between Labour and the Liberal Democrats would have had something like 366 seats, which would have been a clear overall majority. The Tories could have been kept out of power.
But if a more proportional system had been in place in 2010, then a coalition between Labour and the Liberal Democrats would have had something like 366 seats, which would have been a clear overall majority. The Tories could have been kept out of power. But a tiny consolation of this dismal entrapment is the time it gives us to debate the best system, which would offer something closer to proportionality, and would have a chance of convincing the electorate.
But a tiny consolation of this dismal entrapment is the time it gives us to debate the best system, which would offer something closer to proportionality, and would have a chance of convincing the electorate.


 Dictators and populists are fond of referendums because they deploy “the will of the people” against constitutional safeguards. Hitler held a referendum in 1933, to garner mass support to withdraw from the League of Nations. In 1934 he held another referendum, which endorsed his bid for supreme power in Germany. Yet another referendum in 1936 ratified Hitler’s military occupation of the Rhineland and his one-party state. A fourth referendum in 1938 approved Hitler’s annexation of Austria. All propositions in these plebiscites received huge majorities.
Dictators and populists are fond of referendums because they deploy “the will of the people” against constitutional safeguards. Hitler held a referendum in 1933, to garner mass support to withdraw from the League of Nations. In 1934 he held another referendum, which endorsed his bid for supreme power in Germany. Yet another referendum in 1936 ratified Hitler’s military occupation of the Rhineland and his one-party state. A fourth referendum in 1938 approved Hitler’s annexation of Austria. All propositions in these plebiscites received huge majorities. In the UK in 1983, around 75 per cent of people were in favour of the death penalty. Although
In the UK in 1983, around 75 per cent of people were in favour of the death penalty. Although  By these measures, according to “the will of the people” homosexual acts should not have been made legal in 2003 or 2004.
By these measures, according to “the will of the people” homosexual acts should not have been made legal in 2003 or 2004. Instead, they must be the subject of ongoing, informed debate, guided by the need to minimise harm, alongside “an egalitarian conception of the good, focusing on equal opportunities for a worthwhile life” (as Philip Kitcher puts in his important book on The Ethical Project).
Instead, they must be the subject of ongoing, informed debate, guided by the need to minimise harm, alongside “an egalitarian conception of the good, focusing on equal opportunities for a worthwhile life” (as Philip Kitcher puts in his important book on The Ethical Project).  In the case of climate change, there is a strong consensus that human activity is leading to global warming. Albeit imperfect, this is the best indication we have of scientific truth. It is not the opinion of the general public, most of whom do not understand climate science.
In the case of climate change, there is a strong consensus that human activity is leading to global warming. Albeit imperfect, this is the best indication we have of scientific truth. It is not the opinion of the general public, most of whom do not understand climate science. If this were a valid guiding rule, then MPs would be redundant. They could be replaced by online opinion polls on every question. The public would be invited to vote over every piece of legislation and “the will of the people” could be upheld.
If this were a valid guiding rule, then MPs would be redundant. They could be replaced by online opinion polls on every question. The public would be invited to vote over every piece of legislation and “the will of the people” could be upheld.


 Marxist-led national liberation movements in Cuba, Indochina and elsewhere kept the collectivist vision alive for the Left around the world. Liberalism was see as the fake ideology of American imperialism and the global bourgeoisie.
Marxist-led national liberation movements in Cuba, Indochina and elsewhere kept the collectivist vision alive for the Left around the world. Liberalism was see as the fake ideology of American imperialism and the global bourgeoisie.











 Of course, Muslims and others suffer significant discrimination, in
Of course, Muslims and others suffer significant discrimination, in  But much of the political debate is about immigrant numbers. The Tories ignore the economic evidence and start a Dutch auction of targets, to stem numbers. A large part of the Labour Party, facing a seepage of its working class support to UKIP, moves in a similar direction.
But much of the political debate is about immigrant numbers. The Tories ignore the economic evidence and start a Dutch auction of targets, to stem numbers. A large part of the Labour Party, facing a seepage of its working class support to UKIP, moves in a similar direction.


 After coming to power in 1997, Labour Prime Minister
After coming to power in 1997, Labour Prime Minister 


 After several years he renounced his former extremism, but retained his Islamic faith. In an interview he revealed the segregated life of his upbringing:
After several years he renounced his former extremism, but retained his Islamic faith. In an interview he revealed the segregated life of his upbringing: Some on the Far Left disowned Butt for betraying the struggle against “Western imperialism”. He was also criticized by one member of the “Stop the War” movement, who is a leading supporter of the Muslim Brotherhood, for his “call to change the face of Islam” (Cohen 2007, pp. 371-2).
Some on the Far Left disowned Butt for betraying the struggle against “Western imperialism”. He was also criticized by one member of the “Stop the War” movement, who is a leading supporter of the Muslim Brotherhood, for his “call to change the face of Islam” (Cohen 2007, pp. 371-2). But the official government document outlining this policy mentions respect and tolerance for other races but fails to mention discrimination against women or gays. It rightly mentions the freedom to “choose and hold” any faith, but not the freedom to exit a religion without sanction. It mentions “individual liberty” only once, and fails to uphold freedom of non-violent expression, including when it may cause offence.
But the official government document outlining this policy mentions respect and tolerance for other races but fails to mention discrimination against women or gays. It rightly mentions the freedom to “choose and hold” any faith, but not the freedom to exit a religion without sanction. It mentions “individual liberty” only once, and fails to uphold freedom of non-violent expression, including when it may cause offence. Another problem here is not the values as such, but their nationalistic description as “British”. Democracy was not invented in Britain: Ancient Athens and Viking Iceland have much earlier precursors. The US and France have much earlier claims to the values of liberty and religious tolerance. Britain legally discriminated against Protestant nonconformists and Catholics until the nineteenth century, and it still bars any Catholic from becoming its sovereign.
Another problem here is not the values as such, but their nationalistic description as “British”. Democracy was not invented in Britain: Ancient Athens and Viking Iceland have much earlier precursors. The US and France have much earlier claims to the values of liberty and religious tolerance. Britain legally discriminated against Protestant nonconformists and Catholics until the nineteenth century, and it still bars any Catholic from becoming its sovereign.





 Putting the blame on “neoliberalism” underestimates the way in which outsiders such as Trump and Farage have created populist movements that blame “the elite” and offer simplistic solutions, such as to “curb immigration”. Blaming “neoliberalism” underestimates the pernicious influences of racism and anti-Muslim prejudice.
Putting the blame on “neoliberalism” underestimates the way in which outsiders such as Trump and Farage have created populist movements that blame “the elite” and offer simplistic solutions, such as to “curb immigration”. Blaming “neoliberalism” underestimates the pernicious influences of racism and anti-Muslim prejudice. 


 Unlike any false claim that “neoliberalism” has reduced overall taxes, the increase of privatisation is manifest. In addition, it has sometimes led to deleterious consequences including lower pay for workers and a reduced quality of services.
Unlike any false claim that “neoliberalism” has reduced overall taxes, the increase of privatisation is manifest. In addition, it has sometimes led to deleterious consequences including lower pay for workers and a reduced quality of services. Ken Loach’s moving film, I, Daniel Blake, portrays the heart-breaking human consequences of the UK Conservative government’s shredding of the welfare safety net for the poor. Attempts to reduce public spending in many countries have led to millions of human tragedies like this.
Ken Loach’s moving film, I, Daniel Blake, portrays the heart-breaking human consequences of the UK Conservative government’s shredding of the welfare safety net for the poor. Attempts to reduce public spending in many countries have led to millions of human tragedies like this. All this is real, and tragic. Millions have suffered because of such misguided policies. But we should not jump to the conclusion that “neoliberalism” has been successful in moving toward a minimal economic role for the state.
All this is real, and tragic. Millions have suffered because of such misguided policies. But we should not jump to the conclusion that “neoliberalism” has been successful in moving toward a minimal economic role for the state.
 The first sentence is valid and important. The second is simplistic. As I elaborate in my book
The first sentence is valid and important. The second is simplistic. As I elaborate in my book  Impersonal relations occur in bureaucracies as well as in markets. Large-scale systems of national planning also make much interaction impersonal. People become atomised; they become numbers, to be processed by bureaucrats and computers.
Impersonal relations occur in bureaucracies as well as in markets. Large-scale systems of national planning also make much interaction impersonal. People become atomised; they become numbers, to be processed by bureaucrats and computers. But such nuances have been lost in a global storm of “neoliberal” accusations. Klein and Monbiot have added some force and authority to this widening tempest.
But such nuances have been lost in a global storm of “neoliberal” accusations. Klein and Monbiot have added some force and authority to this widening tempest.
 Jeremy Corbyn is very different from Nigel Farage and Donald Trump. Corbyn is neither a racist nor a misogynist (
Jeremy Corbyn is very different from Nigel Farage and Donald Trump. Corbyn is neither a racist nor a misogynist (



 Consider the example of the EU referendum in June 2016. After the result, Corbyn took it for granted that Britain should leave the EU and immediately trigger Brexit, irrespective of the outcome of Britain’s negotiations on the terms of leaving. Like his fellow-populist Farage, Corbyn accepted that ‘the people had spoken’. For him, the expression of popular will was the end of the matter.
Consider the example of the EU referendum in June 2016. After the result, Corbyn took it for granted that Britain should leave the EU and immediately trigger Brexit, irrespective of the outcome of Britain’s negotiations on the terms of leaving. Like his fellow-populist Farage, Corbyn accepted that ‘the people had spoken’. For him, the expression of popular will was the end of the matter.

 Trotskyists are socialists who believe in the common ownership of the means of production. This goal was stated in Labour’s Clause Four from 1918 to 1995, so why shouldn’t Trotskyists be allowed to join Labour?
Trotskyists are socialists who believe in the common ownership of the means of production. This goal was stated in Labour’s Clause Four from 1918 to 1995, so why shouldn’t Trotskyists be allowed to join Labour?
 Writing in 1918, Lenin described the desired ‘dictatorship of the proletariat’ as ‘rule based directly upon force and unrestricted by any laws. The revolutionary dictatorship of the proletariat is rule won and maintained by the use of violence by the proletariat against the bourgeoisie, rule that is unrestricted by any laws.’ Trotsky supported Lenin in this and most other respects.
Writing in 1918, Lenin described the desired ‘dictatorship of the proletariat’ as ‘rule based directly upon force and unrestricted by any laws. The revolutionary dictatorship of the proletariat is rule won and maintained by the use of violence by the proletariat against the bourgeoisie, rule that is unrestricted by any laws.’ Trotsky supported Lenin in this and most other respects. Throughout his life, Trotsky defended the decisions of the first four congresses of the Communist International, which took place when Lenin was alive and before Stalin seized power.
Throughout his life, Trotsky defended the decisions of the first four congresses of the Communist International, which took place when Lenin was alive and before Stalin seized power. First, by hanging on to the word ‘socialism’, after abandoning its original meaning, it is difficult to exclude those who are more genuinely socialist in the classical sense of common ownership. Labour’s obligatory (but now shallow) rhetoric of ‘socialism’ is a green light for socialist entryists of all kinds.
First, by hanging on to the word ‘socialism’, after abandoning its original meaning, it is difficult to exclude those who are more genuinely socialist in the classical sense of common ownership. Labour’s obligatory (but now shallow) rhetoric of ‘socialism’ is a green light for socialist entryists of all kinds. Of course, Labour in practice has put aside the notion that it is speaking for one section of society only. But its name remains a problem, both for broadening its appeal and for barring the more energetic and extreme exponents of working class representation and power.
Of course, Labour in practice has put aside the notion that it is speaking for one section of society only. But its name remains a problem, both for broadening its appeal and for barring the more energetic and extreme exponents of working class representation and power.