Category: Labour Party
September 20th, 2017 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
I was born in 1946. I lived in a council house until I was 16. My family were Labour. My privilege was not money, but that my parents and grandparents all valued education and culture. But none of them obtained a university degree, because they were less accessible at the time.

Harold Wilson
I became involved in the Labour Party in 1964 and then saw myself as a Tribune socialist following the steps of great radicals such as Michael Foot. After welcoming Harold Wilson’s election victory in 1964, I became critical of the new Prime Minister because of his nominal support for the US in the Vietnam War.
Vietnam and Marxism
For my baby-boom generation, the Vietnam War was a great generator of radicalism. Like many of my university friends, I became a Marxist in 1966. We were drawn into a turbulent and exciting world that combined activism with ideas and debate. I saw myself as a Marxist until about 1980.
I studied mathematics and philosophy from 1965 to 1968 and economics from 1972 to 1974. Both periods were at the University of Manchester. In the intervening years I taught myself Marxist economics. My knowledge of economics became enduringly significant in my political evolution.
 I was at the LSE student occupation in 1967 and one of the Grosvenor Square demonstrations in 1968. In that year I copied Bertrand Russell and tore up my Labour Party membership card in protest against US aggression in Vietnam.
I was at the LSE student occupation in 1967 and one of the Grosvenor Square demonstrations in 1968. In that year I copied Bertrand Russell and tore up my Labour Party membership card in protest against US aggression in Vietnam.
Marxists dominated the activists on the university campuses. The left was divided and fractious. There were Soviet Bloc loyalists in the Communist Party of Great Britain. There were lovers of Mao Zedong and several rival Trotskyist sects. I could not bring myself to support any totalitarian regime – East or West – so I joined the forerunner of what is now the Socialist Workers’ Party, which saw everything existing as “capitalist”.
My departure from the SWP came in 1971 when they expelled a dissident faction with which I sympathised. (That critical faction eventually became the Alliance for Workers’ Liberty, of Momentum fame in the Corbyn Era.)
I flirted briefly with the International Marxist Group, which included glamorous figures such as Tariq Ali, and Robin Blackburn of the New Left Review. The IMG was stronger in its support for the women’s movement and for gay rights.
After a few years among the sects I could see that something was wrong. These groups were aiming to help create a much better society, but they were generally dogmatic and intolerant. Some were ruthless, pugnacious and fanatical. I did not want to see any social system facilitated or run by these people.

But on the other hand I then accepted the Marxist view that capitalism was exploitative and frequently led to oppression and war. The evidence of this was seemingly before our eyes.
Re-joining Labour and changing strategy
After Labour’s electoral defeat in 1970, there was a strong and growing left in the Labour Party and that seemed the best hope for socialists. Against the advice of Ralph Miliband (whom I knew personally) and others, I re-joined Labour in 1974.
In 1975 I published a pamphlet entitled Trotsky and Fatalistic Marxism. This tried to explain the fanaticism and intolerance of many Marxists in terms of their belief in the imminent decay and collapse of capitalist democracies. Trotskyists had failed to appreciate the enormous expansion and dynamism of capitalism after 1945. Their explanations of the survival of capitalism were weak.
Published in 1977, a longer work entitled Socialism and Parliamentary Democracy elaborated more of my thinking. Marxist-Leninists believed that parliament and the capitalist state should be “smashed”. Influenced by Max Weber and others, I argued that in modern democracies, government drew their perceived legitimacy from parliamentary elections. If socialism became a majority view, then socialists could and should gain a majority in parliament.
In the book I criticised the 1968 revolutionary movement in France for boycotting the elections called by President Charles de Gaulle in that year. Victory in the elections gave de Gaulle legitimacy. The huge movement of students and workers was crushed.

Paris – May 1968
As I had anticipated, my heresies were dismissed out of hand by the far left sects. But the book proved to be rather influential in the UK and internationally. It received a strongly sympathetic hearing on the Labour left. It was translated into Italian, Japanese, Spanish and Turkish. It persuaded a leading member of the violent Basque separatist group ETA to abandon terrorism.
I don’t know if he read my book, but Daniel Cohn-Bendit, the leader of the revolutionary movement in France in May 1968, later argued that it had been a mistake to boycott the French parliamentary elections.
Labour had been reconciled to the parliamentary road to socialism since its formation. The sects argued that it wouldn’t work. My response was that insurrection would not work either. In democracies we needed a combination of parliamentary and extra-parliamentary action.
Questioning ends as well as means
The killing fields in Cambodia affected me deeply. After seizing power in 1975 the Khmer Rouge forced everyone into the countryside and obliterated about two million people – a quarter of the Cambodian population – in the pursuit of their communist utopia.
I could not dismiss this as an aberration. After all, the Khmer Rouge aims, which included the abolition of money, private property and markets, were central to the Communist Manifesto by Karl Marx and Frederick Engels.

Khmer Rouge Killing Fields
The far left were able to publish papers and debate ideas because they lived in a democracy that tolerated freedom of expression. But the ideas and actions of the sects, if they gained influence or power, would curtail these very liberties upon which they had depended.
Crucially, I was not naïve enough to believe that freedom and political pluralism could be guaranteed simply by the goodwill of a more enlightened Marxist leadership, who valued these things more than the Khmer Rouge. Good intentions were not enough.
I had retained a good lesson from Marxism. Effective ideas and practices draw their strength from agglomerations of power sustained by the structures of the politico-economic system. Hence a genuinely pluralist and tolerant political sphere depended on pluralism and decentralisation in the economic domain. A pluralist polity requires a pluralist economy.

Beatrice & Sidney Webb
Prominent Labour thinkers such as Beatrice Webb, Sidney Webb and G. D. H. Cole had all argued for a decentralised socialist system. But they still sought the abolition of private property and markets. The state would ultimately own everything. So what institutional, legal or other politico-economic forces could stop it retrieving all delegated powers to the centre, when deemed required, or when goodwill wore thin?
Any viable socialism always needs markets
I came to the view that genuine and lasting decentralisation would depend on the existence of organisations with some genuine autonomy and legal independence, providing powers to own property and trade with other organisations. Any viable socialism would always need markets – it was not simply a matter of tolerating or compromising with them.
This crucial transition of my thinking occurred between 1977 and 1980. I cannot recall the detailed influences. But I am sure that the initial impetus did not come from Ludwig von Mises or Friedrich Hayek. I did not delve deeply into their works until the early 1980s.

János Kornai
There had been several socialist proposals to nationalise the sector producing capital goods but retain competition and markets for consumer goods. I was more attracted by the Hungarian economist János Kornai’s more sophisticated proposal (originally published in 1965) to use a dynamic combination of markets and planning, where planning provided strategic impetus, and markets signalled information and gave scope for innovation and planning adjustment.
Over the new year of 1979-1980 I went on a short tourist group visit to the Soviet Union. Some of my companions were dewy-eyed admirers of the system, but I was prepared for its flaws, including the ubiquitous black markets and corruption.
I had been given the address in Moscow of an Englishman married to a Russian. As a former Communist, he explained in detail in his apartment how and why his views had quickly changed: “I challenge any supporter of the Soviet Union to live here just for six months.”

Alec Nove
When Alec Nove published a classic article on feasible socialism in New Left Review in early 1980 I was ready for it. Nove also argued that markets were essential to any viable socialism. He realised that he was attacking deeply-ingrained orthodoxy on the left.
(Later I had the pleasure of meeting both Kornai and Nove several times. Nove died in 1994 but Kornai is still alive. I am delighted to be invited as a keynote speaker at a conference in his honour in Budapest in 2018.)
Labouring as a revisionist
Any acceptance of markets was an anathema to followers of both Karl Marx and Tony Benn. Benn distanced himself from those who supported the persistence of markets.
But I found common ground with Benn and others over what was called “the alternative economic strategy”. I outlined my positive views on this in a pamphlet entitled Socialist Economic Strategy in 1979. It was published by Independent Labour Publications.
Independent Labour Publications was the residue of the old Independent Labour Party, which had played a central role in Labour history from the 1890s to the 1940s. The Independent Labour Party split from the Labour Party in 1931. But in 1975 it formally dissolved as a party and rejoined Labour as Independent Labour Publications.
I was involved in this organisation briefly. Despite outward appearances they turned out to be another sect, lacking any vision of a workable socialism. They too were uneasy about my revisionism. Although my Socialist Economic Strategy was a bestseller by their standards, they refused to reprint it. We parted company in 1981.

Geoff Hodgson, Jean Shepherd & John Maguire in 1979
In 1979 I was the unsuccessful Labour Parliamentary Candidate for Manchester Withington. The seat became Labour in 1987.
I met Benn a few times and supported him in the 1981 deputy leadership election. This alignment was marked in my book Labour at the Crossroads, published in that year. Therein I again supported the alternative economic strategy. But against Benn himself, I argued in that book that in some sectors of the economy “there is no substitute for competition and a market” (p. 206).
(In his important book on The Labour Party’s Political Thought, Geoffrey Foote quotes me (pp. 320, 347) as a “Bennite”. But because of my explicit acceptance of markets, I was unrepresentative of the Bennite stream of thought.)
Subsequently my opinion of Benn shifted. He was a magnificent speaker, but his writings on socialism are vague and unclear. His use of history is unscholarly and cavalier. He was not a well-read intellectual like Michael Foot.

Tony Benn at a Militant meeting
While Benn’s “alternative economic strategy” accepted markets and a private sector for the present, it seemed to me that he wanted to move eventually toward a socialist economy without any markets at all. It was no accident that Benn and his followers defended the Trotskyist sect Militant when they were pushed out of the party from 1985 to 1992.
In 1984 I published my book on The Democratic Economy, where I set out my view on the importance and complementarity of both markets and planning. My argument was framed in socialist language but therein I distanced myself from Marxism. The book received a critical response from many on both the soft and hard left.
The Labour Coordinating Committee
Margaret Thatcher came to power in 1979. One of Thatcher’s most popular policies was to promote the sale of council-owned housing to the tenants. Labour had opposed this policy. The disastrous 1983 defeat of Labour on a Bennite manifesto prompted a rethink, on this and several other issues.
For some of us, this rethink amounted to more than expedient doctrinal trimming. Encouraging home ownership was really a good idea: why should all property be owned by the rich? But while supporting home ownership, we argued that the government should also build more social housing and enlarge the stock available for rent by low-income families.
But these ideas met stiff resistance in the Labour Party ranks, and not simply from Trotskyist entryists such as Militant. The resistance from Benn and his supporters was substantial and even more enduring. It was clear that old-fashioned socialist ideas still had a tenacious appeal among Labour’s membership.
The Labour Coordinating Committee (LCC) became one of the primary modernising forces within Labour. Its leadership included Hilary Benn, Cherie Blair, Mike Gapes, Peter Hain, Harriet Harman, Kate Hoey (the Brexiteer) and others of enduring fame. I was elected to the LCC executive committee. We worked closely with the new leader Neil Kinnock, and with members of his shadow cabinet, including Robin Cook.
Changing Clause Four
I have detailed elsewhere my LCC attempt to bring about discussion to change Labour’s Clause Four. The version that had been in place since 1918 called for the “common ownership of the means of production, distribution and exchange”. This provided for no exception: all production would be in common ownership and there would be no private sector.
Although some Labour Party thinkers began to entertain the possibility of some private enterprise, many party members remained resolutely in support of widespread common ownership.
Against my efforts, the 1983 AGM of the Labour Coordinating Committee defeated the proposal that Clause Four should be rewritten. This was out of fear of antagonising the Benn wing. Instead, the LCC resolved that Clause Four should be “clarified”.
But a resolution on long-term aims, which I had helped to draft, was passed by a large majority. The resolution called for the Labour Party to draft a new statement of aims, upholding “that socialism involves extended democracy and real equality. Democracy under socialism is extended to industry and the community … and must involve a substantial decentralisation of power.”
There was a commitment to “political pluralism” and to “economic pluralism” involving “a variety of forms of common ownership … and the toleration of a small private sector including self-employed workers and other private firms.” The economy must be dominated by mechanisms of “democratic planning … but also accommodating a market mechanism in some areas.”
But there was strong hostility to these mildly revisionist ideas from within Labour’s ranks at the time, including from Jeremy Corbyn and Tony Benn.

Tony Benn & Jeremy Corbyn
The Guardian newspaper reported the LCC conference with the headline: “Labour breaks taboo on ownership”. For a while, the LCC tried to keep the conversation going on the need to revise Labour’s aims. The LCC held a conference in Liverpool in June 1984 on “The Socialist Vision”. But enthusiasm for this discussion fizzled out. By 1985 the LCC’s revisionist initiative had been kicked into the long grass. My efforts had failed.
But to their credit, Neil Kinnock and his deputy Roy Hattersley saw the need for Labour to modernise its aims. I advised them both for a while. But after 1987 I became less active in the Labour Party. My inactivity was born partly out of frustration that it was so difficult to shift Labour from its congenital hostility to markets and private enterprise.
But after a fourth election defeat in 1992 the party became more pliable. Tony Blair was elected as leader in 1994. Blair successfully changed the wording of Clause Four to endorse a strong private sector, but the dramatic rise of Corbyn in the party since 2015 shows that the old collectivist DNA has endured.
Towards liberalism
In many ways I have always been a liberal, especially in my support for freedom of expression, other human rights and democracy. By the late 1970s I also accepted the importance of markets and private property. But the emphasis in my thinking has shifted further in the last 30 years.
My academic works show a few markers of my political evolution. On page xvi of my 1999 book Economics and Utopia I wrote of my common ground with the US liberal John Dewey and with
“British social liberalism, which stretches from John Stuart Mill through Thomas H. Green to John A. Hobson, John Maynard Keynes and William Beveridge.”
These thinkers still inspire me. But I would now also stress the importance of Thomas Paine. Other heroes include George Orwell and Arthur Koestler.
So by 1999 I was a true liberal, of social-democratic stripe. I had already moved some distance from the ideas in my 1984 book, which had over-stressed the possibilities for large-scale planning and for extensive democratic decision-making in large, complex economies.
But I still believe in judicious state intervention and regulation, and I am still an enthusiast for experiments with worker cooperatives and other forms of worker and community participation. With their lower levels of economic inequality, I see the Nordic countries as good role models for in the rest of the capitalist world.
From leaving Labour to joining the Liberal Democrats
In 2001 I left the Labour Party because of Blair’s energetic support for faith schools, Labour’s inadequate proposal for House of Lords reform and its neglect of the problem of economic inequality. I would have left over the Iraq War. Previously I had sometimes voted tactically for the Liberal Party, when they were second behind the Tories in my constituency. But what was tactical was also in growing part a matter of conviction.
I voted Liberal Democrat in the 1997, 2001, 2005 and 2010 general elections. But I did not approve of the coalition with the Tories. So the Liberal Democrats did not get my vote in 2015.
I re-entered political activity in 2016 after the Brexit referendum. My wife (Vinny Logan) had been a critical but close companion on my long journey since 1980. But unlike me she had always voted Labour. After the Brexit vote she joined the Liberal Democrats and I followed her after a few days. It will be a long hard slog to change British politics for the better, but it is vital that we try.
My wife and I were each brought up in a social culture where the Tories and the Establishment were the enemy, and the Liberals were seen as wishy-washy waverers in the class war. Labour was the only game in town.
It takes a long time to remove these ingrained preconceptions and learn that liberalism is the greatest legacy of the Enlightenment. It is the strongest guardian of both prosperity and freedom. Although Liberals have been in a minority, they are largely responsible for the foundation of the British welfare state. The NHS was originally a Liberal proposal. The Liberal Democrats constitute the most pro-EU party in the UK.
But some Liberal Democrats do not understand that it is the job of government in a recession to increase effective demand, particularly by increasing investment and raising disposable incomes for the poor. But the party is a broad church, and I will argue my corner in favour of Keynesian liberal economic policies.
 I am a radical liberal. I believe in social solidarity with the less-privileged, as well as in individual rights. As Charles Kennedy showed when he was leader, the Liberal Democrats can succeed when they take principled, radical positions on justice, equality and war.
I am a radical liberal. I believe in social solidarity with the less-privileged, as well as in individual rights. As Charles Kennedy showed when he was leader, the Liberal Democrats can succeed when they take principled, radical positions on justice, equality and war.
Today, both the Conservatives (now ruled by deceitful nationalists) and Labour (where the rising hard left dominate the timid moderates) are dangerous threats to the liberal and democratic rights and values that in the past we have taken too much for granted. We must now stand up to defend those rights and values, against dogma, ignorance, intolerance, petty nationalism and deceit.
20 September 2017
Minor edits – 25 September 2017, 22 October 2017, 10 April 2018.
This book elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Published by University of Chicago Press in January 2018 
Bibliography
Foote, Geoffrey (1997) The Labour Party’s Political Thought: A History, 3rd edn. (London: Palgrave).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (1975) Trotsky and Fatalistic Marxism (Nottingham: Spokesman).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (1977) Socialism and Parliamentary Democracy (Nottingham: Spokesman).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (1979) Socialist Economic Strategy (Leeds: Independent Labour Publications).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (1981) Labour at the Crossroads: The Political and Economic Challenge to Labour Party in the 1980s (Oxford: Martin Robertson).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (1984) The Democratic Economy: A New Look at Planning, Markets and Power (Harmondsworth: Penguin).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (1999) Economics and Utopia: Why the Learning Economy is not the End of History (London and New York: Routledge).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2017) Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, forthcoming).
Kornai, János (1965) ‘Mathematical Programming as a Tool of Socialist Economic Planning’, reprinted in Nove, Alec and Nuti, D. M. (eds) (1972) Socialist Economics (Harmondsworth: Penguin), pp. 475-488.
Nove, Alec (1980) ‘The Soviet Economy: Problems and Prospects’, New Left Review, no. 119, January-February, pp. 3-19.
Nove, Alec (1983) The Economics of Feasible Socialism (London: George Allen and Unwin).
Nove, Alec and Nuti, D. M. (eds) (1972) Socialist Economics (Harmondsworth: Penguin).
Posted in Bertrand Russell, Common ownership, Democracy, Jeremy Corbyn, Karl Marx, Khmer Rouge, Labour Party, Left politics, Liberalism, Ludwig von Mises, Mao Zedong, Markets, Nationalization, Private enterprise, Property, Right politics, Socialism, Soviet Union, Tony Benn
September 13th, 2017 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
Many people still call themselves socialists. But rarely is it made clear what they mean by the description. Few seem aware of its original definition, which persisted from the 1830s to the 1950s. Some will argue that the word has acquired a new meaning since then. Words do change their meanings. But there is no consensus on what that new meaning is.
Despite its idealistic connotations of purity and principle, the word socialism hangs around the neck of left parties. It serves as an invitation for infiltration by Marxists and others, who may enter any party proclaiming their “democratic socialism” or their “socialist principles”.
Having being invited by the s-word, they simply have to point to its original meaning to justify their maximalist stances on class struggle and public ownership. The retention of the s-word will always feed the hard left.
Owenites and Marxists
The term socialist emerged in English for the first time in 1827 in the Co-operative Magazine, which was published in London by followers of Robert Owen. It moved into wider usage in the 1830s. For Owen and his followers, socialism meant the abolition of private property. It also acquired the broader ideological connotation of cooperation, in opposition to selfish individualism.

Robert Owen
As Owen argued in 1840, “virtue and happiness could never be attained” in “any system in which private property was admitted”. He aimed to secure “an equality of wealth and rank, by merging all private into public property”.
Owen and his followers attempted to establish several socialist communities in the UK and USA. All failed within a few years. The young Frederick Engels attended an Owenite meeting in Manchester in 1843, and was inspired by Owen’s notion of socialism.
Marx and Engels wanted the complete abolition of the “free selling and buying” of commodities. They advocated common ownership of all means of production and the abolition of commodity exchange and markets.
Hence, from the 1830s until the 1950s, socialism was almost universally defined in terms of the abolition or minimisation of private property and some form of widespread common ownership.
Statist socialism
Marx and Engels insisted that markets should be abolished and all means of production should be placed in the hands of the state.
Karl Marx
Marx and Engels often used the term communism instead of socialism. But this was primarily to distance themselves from the naïve ideas of contemporary socialists rather than to postulate a radically different objective. For them, communism was a label for their movement, rather than their goal. Thus in 1845 they wrote:
 Sometimes, as in his Critique of the Gotha Programme of 1875, Marx referred to the “lower” and “higher phases” of communism, instead of socialism.
Sometimes, as in his Critique of the Gotha Programme of 1875, Marx referred to the “lower” and “higher phases” of communism, instead of socialism.
In 1917 Vladimir Ilych Lenin was writing his State and Revolution, on the eve of the Bolshevik seizure of power. Some left critics had argued that Russia was insufficiently developed for socialist revolution.
So Lenin redefined socialism as a transitional stage (still involving extensive state ownership) between capitalism and communism.
By contrast, Marx and Engels did not use the term socialism to refer to a future stage between capitalism and communism. Their aim was described interchangeably as socialism or communism.
French lessons
Engels’ description of Charles Fourier and Claude-Henri de Saint-Simon as “utopian socialists” is inaccurate because – unlike Owen – they supported private ownership of the means of production. They imagined harmonious communities without poverty or strife. But some of Saint-Simon’s followers moved toward socialism.
Philippe Buchez was inspired by Saint-Simon. He promoted worker cooperatives as early as 1831, and his ideas became prominent during the French Revolution of 1848.
Contrary to most of his contemporary socialists and communists, Buchez and his followers eventually recognized the need for multiple, autonomous, worker co-operatives, each owning property and engaging in contracts and markets.
But this tolerance of markets was too much for Marx. In 1875 he described Buchez’s ideas as “reactionary”, “sectarian”, opposed to the workers’ “class movement”, and contrary to the true revolutionary aim of “cooperative production … on a national scale”.

Pierre Joseph Proudhon
In 1840 Pierre Joseph Proudhon published his What is Property? He used both socialism and anarchism to describe his proposed future society. But, like Buchez, Proudhon proposed a system of worker cooperatives linked by contracts and trade. This enraged Marx and Engels, who relentlessly attached Proudhon’s ideas.
Non-statist versions of socialism endured but were overshadowed by statist variants. From the 1870s to the 1950s the dominant view of socialism involved state ownership and control. To emphasise their dissent, Proudhon and other opponents of statist socialism often described themselves as anarchists.
Fabianism
The idea that private property and markets should be abolished was thematic to socialism and unconfined to Marxism. It pervaded the writings of socialists as diverse as Continental revolutionary communists and British Fabians. At least until the 1950s, hostility towards markets and private property were thematic for socialism as a whole. The founding influences of Owen and Marx were long-lasting.

Beatrice & Sidney Webb
Drafted by leading Fabians Sidney and Beatrice Webb, Clause Four, Part Four of the Labour Party Constitution encapsulated collectivist thinking when it was adopted in 1918:
“To secure for the workers by hand or by brain the full fruits of their industry and the most equitable distribution thereof that may be possible upon the basis of the common ownership of the means of production, distribution and exchange, and the best obtainable system of popular administration and control of each industry or service.”
This provided for no exception: all production would be in common ownership and there would be no private sector. Although some Labour Party thinkers began to entertain the possibility of some private enterprise, many party members remained resolutely in support of widespread common ownership.
Some Fabian socialists tried to lay out more detail on how socialism would work. The Webbs laid out their ultimate vision of a fully planned and consciously controlled socialist economy where all markets and private ownership of the means of production had been marginalized to insignificance. They wanted private ownership of the means of production to be ended: it was a “perversion”.
They envisaged a massive, complex structure of national, regional and local committees, all involved in decision-making over details of production and distribution. How would these cope with the huge amounts of information and specialized knowledge in modern complex economies? It was simply assumed that this was relatively easy to sort out in some rational manner.
Guild socialism

G D H Cole
The British Fabian G. D. H. Cole is sometimes described as a “libertarian socialist” and as an advocate of “decentralized” or “guild” socialism. But he supported the wholesale nationalisation of industry and the abolition of private enterprise. To his great credit, and unlike most Marxists, Cole did actually try to explain how a future socialist society would work. But his explanation is a failure.
Cole did not show how devolved democracy could function and endure in a society where private property was abolished. His hyper-democratic account of socialism, where individuals make decisions throughout industry as well as the polity, failed to consider the problems of necessary skill in judgment, of obtaining relevant knowledge, and the overwhelming number of meetings and decisions involved.
Cole’s vision of socialism was of an integrated, national system where “a single authority is responsible both for the planning of the social production as a whole and for the distribution of the incomes which will be used in buying it.” Within this “single authority” he also sought devolved worker control. He wanted local autonomy of manufacturing, modelled on the medieval guild.
But Cole was tragically unclear about how the two were to be reconciled. How would the autonomous powers of the latter be protected from the control and centralizing ambitions of the “single authority”? There was no adequate answer. His whole system was unworkable.
Clement Attlee and Bertrand Russell
In 1937, eight years before he became UK Prime Minister, Clement Attlee wrote of the “evils” of capitalism: their “cause is the private ownership of the means of life; the remedy is public ownership.” Attlee then approvingly quoted the words of Bertrand Russell:
“Socialism means the common ownership of land and capital together with a democratic form of government. … It involves the abolition of all unearned wealth and of all private control over the means of livelihood of the workers”.

Bertrand Russell
Even within the moderate and non-Marxist Labour Party, the word socialism endured with these collectivist connotations, posed in opposition to private firms, competition and markets.
Russell represented an important strain of thinking within the British left. He wholeheartedly supported the notion of a publicly-owned and planned economy, but he rejected “Bolshevik methods”.
But is it possible to promote a state monopoly of economic power, while preventing a central-state monopoly and potential despotism of political power? In no historical case has the first happened and the second been prevented. Statist socialism, with viable democracy, political pluralism and effective decentralisation, exits only in the imagination of impractical idealists.
‘Market socialism’?
In the 1930s the economist Oskar Lange and others claimed that mainstream economic theory can show how socialism could work. Lange and his co-workers argued that managers of firms should be instructed to expand production until marginal costs were equal to the declared market price of the product.

Oskar Lange
But this assumed that marginal costs could be calculated and that the central planners could smoothly and readily assess whether there were surpluses or shortages, and adjust prices accordingly. Lange and others wrongly assumed that such information was readily available.
These proposals for “market socialism” attempted to simulate markets within a planning system, rather than to establish true markets with private ownership and commodity exchange. There was no private ownership and no capacity for firms to make contracts. The models developed by Lange and his collaborators involved a high degree of centralised co-ordination that excluded any real-world market.
Significantly, no attempt has ever been made to implement a Lange-type model in reality. Lange himself made no effort to persuade the post-1945 “socialist” government in his native Poland of the value of the idea.
Hence the use of the term “market socialism” in this context is highly misleading. Unlike the proposals of Buchez or Proudhon, and unlike the system of worker cooperatives established under Josip Tito in Yugoslavia after the Second World War, Lange’s proposal did not involve true markets.
Post-war revisionism
In 1956 C. Anthony Crosland published The Future of Socialism. This began Labour’s slow reconciliation with markets, private enterprise and a mixed economy. Signalling an attempted shift of meaning, Crosland argued that the central aim of socialism was not necessarily common ownership, but social justice and economic equality, and these could be achieved by different means. But although his argument was highly influential, it was widely attacked within the Labour Party and elsewhere.

Hugh Gaitskell
In 1959 the (West) German Social Democratic Party abandoned the goal of widespread common ownership. In the same year, Hugh Gaitskell tried to get the British Labour Party to follow this lead, but met stiff resistance. The party did not ditch its Clause Four commitment to the complete “common ownership of the means of production, distribution and exchange” until 1995.
Richard Toye noted that the Labour Party assumed widespread public ownership and failed to develop adequate policies concerning the private sector:
“Labour, until at least the 1950s, showed little interest in developing policies for the private sector. During the 1960s, the party demonstrated continuing ambiguity about whether or not competition was a good thing. This ambiguity continued at least until the 1980s.”
Tony Blair and New Labour
But in 1995, after 77 years, Labour’s Clause Four was changed. Tony Blair successfully ended the Labour Party’s longstanding constitutional commitment to far-reaching common ownership. But this was not without opposition. Tony Benn protested: “Labour’s heart is being cut out”.

Tony Blair
The new wording of “Clause IV: Aims and Values” declared that: “The Labour Party is a democratic socialist party.” But the clause ceased to promote unalloyed common ownership and the full text admitted a positive role for markets and a private sector.
By contrast, the 1918 formulation did not use the word socialism – it had undiluted common ownership instead.
Blair introduced the word socialism in 1995, but he attempted to change its meaning. He promoted “social-ism”, which now meant recognizing individuals as socially interdependent. It also signalled social justice, cohesion and equality of opportunity, within a mixed economy involving both private and public ownership.
Hence, instead of tackling the problem of Labour’s old collectivist DNA more directly, Blair tried to change the meaning of socialism and to airbrush Labour’s history. He failed to promote an adequate alternative vision or philosophy within Labour to replace old-fashioned common ownership. To the traditional left, it appeared as the substitution of purity and socialist principle by fudge and capitalist compromise.
But oddly Blair was responsible for the explicit insertion of socialism in its aims. This inadvertently played into the hands of the party’s enduring, backward-looking left.
Learning no lessons
Blair’s invasion of Iraq in 2003 and the financial crash of 2008 helped to turn the Labour membership against Blair and his compromises with capitalism. As evidence of the Freudian defence mechanism of regression as a response to severe stress, Labour reverted to an earlier stage of its history, re-adopting its infant ideological comforts of collectivism and state control.
The ghost of Tony Benn emerged. His Campaign Group in parliament moved from the margins to the party mainstream.
Like Benn, the current leadership of the UK Labour Party shows little awareness of the chronic problems of managing a modern, complex, centrally-planned economy. They now accept a “mixed economy” as a transition stage, but fail to promote the virtues or enduring role of the private sector.

Jeremy Corbyn
To take one example, Jeremy Corbyn’s 2015 address to the UK Co-operative Party is overwhelming in its blandness and naivety. Therein Corby shows no awareness that viable and meaningful decentralisation of economic power must involve (cooperative or other) firms with the right to own, set prices for, and trade their outputs. He rightly mentions the virtues of worker and consumer participation in decision-making, but shows no awareness of the practical limits of such participation.
Corbyn simply waved the magic wand of “democracy” without any apparent appreciation that it is impossible to involve everyone in more than a tiny fraction of all the complex decisions involved in any modern economy. Corbyn showed no awareness of the practical problems of complex decision-making in large organisations, which are dependent on multiple, localised, skills and expertise.
Withering socialism
Following Labour’s advances in the 2017 general election, the leadership of Corbyn and his allies seems entrenched. Recently they have gained control of the powerful National Executive Committee of the party. For future nominations for the Labour leadership or deputy leadership, it is probable that the 15 per cent threshold of support from Labour MPs will be lowered, making ongoing hard left prominence more likely.
In the 1980s and 1990s the hard left were pushed back with the help of large, moderate trade unions that were affiliated to Labour. Those countervailing forces have gone. The unions are smaller and some are more inclined to the hard left.
 With the Brexit vote in 2016, Britain has entered its most dangerous political crisis since the Second World War. The country is governed by an inept Conservative Party that is tearing up the UK constitution and concentrating unprecedented power in the hands of its duplicitous ministers.
With the Brexit vote in 2016, Britain has entered its most dangerous political crisis since the Second World War. The country is governed by an inept Conservative Party that is tearing up the UK constitution and concentrating unprecedented power in the hands of its duplicitous ministers.
Labour’s 2017 electoral advances were partly due to Tory incompetence. In this volatile climate it is possible that Corbyn could soon become prime minister. Subsequently, an obvious danger would be that the concentration of executive power legislated by Tory opponents would prove too tempting for Labour in power to relinquish. After growing authoritarianism from the reactionary right, we might experience a new, collectivist authoritarianism from Labour.
A Labour government committed to dealing with the severe crises in the health, education and housing sectors can bring positive benefits. Substantial state intervention is needed to regulate markets, especially in the area of finance. But such a programme needs to be tempered by heavy measures of pragmatism, pluralism, cautious experimentation and ideological humility that are alien to the current leadership.
They show no sign that they have abandoned their old, statist socialism. There is no recognition that markets and substantial private enterprise are necessary to sustain autonomy and decentralisation. As has become apparent in Corbyn’s favourite socialist experiment in Venezuela, the road to hell is paved with good intentions.
Conclusion – More French lessons
However outdated, it is difficult to dislodge the core principles upon which any party is founded. France provides an important illustration. Michel Rocard was a leading member of the French Socialist Party and a prime minister under François Mitterand. He long argued that French socialists

Emmanuel Macron
had failed to modernise and to accept the enduring importance of private property and markets.
Emmanuel Macron was a protégée of Rocard. Macron gained presidential power after breaking from the fractured Socialist Party and building a powerful centre force. Perhaps there are some lessons for progressives in Britain. It would not be the first time that the French have shown us the way forward.
13 September 2017
Minor edits: 16, 21 September 2017
This book elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Published by University of Chicago Press in January 2018

Bibliography
Attlee, Clement R. (1937) The Labour Party in Perspective (London: Gollancz).
Bestor, Arthur E., Jr (1948) ‘The Evolution of the Socialist Vocabulary’, Journal of the History of Ideas, 9(3), June, pp. 259-302.
Blair, Tony (1994) Socialism, Fabian Pamphlet 565 (London: Fabian Society).
Cole, George D. H. (1920) Guild Socialism Re-Stated (London: Parsons).
Crosland, C. Anthony R. (1956) The Future of Socialism (London: Jonathan Cape).
Harrison, J. F. C. (1969) Robert Owen and the Owenites in Britain and America (London: Routledge and Kegan Paul).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2017) Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, forthcoming).
Owen, Robert (1991) A New View of Society and Other Writings (Harmondsworth: Penguin).
Landauer, Carl A. (1959) European Socialism: A History of Ideas and Movements from the Industrial Revolution to Hitler’s Seizure of Power, 2 vols. (Berkeley: University of California Press).
Lange, Oskar R. and Taylor, Frederick M. (1938) On the Economic Theory of Socialism (Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press).
Proudhon, Pierre Joseph (1890) What is Property?: An Inquiry into the Principle of Right and Government, translated from the French edition of 1840 (New York: Humbold).
Russell, Bertrand (1920) The Practice and Theory of Bolshevism (London: George Allen and Unwin).
Steele, David Ramsay (1992) From Marx to Mises: Post-Capitalist Society and the Challenge of Economic Calculation (La Salle, Illinois: Open Court).
Toye, Richard (2004) ‘The Smallest Party in History’? New Labour in Historical Perspective’, Labour History Review, 69(1), April, pp. 83-104.
Webb, Sidney J. and Webb, Beatrice (1920) A Constitution for the Socialist Commonwealth of Great Britain (London: Longmans Green).
Posted in Bertrand Russell, Brexit, Common ownership, Democracy, Jeremy Corbyn, Karl Marx, Labour Party, Left politics, Lenin, Markets, Nationalization, Private enterprise, Robert Owen, Socialism, Tony Benn, Tony Blair, Tony Blair, Venezuela
August 14th, 2017 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
The world is full of injustice and poverty, while the rich protect their wealth by manipulating the system of power. Consequently, many of the informed and intelligent are lured like moths to the lights of socialist revolution, promising social justice for the many not the few.
Vladimir Ilyich Lenin was a blazing light in Russia a century ago. Many intellectuals were attracted to his Soviet regime. Lenin is said to have coined the term “useful idiot” to describe the naïve among them (but no evidence has been found to support that attribution).
But in 1913 Lenin definitely did quote the old adage that “the road to hell is paved with good intentions”. This was unwittingly self-referential and rather prophetic. Lenin’s post-1917 Bolshevik regime became a hell, in part of his own making. The good-intentioned (with sufficient means or influence) were invited from abroad to visit the young Soviet Republic.
Venezuela – “another world is possible”
But first let us consider the current case of Venezuela. Its experiment in radical socialism began in 1998 when Marxist Hugo Chávez was elected as President. Using the plentiful oil revenues during 1999-2007, his government expanded access to food, housing, healthcare, and education, especially for the poor and the indigenous minorities.

Hugo Chávez
Chávez nationalized key industries and created participatory Communal Councils. He whipped up popular support against the rich elite and their perceived allies in the United States. But constitutional checks and balances slowed down his radical reforms. Criticism from the private press and political opposition countered the populist movement.
So in 1999, the new Constitutional Assembly, filled with elected supporters of Chávez, drafted a new constitution that made censorship easier and granted the executive branch of government more power.
The Constitutional Assembly extended the presidential term. It abolished the two houses of Congress. It also granted Chávez the power to legislate on citizen rights, to promote military officers and to oversee economic and financial matters.
In 2002 Chávez was briefly deposed in a coup, which probably had support from the CIA. But Chávez was restored to power by the army and popular mobilisations.
Chávez then seized control of the courts and the electoral authority, and suppressed much of the opposition media. He removed political checks and balances, seeing them as obstacles to his socialist revolution.
Accordingly, the device of populist democracy was used to push the country in the direction of dictatorship. His supporters were persuaded to approve increases in presidential powers, to protect the “socialist revolution” against its enemies. Since 2004, “defamation” of the government, including “disrespect for the authorities”, has been a criminal offence.
Chávez failed to diversify the economy and reduce its reliance on oil. He antagonised private investors. The state-centred economy was not robust enough to withstand the post-2008 oil price collapse.
Venezuela’s descent into hell
In a state-run economy, business corruption is encouraged by bureaucratic failure. Political corruption is facilitated by the gathering of powers in the hands of the ruling party and the state machine. The Venezuelan government became one of the most corrupt in the world. Serious shortages of food and medicine emerged.

“There’s no food”
Chávez died of cancer in 2013 and was replaced as President by Nicolás Maduro.
In 2015 and 2016, blaming internal “fascists” and US intervention for the severe shortages, President Maduro declared two states of emergency. These gave him powers to intervene in the economy. Arbitrary detentions of dissidents became more common.
The regimes of Chávez and Maduro wasted and misspent much of the money made in the oil boom, while over-extending the powers of their corrupt governments. The private sector was hobbled. The ultimate outcome of Venezuela’s experiment with populist socialism has been authoritarianism, destitution and starvation.
Because of a populist mistrust of liberal, pluralist institutions, Venezuela is lurching toward dictatorship. Press freedom is limited and critical journalists and opposition leaders are jailed.
Supporters of Chávez and Maduro blame the hostility of the US for Venezuela’s distress, just as it was blamed for economic problems in Cuba after its 1959 revolution. US belligerence made things worse, and will probably continue to do so.
But the major cause of economic stagnation in Cuba and Venezuela is the unchecked concentration of excessive political, legal and economic power in the hands of the overbearing state.
Los idiotas útiles
Back in the UK, Jeremy Corbyn attended a 2013 vigil following the death of Chávez, hailing him as an “inspiration to all of us fighting back against austerity and neo-liberal economics in Europe”. As late as 2015, when Venezuela was in ever-deepening crisis, Corbyn’s enthusiasm for the regime was undiminished. He remarked:
“we celebrate, and it is a cause for celebration, the achievements of Venezuela, in jobs, in housing, in health, in education, but above all its role in the whole world … we recognise what they have achieved.”
Corbyn has since been challenged to come out against the hellish Maduro regime. Maduro’s government has been accused of arbitrary arrest, extra-judicial killings and torture.

Jeremy Corbyn and Hugo Chávez
Having managed to dupe many people with the mantra that he was a “peacemaker” in Northern Ireland (rather than a supporter of the IRA), Corbyn tried the same trick with Venezuela.
First he removed all mention of “Venezuela” from his website. Then, in an August 2017 interview, he condemned the “violence done by all sides”.
The Venezuelan opposition includes both rightist agitators and defenders of human rights. By simply condemning violence, Corbyn appeared as morally neutral between the regime and its diverse opponents. He ignored the politico-economic conditions that had given rise to the violence, and the previous actions of the Chavistas in creating them.
I wonder if Corbyn could be taken back in a time machine to the 1793-94 Terror of the French Revolution, or the Soviet Great Terror of the 1930s, or the occasion of Hitler’s invasion of the Sudetenland in 1938, and be asked to condemn with detached neutrality the “violence done by all sides”.
In the same interview Corbyn called for respect for “the independence of the judiciary and … the human rights of all”. He failed to note that Chávez and Maduro were primarily responsible for undermining both.
Questioned about his support for Maduro, Corbyn fudged:
“I gave the support of many people around the world for the principle of a government that was dedicated towards reducing inequality and improving the life chances of the poorest people.”
He omitted to mention that that same socialist Venezuelan government was now responsible for widespread starvation, rampant corruption and mass emigration.
But Jeremy of Islington is in search of socialist sainthood. He does not want the blood of any regime on his hands. He wants to go down as a peacemaker. He left it to his Corbynista Praetorian Guard to make a more forceful case for the Chávez-Maduro regime.
Over to the Corbynistas
Labour MP Chris Williamson tweeted on 11 August 2017 that the violence in Venezuela is “for the purpose of overthrowing democracy, not saving it”. Unlike Corbyn, this blamed all the violence on the opposition. It also overlooked the fact that Chávez and Maduro had been more effective in undermining democracy in Venezuela than anyone else.

Chris Williamson MP & Jeremy Corbyn MP
On the following day, Williamson Tweeted: “The US and global corporations are indulging in economic sabotage in Venezuela to bring down the government”. To a degree this may be true. But the statement ignores the greater part played by Chavista populism and its power-grabbing statist socialism in bringing about the economic and political catastrophe.
Other pro-Chavista idiotas útiles include Alexis Tsipras the Greek Prime Minister, Pablo Iglesias of Podemos in Spain, Jean-Luc Mélenchon the leftist French presidential candidate, Pope Francis and the Five-Star Movement in Italy.
The erosion of civil liberties and human rights has its roots in the concentration of economic and political powers in the hands of the state, whatever the “good intentions” that originally motivated the leaders and their supporters.
Stalin the Fabian and the Stalinist Fabians
Sadly, this is an old pattern. The Fabian socialist George Bernard Shaw visited the Soviet Union in 1931 and met Joseph Stalin. Shaw declared that Russia was becoming “a Fabian society”. This was at a time of mass famine and forced collectivisation.

George Bernard Shaw
In the preface to his 1933 play On the Rocks, Shaw defended the Russian secret police’s “liquidation” of detainees who could not give satisfactory answers to queries about “pulling your weight in the social boat” or “giving more trouble than you are worth” or had not “earned the privilege of living in a civilized community”.
In a letter published in the Manchester Guardian in 1933, Shaw and others dismissed reports of famine in the Soviet Union as “slander” resulting from a “lie campaign” against the “Workers Republic of Russia”. In fact, from 1932 to 1933, about six to eight million people died there from hunger.
Shaw subsequently attempted to justify the extermination of the Russian peasantry: “For a Communist Utopia we need a population of Utopians. Peasants will not do.” In 1936 Shaw defended Stalin’s purges and mass executions. In 1948 he declared that Stalin was “a first rate Fabian”.

Beatrice & Sidney Webb
Leading Fabians Sidney and Beatrice Webb were highly influential intellectuals in the British Labour Party. In 1932 they made a three-week visit to the Soviet Union. Their generally favourable impressions were reported in 1935 in their massive two-volume study, Soviet Communism: A New Civilisation? In the 1937 edition the question mark was removed from the title.
Their assessments of the Soviet Union were more cautious than those of Shaw, but they also denied the existence of a famine in the Ukraine in 1932-1933 and they opined that the liquidation of rich peasants (kulaks) may have been necessary to collectivize agriculture and increase its productivity. Their book received favourable reviews from left writers and it played a role in nurturing sympathy in the Labour Party for the Soviet Union, at least until the onset of the Cold War in 1948.
“Humane” Mao and the “Korean miracle”
Communism achieved another victory when Mao Zedong came to power in China in 1949. Professor Joan Robinson was a leading Cambridge economist, influenced by both Karl Marx and John Maynard Keynes. An enthusiastic supporter of Mao, she visited China several times.
Despite this first-hand experience, she failed to acknowledge that Mao’s Great Leap Forward in 1958-1961 had been an economic disaster: it had led to catastrophic famine and about 40 million deaths. In defiance she wrote: “the Great Leap [Forward] was not a failure after all, but the Rightists were reluctant to admit it.”

Joan Robinson
In the 1960s Robinson lauded the Cultural Revolution, approving of attempts by Mao and the Red Guards to root out “capitalist roaders” within Chinese society. She praised Mao’s “moderate and humane” intentions. In fact, the Cultural Revolution led to at least half a million and perhaps as many as two million deaths.
Violent struggles ensued across the country and paralyzed the economy for years. Many more millions of people were persecuted at whim by the Red Guards: they suffered public humiliation, arbitrary imprisonment, torture or execution. Countless more died when the army tried to re-establish order. In China’s totalitarian system they had no refuge or legal protection.
 As late as 1973 Robinson opposed “market socialism” and advocated a centrally-planned economy. She wrote of the “success of the Chinese economy in reducing the appeal of the money motive”. After extolling the virtues of Mao’s system, she reported that “Chinese patriotism and socialist ideology are pulling together”.
As late as 1973 Robinson opposed “market socialism” and advocated a centrally-planned economy. She wrote of the “success of the Chinese economy in reducing the appeal of the money motive”. After extolling the virtues of Mao’s system, she reported that “Chinese patriotism and socialist ideology are pulling together”.
But a few years later, shortly after Mao’s death in 1976, the country overturned the anti-market policies that Robinson had celebrated in her writings. After accepting markets, Chinese growth took off.
 In 1964 Robinson visited Communist North Korea and extolled the “Korean miracle” in its economy. She attributed its claimed success to public ownership and central planning.
In 1964 Robinson visited Communist North Korea and extolled the “Korean miracle” in its economy. She attributed its claimed success to public ownership and central planning.
But, within fifteen years, capitalist South Korea was surging ahead of its Northern neighbour. By the 1990s North Korea was experiencing mass famines. By 2010, GDP per capita in the South was about 17 times greater than in the North.
The “human face” of Soviet Communism

E P Thompson
The historian Edward P. Thompson left the British Communist Party after the 1956 Hungarian Uprising and subsequently played a major part in the formation of the New Left Review. But as late as 1973 he had sufficient residual sentimentalism for the Soviet Union to write of the
“times when [Soviet] communism has shown a most human face, between 1917 and the early 1920s, and again from the battle of Stalingrad to 1946.”

Leszek Kolakowski
Leszek Kolakowski’s response to these rose-tinted words was devastating. He asked what Thompson might have meant by the “human face” of the Soviet Union during these years. Did it mean the “attempt to rule the entire economy by police and army, resulting in mass hunger with uncountable victims, in several hundred peasants” revolts, all drowned in blood”?
“Or do you mean the armed invasion of seven non-Russian countries which had formed their independent governments …? Or do you mean the dispersion by soldiers of the only democratically elected Parliament in Russian history …? The suppression by violence of all political parties, including socialist ones, the abolition of the non-Bolshevik press and, above all, the replacement of law with the absolute power of the party and its police in killing, torturing and imprisoning anybody they wanted? … And what is the most human face in 1942-46? Do you mean the deportation of eight entire nationalities of the Soviet Union with hundreds of thousands of victims … ? Do you mean sending to concentration camps hundreds of thousands of Soviet prisoners of war handed over by the Allies?”
Kolakowski searched for an explanation of Thompson’s incredible description of these events as “a most human face” of Communism. Perhaps this phrase is being used “in a very Thompsonian sense which I do not grasp”? A commentator on Kolakowski’s response wrote: “no one who reads it will ever take E. P. Thompson seriously again.”
Another “distortion”: the killing fields of Cambodia
Robinson and Thompson were not the only top-rank academics to be deluded by ideology. Consider the most important linguist of the twentieth century. Noam Chomsky loathed the American war in Vietnam. For him, to hide its own acts of oppression and mass murder, the West had duped the masses with its slick corporate propaganda. The West was fascism, with a fake mask of democracy.

Noam Chomsky
But when reports emerged that the Communists were also capable of mass atrocities, he suspected an American conspiracy to exaggerate and to draw attention away from their own crimes. Then the evidence emerged of the killing fields of the Khmer Rouge in 1975-1979. Chomsky accused the publishers of the evidence of “extreme anti-Khmer Rouge distortions”.

Khmer Rouge Killing Fields
We now know that the Khmer Rouge obliterated about two million people – a quarter of the Cambodian population – in the pursuit of their Communist utopia. Chomsky’s reputation as a political thinker has never recovered.
Conclusion: what can we learn?
The first lesson is that thousands of highly intelligent people can be political idiots. We know that unintelligent people can be idiots (and even become presidents) but the task at hand is to explain intelligent idiocy. All it takes is a good dose of utopian idealism, combined with the view that the existing system is beyond reform.
Then when the likes of Lenin, or Mao, or Kim Il-sung, or Castro, or Pol Pot, or Chávez raise the red flag, the utopian intellectual flies to the light. A dose of reality may burn the wings. But the light of intellectual hope is so important that it must remained undimmed. Consequently, events as big as famines are based on the dark capitalist forces outside, or their devious agents within.
Many intellectuals are not practical people. They have lingered in their ivory towers. They know little of running organizations or state bureaucracies. Because of their well-motivated discontent and their search for hope, they can be attracted to Corbynism and other versions of leftist populism. But those lights are dangerous. They are ignited by opposition: without practical experience or feasible solutions.
Given such centralized powers, even well-motivated leaders will be tempted to curtail dissent and bully minority interests, in the name of the many against the few. Once on this slippery slope, human rights are eroded and the politico-economic system slides toward totalitarianism.
A lesson of the twentieth century is that classical socialism is a dead end. Viable democracies survive because there are countervailing, political and economic powers, which themselves depend upon mixed economies with large private sectors. Classical socialism unavoidably undermines the politico-economic foundations of democracy.
Instead we need to look to ways to making capitalism more egalitarian and inclusive, rather than chasing the dangerous dream of its abolition. Intelligent dreamers need to use their intelligence more wisely.
14 August 2017
Minor edits – 16, 20 August 2017, 27 September, 13 December 2017

This book elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Published by University of Chicago Press in January 2018
Bibliography
Barsky, Robert F. (1997) Noam Chomsky: A Life of Dissent (Cambridge, MA: MIT Press).
Borger, Julian (2016) ‘Venezuela’s worsening economic crisis’, The Guardian, 22 June. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2016/jun/22/venezuela-economic-crisis-guardian-briefing
Canning, Paul (2016) ‘Venezuela: The Left’s Giant Forgetting’. http://paulocanning.blogspot.co.uk/2016/09/venezuela-lefts-giant-forgetting.html
Cohen, Nick (2007) What’s Left? How the Left Lost its Way (London and New York: Harper). See pp. 157-68.
Cunliffe, Rachel (2016) ‘Corbyn looks the Other Way as Venezuela Self-Destructs’, 18 January, http://capx.co/corbyn-looks-the-other-way-as-venezuela-self-destructs/.
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2015) Conceptualizing Capitalism: Institutions, Evolution, Future (Chicago: University of Chicago Press).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2017) Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, forthcoming).
Hollander, Paul (1998) Bernard Shaw: A Brief Biography (Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press).
Jones, Bill (1977) The Russia Complex: The British Labour Party and the Soviet Union (Manchester: University of Manchester Press).
Judt, Tony (2006) ‘Goodbye to All That?’ New York Review of Books, 21 September 2006.
Kolakowski, Leszek (1974) ‘My Correct Views on Everything: A Rejoinder to Edward Thompson’s “Open Letter to Leszek Kolakowski”’, Socialist Register 11. See pp. 4-5. Available at http://socialistregister.com/index.php/srv/article/view/5323/2224#.VXBUKrFwYy8.
Minney, Rubeigh J. (1969) The Bogus Image of Bernard Shaw (London: Frewin).
Robinson, Joan (1969) The Cultural Revolution in China (Harmondsworth: Penguin). See pp. 19, 35-36.
Robinson, Joan (1973) Economic Management in China 1972 (London: Anglo-Chinese Educational Institute). See pp. 4, 13, 37.
Shaw, George Bernard (1934) Prefaces by Bernard Shaw (London: Odhams Press). See p. 341.
Staples-Butler, Jack (2017) “Starvation and Silence: The British Left and Moral Accountability for Venezuela”, 7 July. https://historyjack.com/2017/07/07/starvation-and-silence-british-left-and-venezuela/
Telesur (2015) ‘British MP Jeremy Corbyn speaks out for Venezuela’, 6 June. http://www.telesurtv.net/english/news/British-MP-Jeremy-Corbyn-Speaks-Out-For-Venezuela-20150605-0033.html.
Thompson, Edward P. (1973) ‘An Open Letter to Leszek Kolakowski’, Socialist Register 10. See p. 77, emphasis added. Accessible on http://socialistregister.com/index.php/srv/article/view/5351#.VXBrZLFwYy8.
Turner, Marjorie S. (1989) Joan Robinson and the Americans (Armonk NY: M. E. Sharpe). See p. 90.
Webb, Sidney J. and Webb, Beatrice (1935) Soviet Communism: A New Civilisation? (London: Longmans Green).
Posted in Common ownership, Democracy, E P Thompson, George Bernard Shaw, Jeremy Corbyn, Joan Robinson, Karl Marx, Khmer Rouge, Labour Party, Left politics, Lenin, Leszek Kolakowski, Mao Zedong, Markets, Nationalization, Noam Chomsky, Populism, Private enterprise, Socialism, Soviet Union, Venezuela
May 21st, 2017 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
Although the two biggest UK political parties are very different in important respects, Labour under Jeremy Corbyn and the Conservatives under Theresa May have each converged on different forms of pro-Brexit, economic nationalism.
Economic nationalism prioritises national and statist solutions to economic problems. Although it does not shun them completely, it places less stress on global markets, international cooperation and the international mobility of capital or labour. It believes that the solutions to major economic, political and social problems lie within the competence of the national state.
 Other countries have turned in the same direction, including the United States under Donald Trump and Russia under Vladimir Putin. Previously, both Soviet-style and fascist economies have embraced economic nationalism. China has continued along this road, even after its acceptance of private enterprise and a market economy.
Other countries have turned in the same direction, including the United States under Donald Trump and Russia under Vladimir Putin. Previously, both Soviet-style and fascist economies have embraced economic nationalism. China has continued along this road, even after its acceptance of private enterprise and a market economy.
Economic nationalism has been used successfully as a tool of economic development, by creating a state apparatus to build an institutional infrastructure and mobilise resources. But it brings severe dangers as well as some advantages. Its reliance on nationalist rhetoric can feed intolerance, racism and extremism.
Furthermore, as it concentrates economic and political power in the hands of the state, economic nationalism undermines vital checks and balances in the politico-economic architecture.
As numerous social scientists (from Barrington Moore to Douglass North) have shown, democracy and human rights cannot be safeguarded without a separation of powers, backed by powerful countervailing politico-economic forces that keep the state in check.
From Thatcherism to Mayhem: Tory economic nationalism

Margaret Thatcher
In the 1970s, Margaret Thatcher changed the Tory party from a paternalist party of the elite to a more radical, free-market and individualist force, embracing the ideologies of Friedrich Hayek and Milton Friedman.
A logical consequence of this market fundamentalism was to embrace the European Single Market, which her successor John Major did in the Maastricht Treaty of 1992. But this was too much for the Tory nationalists, who were already turning against the European Union and all its works.
The tension grew within the Tories between those that pursued international markets in the name of market fundamentalism, and those who worried that global trade and the free movement of labour were undermining the powers of the British nation state.
A compromise option – widely touted during the June 2016 EU referendum – was to exit the EU but remain in the single market. But a major implication of this was that the free movement of labour to and from the EU would have to be retained. May became prime minister and declared that Britain would leave the single market as well as the EU.
This marks a major ideological shift within the Conservative Party. The pursuit of free markets, promoted so zealously by Thatcher, has moved down the Tory agenda, in favour of nationalism, increased state control, reduced parliamentary scrutiny, and lower immigration, whatever the economic costs.
Forward together: the new-old Toryism
This shift is signalled by a remarkable passage in the 2017 Conservative general election manifesto:
“We do not believe in untrammelled free markets. We reject the cult of selfish individualism.”
This could be interpreted as a cynical attempt to attract some Labour voters. Probably, in part, it is. But there is much more to it than that. It shows how all the whingeing about “neoliberalism” is now outdated and much off the mark.
Crucially, the Tory Party was traditionally opposed to “untrammelled free markets” and it worried about the destructive and corrosive effects of individualism and greed.
As Karl Polanyi pointed out in his classic book on The Great Transformation, the first fighters for factory and employment legislation, to protect workers from the results of reckless industrialization in the 1830s and 1840s, were from the ranks of the church and the Tory Party:
“The Ten Hours Bill of 1847, which Karl Marx hailed as the first victory of socialism, was the work of enlightened reactionaries.”1

Benjamin Disraeli
Tories like Anthony Ashley-Cooper, the Seventh Earl of Shaftesbury, were great nineteenth-century social reformers. The Tory Prime Minister Benjamin Disraeli railed against selfish individualism, particularly in his novels. For Disraeli, British imperialism was more important than unalloyed individualism.
May has brought the Tory party back to its pre-Thatcher roots. But, less enlightened than Shaftesbury or Disraeli, she has little appetite for protective legislation or constitutional reform. Instead, she celebrates her own powers of leadership and seeks a mandate to concentrate power in her hands.
She has little enthusiasm for democracy either. If it were not for the heroic efforts of Gina Miller and the decision of the Supreme Court, the triggering of Article 50 – to start the process of leaving the European Union – would have been taken by the executive without a parliamentary vote.
The 2017 Tory manifesto is a maypole for nationalism. “Britain” is one of its most-used words. It says that immigration will be brought down, while existing powers by the British state to read emails and monitor your activity on the web will be increased. She will create an Internet that is controlled by the state. May is developing the infrastructure of an authoritarian nationalist regime.
Bringing the state back in: Labour’s new-old economic nationalism
At least on the surface, there are dramatic differences with Labour’s manifesto, which, for example, contains more measures targeted at the poor and elderly. Labour also gives much more verbal emphasis to human rights and democracy.
But at the core of Labour’s 2017 manifesto is a strong dose of economic nationalism, with Labour’s greatest commitment to public ownership since the “suicide note” manifesto of 1983. There are plans to bring the railways, energy, water and the Royal Mail all back into public ownership.
The 2017 manifesto declares: “Many basic goods and services have been taken out of democratic control through privatization.” But there is little explanation of what “democratic control” would mean under public ownership.
How would it work? Would parliament take decisions on everything? In reality these proposals – whatever their other merits – would enlarge state bureaucracy: there is no explanation how they would extend democracy.
The words “control” or “controls” appear 32 times in the 2017 manifesto. There is insignificant explanation of how “controls” work. The Labour manifesto envisions a concentration of economic power in the hands of the state, notwithstanding its verbal commitment to regional and local, as well as national, public management.
While there are commendable measures to enhance and enlarge an autonomous sector of worker-owned enterprises, there is little recognition of the importance of having a viable and dynamic private sector as well.
Corbyn’s Labour: forward to the past
As May has brought the Tories back to the pre-Thatcher years, Corbyn has brought Labour back to its traditional roots, before the leadership of Tony Blair.
 With his 1995 changes to Clause Four of the Labour Party Constitution, Blair brought in an explicit commitment to a dynamic private sector. Labour stood for an economy where “the enterprise of the market and the rigour of competition are joined with the forces of partnership and co-operation”. Corbyn has returned to the spirit of Labour pre-1995 constitution, even if he has not yet changed the wording.
With his 1995 changes to Clause Four of the Labour Party Constitution, Blair brought in an explicit commitment to a dynamic private sector. Labour stood for an economy where “the enterprise of the market and the rigour of competition are joined with the forces of partnership and co-operation”. Corbyn has returned to the spirit of Labour pre-1995 constitution, even if he has not yet changed the wording.
Corbyn has proposed that Britain can be “better off” outside the EU. He argued that EU rules block the kind of state-heavy industrial policy that he favours. But EU countries such as France and Germany already have strong interventionist policies for industrial and infrastructural development. In truth, Corbyn favours repeated doses of statist socialism in one country.
With some Stalinist exceptions in his coterie, Corbyn and his followers are mostly sincere in their commitment to democracy and human rights. But what they do not understand is that their proposed statist concentration of economic power will undermine countervailing politico-economic forces that can help to keep the state leviathan in check.

Jeremy Corbyn and Hugo Chávez
These countervailing and separated powers are vital. Especially in times of hardship or crisis, there will be a temptation by some in power (at the local or national level) to abuse rights and undermine democracy. Every single historical case shows this result.
Attempts “to take control of the economy”, even with measures of decentralization and local power, have led to restrictions on press freedom, arbitrary detentions, abuses of human rights, and even famine.
Forward together: economic nationalists take the helm
Further doses of economic nationalism may be possible in a country as large as the United States. In 2015, exports from the USA amount to about 13 per cent of GDP. Hence economic nationalists in the USA can reduce trade without too much contraction of the economy. It may turn further inwards, cut imports and still survive a loss of exports.
But the UK has become a globally-orientated, open economy, exporting 28 per cent of its GDP in 2015. About 45 per cent of these exports go to the European Union.
 By exiting the EU Single Market, and by walking away from EU trade deals with non-EU countries that benefit EU member states, Labour and the Tories would threaten the UK economy with a massive downturn. The British economy would fall off a cliff.
By exiting the EU Single Market, and by walking away from EU trade deals with non-EU countries that benefit EU member states, Labour and the Tories would threaten the UK economy with a massive downturn. The British economy would fall off a cliff.
In this crisis, rightist economic nationalists will blame foreigners and immigrants, and leftist economic nationalists will blame the rich.
It will be “the few” – designated by their ethnicity or by their assets – who will get the blame. Their rights will be under threat, as so will the liberties of all of us. Whatever variety is chosen, economic nationalism could severely undermine the viability of democracy in the UK.
21 May 2017
Minor edits – 23, 28 May, 29 June
|
This book elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost
Published by University of Chicago Press in January 2018
|
Endnote
Bibliography
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2017) Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, forthcoming).
Moore, Barrington, Jr (1966) Social Origins of Dictatorship and Democracy: Lord and Peasant in the Making of the Modern World (London: Allen Lane).
North, Douglass C., Wallis, John Joseph and Weingast, Barry R. (2009) Violence and Social Orders: A Conceptual Framework for Interpreting Recorded Human History (Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press).
Polanyi, Karl (1944) The Great Transformation: The Political and Economic Origins of Our Time (New York: Rinehart). See esp. pp. 165-66.
Posted in Brexit, Common ownership, Democracy, Donald Trump, Immigration, Jeremy Corbyn, Labour Party, Left politics, Liberalism, Markets, Nationalization, Politics, Populism, Private enterprise, Property, Right politics, Tony Blair, Tony Blair, Uncategorized, Venezuela
May 8th, 2017 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
This is in part a personal memoir – concerning my role in a minor episode in political history. More importantly, it has lessons concerning Labour’s ideological inertia – the difficulty of modernising the party and bringing it from the nineteenth to the twenty-first century.
Socialism and Labour’s Clause Four
Both Robert Owen and Karl Marx defined socialism as “the abolition of private property”. This kind of collectivist thinking was encapsulated in Clause Four, Part Four of the Labour Party Constitution when it was adopted in 1918:
“To secure for the workers by hand or by brain the full fruits of their industry and the most equitable distribution thereof that may be possible upon the basis of the common ownership of the means of production, distribution and exchange, and the best obtainable system of popular administration and control of each industry or service.”
This provided for no exception: all production would be in common ownership and there would be no private sector. Although some Labour Party thinkers began to entertain the possibility of some private enterprise, many party members remained resolutely in support of widespread common ownership.

Clement Attlee
In 1937, eight years before he became Prime Minister, Clement Attlee approvingly quoted the words of Bertrand Russell: “Socialism means the common ownership of land and capital together with a democratic form of government. … It involves the abolition of all unearned wealth and of all private control over the means of livelihood of the workers.”
After 1945, the position of many leading Labour Party members began to shift. First the realities of gaining and holding on to power – as a majority party for the first time – dramatized the political and practical unfeasibility of abolishing all private enterprise. Some nationalization was achieved, but a large private sector remained.
In 1956 C. Anthony Crosland published The Future of Socialism. This sought a reconciliation with markets, private enterprise and a mixed economy. In 1959 the (West) German Social Democratic Party abandoned the goal of widespread common ownership. In the same year, Hugh Gaitskell tried to get the British Labour Party to follow this lead, but met stiff resistance. Clause Four remained intact.
Richard Toye noted that the Labour Party assumed widespread public ownership and failed to develop adequate policies concerning the private sector:
“Labour, until at least the 1950s, showed little interest in developing policies for the private sector. During the 1960s, the party demonstrated continuing ambiguity about whether or not competition was a good thing. This ambiguity continued at least until the 1980s.”
The Thatcher Revolution
There were Labour governments from 1964 to 1970 and from 1974 to 1979. But then Margaret Thatcher came to power.
After this defeat, Labour’s instinct was to turn to the left, in the belief that it could have held onto power if it had held to classical socialist principles. Michael Foot was elected as leader, and Dennis Healey narrowly defeated Tony Benn for the position of deputy leader.

Neil Kinnock
Despite a severe recession with millions unemployed, following the implementation of monetarist austerity policies, Labour suffered a massive defeat in the 1983 general election. Labour’s share of the vote fell below 28 per cent – the party’s lowest figure since 1918. Michael Foot resigned as leader and Neil Kinnock took his place.
Thatcher had boosted her popularity due the Falklands War. One of Thatcher’s most popular domestic policies was to promote the sale of council-owned housing to the tenants. Labour had opposed this policy. The 1983 defeat prompted a rethink, on this and other issues.

Tony Benn
For some of us, this rethink amounted to more than expedient doctrinal trimming. Encouraging home ownership was really a good idea: why should all property be owned by the rich? But while supporting home ownership, we argued that the government should also build more social housing and enlarge the stock available for rent by low-income families.
But these ideas met stiff resistance in the Labour Party ranks, and not simply from Trotskyist entryists such as Militant. The resistance from Tony Benn and his supporters was substantial and even more enduring. It was clear that old-fashioned socialist ideas still had a tenacious appeal for Labour’s membership.
The Labour Coordinating Committee
The Labour Coordinating Committee (LCC) became one of the primary modernising forces within Labour. Its leadership included Hilary Benn, Cherie Blair, Mike Gapes, Peter Hain, Harriet Harman and others of enduring fame. I was elected to its executive committee. We worked closely with Kinnock and members of his shadow cabinet, including Robin Cook.
 I had written a book entitled The Democratic Economy where I argued that socialists should support a permanent private sector in the economy. The book was published by Penguin in 1984. Another influential work at the time was Alec Nove’s Economics of Feasible Socialism, which also argued for a substantial role for markets.
I had written a book entitled The Democratic Economy where I argued that socialists should support a permanent private sector in the economy. The book was published by Penguin in 1984. Another influential work at the time was Alec Nove’s Economics of Feasible Socialism, which also argued for a substantial role for markets.
On 26 November 1983, at the Labour Coordinating Committee AGM in Birmingham, I proposed that Clause Four of the Labour Party constitution should be rewritten to include an acceptance of a private sector and a role for markets. But I was defeated over the idea that Clause Four should be rewritten. This was out of fear of antagonising the Benn wing. Instead, the LCC resolved that Clause Four should be “clarified”.
But a resolution on long-term aims, which I had helped to draft, was passed by a large majority. The resolution called for the Labour Party to draft a new statement of aims, upholding “that socialism involves extended democracy and real equality. Democracy under socialism is extended to industry and the community … and must involve a substantial decentralisation of power.”
Equality meant the “absence of discrimination on the basis of gender and race, universal freedom from poverty, and a widespread distribution of wealth and power, as well as formal equality under the law and universal suffrage.”
 There was a commitment to “political pluralism” and to “economic pluralism” involving “a variety of forms of common ownership … and the toleration of a small private sector including self-employed workers and other private firms.” The economy must be dominated by mechanisms of “democratic planning … but also accommodating a market mechanism in some areas.”
There was a commitment to “political pluralism” and to “economic pluralism” involving “a variety of forms of common ownership … and the toleration of a small private sector including self-employed workers and other private firms.” The economy must be dominated by mechanisms of “democratic planning … but also accommodating a market mechanism in some areas.”
There was also a “commitment to internationalism, disarmament and peace” and “a disengagement from the power blocs” of the West and East.
I think that today Jeremy Corbyn and his followers would accept much or all of this, at least as a temporary stopping-point on the road to full socialism. But in the 1980s there was strong hostility to these revisionist ideas from within Labour’s ranks at the time, including from Corbyn and Tony Benn.
Since then my own views have adjusted. See my Wrong Turnings book. But this blog is not primarily about me. It is about what has happened to the Labour Party and how difficult it is to change its DNA.
For a while, the LCC tried to keep the conversation going on the need to revise Labour’s aims. The Guardian newspaper reported the LCC conference with the headline: “Labour breaks taboo on ownership”.
The LCC held a conference in Liverpool in June 1984 on “The Socialist Vision”. But enthusiasm for this discussion fizzled out. Many leaders of the LCC wanted a political career, and they wished to widen their support on constituency selection committees.
By 1985 the LCC’s revisionist initiative had been kicked into the long grass. My efforts to change Clause Four had failed.
From Kinnock to Blair
But to their credit, Neil Kinnock and his deputy Roy Hattersley saw the need for Labour to modernise its aims. I advised them both for a while. Another election defeat in 1987 spurred a rethink. But by then I had become inactive in the Labour Party.
As Richard Toye has recorded, in 1988 Kinnock and Hattersley presented a new document on “Aims and Values” to Labour’s National Executive Committee. But “it was criticised by John Smith, Bryan Gould and Robin Cook as being too enthusiastic about the benefits of the market, and was watered down accordingly”.

Tony Blair
Clearly, even after a third election defeat there was still strong resistance, from both the “soft” and the “hard left”, to the idea of embracing markets and private property.
After the next election defeat in 1992, Kinnock stood down. He was replaced by John Smith, who died tragically from a heart attack. Then Tony Blair became leader, with a firm resolve to modernize the party. Four election defeats had made the majority of members more receptive to his ideas.
Blair’s Revision of Clause Four
In 1995, after 77 years, Clause Four was changed. Tony Blair successfully ended the Labour Party’s longstanding constitutional commitment to far-reaching common ownership. Tony Benn protested: “Labour’s heart is being cut out”. The new wording of “Clause IV: Aims and Values” began as follows:
“The Labour Party is a democratic socialist party. It believes that by the strength of our common endeavour we achieve more than we achieve alone, so as to create for each of us the means to realise our true potential and for all of us a community in which power, wealth and opportunity are in the hands of the many not the few; where the rights we enjoy reflect the duties we owe and where we live together freely, in a spirit of solidarity, tolerance and respect.”
The 1918 formulation did not use the word socialism – it had common ownership instead. Ironically, Blair introduced the term in 1995. But he attempted to change its meaning. He promoted “social-ism”, which now meant recognizing individuals as socially interdependent. It also signalled social justice, cohesion and equality of opportunity.
The new Clause Four continued, to make a significant statement in support of competiive markets and a private sector. Labour now stood for:
“A DYNAMIC ECONOMY, serving the public interest, in which the enterprise of the market and the rigour of competition are joined with the forces of partnership and co-operation to produce the wealth the nation needs and the opportunity for all to work and prosper with a thriving private sector and high-quality public services …”
The text went on to cover “a just society”, “an open democracy”, “a healthy environment” and “defence and security”.

John A Hobson
Labour’s new aims and values were indistinguishable from the earlier views of radical social liberals, such as T. H. Green, J. A. Hobson and David Lloyd George. And with its endorsement of “the rigour of competition” and “a thriving private sector” it was a hundred miles away from the collectivism of Robert Owen and other original socialists.
Instead of tackling the problem of its old collectivist DNA more directly, Blair tried to change the meaning of socialism and even rewrote parts of its own history. It is unsurprising that the old socialist DNA survived. It remained viable, partly because Labour still declared itself as socialist. Blair made radical changes but also gave succour to the traditional socialist wing of the party.
Blair’s popularity within the party had waned even before his decision in 2003 to support George W. Bush’s Iraq War. Much of this disenchantment was due to his abandonment of wholesale common ownership.
Blair had failed to develop a fully-fledged alternative vision within Labour to replace old-fashioned common ownership. He had made Labour implicitly embrace liberalism in doctrine. But this was unspoken, and masked by the explicit insertion of socialism in its aims. This inadvertently played into the hands of the party’s enduring, backward-looking left.
Labour’s Love Lost
Just as Labour had shifted to the left after losing power in 1979, after its 2010 defeat it shifted slightly leftwards under Ed Miliband. But the new leader had no clear alternative to the economics of austerity. So after another defeat in 2015. the party membership took a massive lunge to the left. It elected the Bennite, retro-Marxist, perennial protestor, Jeremy Corbyn.
 But while old ideas within Labour had survived, the structure of the party and its electoral base had changed enormously in the period from 1983 to 2015. Kinnock had relied on the moderating force of the trade unions, to fight the hard left and move the party toward electability. But by 2015 the unions had been gravely weakened and several had moved toward the hard left.
But while old ideas within Labour had survived, the structure of the party and its electoral base had changed enormously in the period from 1983 to 2015. Kinnock had relied on the moderating force of the trade unions, to fight the hard left and move the party toward electability. But by 2015 the unions had been gravely weakened and several had moved toward the hard left.
In 1983, both the affiliated unions and the Labour MPs had a major role in the election of any new Labour leader. But by 2015 the power was almost entirely in the hands of the Labour Party membership, and the other moderating forces were much diminished.
Labour’s history shows how difficult it has been to change Labour’s old-fashioned socialist DNA. Those that put their faith in a revival of moderation within must take into account the near-collapse of those internal forces that brought the party back to sanity in 1951-1964 and in 1979-1997.
In 1983 there was still a strong, traditional, tribal, Labour vote, part of it based on surviving industries such as coal and steel. By 2015 the working class was much more fragmented, with skilled, aspirational cohorts at one extreme, and uneducated, demoralized, welfare dependents at the other.
The old tribalism was challenged by UKIP and by a revived working class Conservatism, playing the nationalist card. Labour’s potential electoral base has been transformed beyond recognition. The division of labour has become profoundly political, as well as enduringly economic.
Today, there seems little hope for a party that calls itself “Labour”, just as there is no future for a party that retains the word “socialism” or the goal of widespread public ownership. The socialist experiments of the twentieth century testify to their failure. Labour, in short, is an anachronism.
8 May 2017
|
This book elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost
Published by University of Chicago Press in January 2018
|
References
Attlee, Clement R. (1937) The Labour Party in Perspective (London: Gollancz).
Blair, Tony (1994) Socialism, Fabian Pamphlet 565 (London: Fabian Society).
Clarke, Peter (1978) Liberals and Social Democrats (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (1984) The Democratic Economy: A New Look at Planning, Markets and Power (Harmondsworth: Penguin).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2017) Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, forthcoming).
Nove, Alexander (1983) The Economics of Feasible Socialism (London: George Allen and Unwin).
Toye, Richard (2004) ‘The Smallest Party in History’? New Labour in Historical Perspective’, Labour History Review, 69(1), April, pp. 83-104.
Posted in Common ownership, Democracy, Jeremy Corbyn, Karl Marx, Labour Party, Left politics, Liberalism, Markets, Nationalization, Politics, Private enterprise, Property, Robert Owen, Socialism, Tony Benn, Tony Blair, Tony Blair
April 17th, 2017 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
“Bliss was that dawn to be alive.” With Labour’s landslide victory under Tony Blair, the general election of 1st May 1997 ended eighteen years of Tory rule.
The new government set out to implement a series of major reforms, including establishing devolved assemblies in Scotland and Wales, setting a statutory minimum wage, and injecting much-needed money into the education system and the NHS.
After winning two further elections with large majorities – in 2001 and 2005 – Labour’s period of office came to an end on 5th May 2010, when the Conservatives became the biggest party in Parliament. The Liberal Democrats made the mistake of entering into a coalition with the Tories, and paid the price when they lost most of their MPs in 2015.
So began a period of Tory rule that now seems that it could last for decades. But the Tories rule with the support of less than 50 per cent of the voters. If Blair had implemented electoral reform, then what might have happened instead?
Ending “division among the radicals”
Until the day of polling in May 1997, when the scale of his majority became clear, Tony Blair had considered a coalition with the Liberal Democrats after the election, He had negotiated with Paddy Ashdown (the leader of the Liberal Democrats) with that possibility in mind. But once Blair’s overwhelming victory was apparent, a coalition with the Liberal Democrats seemed unnecessary.
 But Blair still wanted to cooperate with the Liberal Democrats on several issues, including on electoral reform. He insisted that the two parties were natural allies, and they should not have gone their separate ways a hundred years earlier. In his first speech to a Labour conference after his landslide election victory, Blair declared:
But Blair still wanted to cooperate with the Liberal Democrats on several issues, including on electoral reform. He insisted that the two parties were natural allies, and they should not have gone their separate ways a hundred years earlier. In his first speech to a Labour conference after his landslide election victory, Blair declared:
“my heroes aren’t just Ernie Bevin, Nye Bevan and Attlee. They are also Keynes, Beveridge, Lloyd George. Division among radicals almost one hundred years ago resulted in a 20th century dominated by Conservatives. I want the 21st century to be the century of the radicals.”
By “division among the radicals” Blair referred to the 1900 decision to set up a party in parliament independent of the Liberals. Blair wished to reverse that mistake and install an enduring radical majority.
Labour’s 1997 promise of electoral reform
Blair wanted Labour and the Liberal Democrats to work together for progressive change, and, if possible, to exclude permanently the Tories from government, at least until they were forced to modernise and to abandon their reactionary, inward-looking nationalism.
“We are committed to a referendum on the voting system for the House of Commons. An independent commission on voting systems will be appointed early to recommend a proportional alternative to the first-past-the-post system.”
After the election, Blair continued his secret talks with Ashdown on co-operation between their two parties, including on the issue of electoral reform.
But what voting system should be chosen?
One problem was that the two parties found it difficult to agree on what “a proportional alternative” might mean. But a possible compromise emerged with a top-up system called “AV+”.
In addition, under AV+, each voter would get a second vote to elect a regional-level representative from a list of candidates for each party. An additional group of MPs would be elected via this route. This “top up” would ensure greater proportionality in Parliament.
Some people dislike AV+ because it creates two types of MP, with not all of them being responsible for a manageable constituency. In addition, AV+ does not satisfy purists who want a more proportional system.
Division of Labour
But the biggest problem with Blair’s strategy for long-term reform was Labour itself.
 While leading figures in his Cabinet such as Robin Cook, Mo Mowlam, Clare Short and Peter Mandelson supported electoral reform, Blair faced the implacable opposition of Chancellor Gordon Brown, Deputy Prime Minister and Secretary of State John Prescott, Home Secretary Jack Straw, numerous trade union leaders and an energetic campaign against proportional representation from Labour’s ranks.
While leading figures in his Cabinet such as Robin Cook, Mo Mowlam, Clare Short and Peter Mandelson supported electoral reform, Blair faced the implacable opposition of Chancellor Gordon Brown, Deputy Prime Minister and Secretary of State John Prescott, Home Secretary Jack Straw, numerous trade union leaders and an energetic campaign against proportional representation from Labour’s ranks.
Reasons for this opposition to electoral reform within Labour were numerous. But perhaps the most enduring argument was that Labour saw itself as a party committed to radical change in favour of working people, which was bound to meet fierce opposition from rich vested interests and the reactionary press.
 I can speak with a little authority here, because this was once my own major objection to proportional representation (PR). As loyal and active Labour party members, Peter Hain and I published a booklet in 1982 entitled Proportional Misrepresentation?
I can speak with a little authority here, because this was once my own major objection to proportional representation (PR). As loyal and active Labour party members, Peter Hain and I published a booklet in 1982 entitled Proportional Misrepresentation?
We argued that PR would favour parties of the centre, against parties like Labour who represented working people and were committed to radical change. The advantage of the existing system was that Labour could gain power and show piecemeal and in practice how socialist measures could work.
Although we were against PR, Peter and I argued for a change to the alternative vote (AV), without a top-up element. A few years’ later, Peter suggested that we develop our pamphlet into a book.
Thatcher in power
But this was after six years of Margaret Thatcher in power. Her Tory Party had won an overall majorities in 1979 and 1983, in both cases with less than 44 per cent of the vote. After 1983 I came to the view that Labour could not win the next election and the Tories could be power for about 15 years.1
 Just as the existing electoral system might be used by a left party for radical reform, it was being used by a newly-radicalised Tory party to divide the country, to undermine the welfare state and to attack the rights of working people.
Just as the existing electoral system might be used by a left party for radical reform, it was being used by a newly-radicalised Tory party to divide the country, to undermine the welfare state and to attack the rights of working people.
I had developed serious doubts about our 1982 arguments. So I declined Peter’s kind offer and he published the book in 1986 under his own name, fully acknowledging our previous joint arguments.
Others developed concerns similar to mine, especially as the years passed and the Tories remained in power with minority support. All this gave the impetus for Blair and others to push for PR in Labour’s 1997 manifesto.
But elements of Labour’s class-based tribalism remained strong, as did commitment to an ever-vague promise of something called “socialism” that only a majority Labour government could deliver. Hence Labour internally remained deeply divided on this issue, as it does to this day.
The Jenkins Commission
In December 1997, in line with the manifesto commitment, Blair set up a parliamentary commission under Lord Roy Jenkins, the former Labour minister and then Liberal Democrat peer. The Jenkins Commission would recommend which particular proportional system should be put before voters in a referendum.
 The Jenkins Commission reported in September 1998 and suggested the alternative vote top-up (AV+) system. Blair immediately faced intense opposition, from within his own Cabinet, from a large number of Labour MPs, from a large section of the Labour Party in the country, and from several trade unions.
The Jenkins Commission reported in September 1998 and suggested the alternative vote top-up (AV+) system. Blair immediately faced intense opposition, from within his own Cabinet, from a large number of Labour MPs, from a large section of the Labour Party in the country, and from several trade unions.
In 1997 Labour came to power with 43 per cent of the vote but won 63 per cent of the parliamentary seats. Any significant move toward greater proportionality would have deprived one hundred or more Labour MPs of their seats. Over one hundred turkeys would have to have voted for Christmas. The political barriers to this reform seemed unsurmountable. The recommendations of the Jenkins Commission were kicked into the long grass.
Several other attempts were taken to revive the project of electoral reform under the 1997-2010 Labour Government. Labour promised a review of the voting system in its 2001 manifesto. In 2003, talks were held between Labour and the Liberal Democrats on electoral reform.

But by 2010, under the new premiership of Gordon Brown, Labour retreated from its earlier promise of moving toward proportionality. Instead, Brown promised a referendum on the alternative vote (AV) without any top-up element. The Jenkins Commission had previously taken the view that such a minor change would not merit a referendum.
In fact, a referendum on AV was held in 2011, under the coalition government. The proposal was defeated by a large majority. This demonstrated the problem of convincing the public of the merit if a more complex system, which cannot be explained easily in one or two sentences. I raise this issue later below.
An alternative future
First we consider what might have happened if the more-proportional system of AV+ had been introduced sometime between 1997 and 2010.
In the 2010 election Tories got 36 per cent of the vote, Labour got 29 per cent and the Liberal Democrats 23 per cent. Under the existing voting system they got 306 seats, 258 seats, and 57 seats respectively. Under a more proportional system they would have got something like 255 seats, 204 seats and 162 seats respectively
Under the existing electoral system, a 2010 coalition between Labour and the Liberal Democrats would have had 315 seats, which is well short of an overall majority in a parliament of 650 seats. It would have been a minority coalition government, or other parties would have had to been involved. This was a significant obstacle, which played a part in scuppering any 2010 deal between Labour and the Liberal Democrats.
 But if a more proportional system had been in place in 2010, then a coalition between Labour and the Liberal Democrats would have had something like 366 seats, which would have been a clear overall majority. The Tories could have been kept out of power.
But if a more proportional system had been in place in 2010, then a coalition between Labour and the Liberal Democrats would have had something like 366 seats, which would have been a clear overall majority. The Tories could have been kept out of power.
Furthermore, Labour would have been obliged to cooperate with a centrist party, giving weight and prestige to its more moderate wing. Sure enough, there would have been protest on the left, led by a Jeremy Corbyn or a John McDonnell, but they would have probably been kept away from Labour’s levers of power.
As the years followed, all sorts of alternative scenarios might have then unfolded. But a referendum on Brexit would have been unlikely, or it would have taken place under conditions more favourable to the Remain campaign.
In short, if the electoral system had been changed in this way before 2010, then we would not be in this mess that we are now. We could still be on the road to a progressive future, rather than fighting a desperate battle against intolerant bigots and nationalists, who would drive the UK economy off a cliff to satisfy an anti-immigration sentiment fed by years of economic failure.
Winning the battle for electoral reform
Electoral reform is highly unlikely under a Tory government and hence the first objective must be to remove the Conservatives from power. This will require a progressive alliance of Labour, Liberal Democrats and Greens, which at present does not seem feasible. Also the Tories might remain in power for some time.
 But a tiny consolation of this dismal entrapment is the time it gives us to debate the best system, which would offer something closer to proportionality, and would have a chance of convincing the electorate.
But a tiny consolation of this dismal entrapment is the time it gives us to debate the best system, which would offer something closer to proportionality, and would have a chance of convincing the electorate.
Some kind of top-up system based on 400-500 single-member constituencies, topped up with a further 100-200 MPs elected from party lists, seems the best way forward. It is a possible compromise that the parties involved can accept, and it is understandable by the public.
But I have now come to the view that the use of AV to elect the MPs for the single-member constituencies is both intrinsically flawed and difficult to explain to the electorate. A better and easier-to-explain alternative exists.
There were several reasons why the AV referendum was lost in 2011, including the fact that many prominent figures in the Labour Party openly opposed it. Another was the complexity of AV itself. As Tom Clark wrote in the Guardian:
“Leaflets from the electoral commission, which were designed to explain what the reform would mean to every household with meticulous neutrality, ended up making AV look horrendously complex. The blurb summed up first-past-the-post in just three sentences, while describing AV with an excessively complex example election, which required three diagrams and text that spilled over four pages.”
A further problem is that AV itself, even if it can be explained to the public, has serious intrinsic flaws.
Why AV is flawed
The alternative vote (AV) is widely criticised by experts on voting systems. We are concerned with systems designed to elect one person, from a list of candidates, to a single position or seat.
Consider an example of a mayoral election with three candidates Ms Left, Ms Centre and Ms Right. Both Ms Left and Ms Right are pretty extreme, and the electorate is polarised. An AV systems is employed and the candidates get the following first-preference votes: Left 33 per cent, Centre 31 per cent and Right 36 per cent. Under the AV system Ms Centre would be eliminated and her second preferences would be allocated to Left or Right. One of the more extreme candidates would win, in a run-off between Left and Right.

Nicolas de Condorcet
But imagine a local newspaper had run an extensive poll which showed that if there had been a run-off between Centre and Right, then Centre would have won. And if there had been a run-off between Centre and Left, then Centre again would have won. In other words, a majority in all cases preferred Ms Centre to any of the extremes.
Technically this is known as a Condorcet winner – a person who would win all two-candidate elections against each of the other candidates in turn.2 A serious problem with AV is that it can often eliminate a Condorcet winner. More generally, a major problem with AV is that it can often militate against strong and popular compromise candidates.
Why Approval Voting is better than AV
If there were (say) four candidates for a parliamentary seat, then the electors may vote (with crosses rather than numbers) for zero, one, two, three or four of the candidates. The votes for each candidate are added up, and the candidate with the highest number of votes is elected. Simple.
Of course, an elector voting for none or four of the candidates in this case would have no effect on the result, except he or she would be helping to give an overall indication of the overall level of approval (or lack of it) for each candidate.
As well as its technical superiority, a huge advantage of approval voting is that it is much easier to explain and to understand.
My proposal is for an approval voting system for single-member constituencies, plus a party-list top-up in regional units, to move closer to proportionality. I propose Approval+.
High stakes
Rising above the technical details, a lot is at stake here. If a more proportional system had been introduced in 1997-2010 then we could have avoided the disastrous prospect of decades of Tory rule, elected each time on 40 per cent or less of the vote.
When asked, the UK public support a more proportional system. A 2015 poll showed that 57 per cent of the public agreed with the principle that “the number of seats a party gets should broadly reflect its proportion of the total votes cast” – compared to only 9 per cent who disagreed.
We need to think about the best and most persuasive system of electoral reform, and set about the task of building a progressive alliance to implement it.
17 April 2017
Minor edits – 18 April, 1, 13, 14 May, 6 June, 14 July, 12 August, 3 September 2017
Footnotes
1. I turned out to be too optimistic: the Tories were in power for 18 years. Using a statistical analysis, I developed my sceptical 1980s view of Labour’s chances while I was on the ruling council of the Labour Coordinating Committee. My assessment was unpopular among budding, ambitious Labour politicians.
2. Nicolas de Condorcet (1743-1794) was a French revolutionary, mathematician, advocate of female suffrage and friend of Thomas Paine.
3. This is a very useful but long video. To cut straight to Approval Voting, the first 36 minutes may be skipped.
References
Hain, Peter and Hodgson, Geoff (1982) Proportional Misrepresentation? (London and Nottingham: Tribune and Institute for Workers Control).
Hain, Peter (1986) Proportional Misrepresentation: The Case against PR in Britain (Guildford: Wildwood House).
Posted in Brexit, Jeremy Corbyn, Labour Party, Left politics, Liberalism, Tony Blair, Tony Blair, Uncategorized
January 28th, 2017 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
The political earthquakes of 2016 are probably the beginning of a series of major ruptures in world politics. Donald Trump was elected in the USA, Britons voted for Brexit, Turkey lurched toward dictatorship, Brazil ejected a democratically-elected president, Russia extended its global influence, and China tightened internal security while building military bases in the South China Sea.
From America to Asia, authoritarian nationalism is on the march. The future of old alliances is cast in doubt, raising a renewed spectre of global war.
These seismic changes should prompt us to reconsider our priorities. Is ‘neoliberalism’ – whatever that means – our main enemy? Or is it rising authoritarianism and nationalism instead?
We have been here before, albeit with much less dangerous military weapons. The rival imperialisms of the nineteenth century led to the First World War. Collapsing imperial dynasties triggered revolution in Central and Eastern Europe. Communists successfully seized power in Russia in 1917. Post-war political and economic turbulence led to the triumph of fascism in Italy, Germany and Spain. Imperial Japan invaded nationalist China.
I am not suggesting that history will repeat itself in the same way. But it is important to understand how the tectonic plates of political change affected the way we understand and map political positions, and the way in which we prioritise political issues.
The thirty-year squeeze (1918-1948)
Europe suffered economic depression for much of the interwar period. The financial crash of 1929 exacerbated the crisis and led to a collapse of world trade. Liberal defenders of the market economy were put on the defensive: capitalism seemed at the end of its tether.

Beatrice & Sidney Webb
Meanwhile, some intellectuals from the USA and Britain – including Labour stalwarts George Bernard Shaw and Sidney and Beatrice Webb – visited the Soviet Union brought back glowing accounts of an expanding economy and a joyful population. (The Soviet propagandists explained away disasters such as the Ukranian Famine as resulting from sabotage by rich peasants or foreign agents.)
With the crisis of capitalism, the rise of fascism and the apparent success of Soviet Russia, many British and American radicals became Communists or fellow travellers. For them, liberalism and the defence of the market economy seemed a weak or unviable option.
The choice seemed to be between two forms of authoritarian government: much better the one that proclaimed equality and opposed racism. (But in reality, the Stalin regime promoted antisemitism, genocide against several other ethnic minorities, and dramatic internal inequalities of power.)

Stalin, Roosevelt and Churchill in 1941
The alliance between Russia and the West in the Second World War smothered criticism of what was really going on within Stalin’s regime. But, with the beginning of the Cold War in 1948, socialists were forced to make a choice between either supporting an antagonistic and undemocratic foreign power, or aligning with the USA and its allied democracies.
Labour under Clement Attlee aligned with the West. But rose-tinted visions of Soviet Russia or (from 1949) Mao’s China lived on among he Left.
In major European democracies, the thirty years between the end of the First World War and the start of the Cold War had seen liberalism squeezed, between socialism on the one hand, and reactionary authoritarianism on the other.
‘American imperialism’ and the rise of neoliberalism
Things were different in the USA, which polarised between forms of Republican conservatism and Democratic liberalism. But rising tensions in the Cold War, and the eruption of the Vietnam War in the 1960s, made American-style liberalism less attractive for the global Left.
 Marxist-led national liberation movements in Cuba, Indochina and elsewhere kept the collectivist vision alive for the Left around the world. Liberalism was see as the fake ideology of American imperialism and the global bourgeoisie.
Marxist-led national liberation movements in Cuba, Indochina and elsewhere kept the collectivist vision alive for the Left around the world. Liberalism was see as the fake ideology of American imperialism and the global bourgeoisie.
Some have argued that neoliberalism was reborn in the 1970s, when conservatives such as Ronald Reagan and Margaret Thatcher adopted a vision of expanding markets and a contracting state. Although the Left could never agree on what ‘neoliberalism’ meant, they mostly agreed that it was the main enemy.
Much of the Left, throughout the world, had never got rid of its agoraphobia – its fear of markets. Private enterprise and market forces were always and everywhere seen as the problem. Liberals, who defended private property and markets as well as human rights, were mocked as the bourgeois enemy.
Our brave new world
But the global tectonic plates are now shifting abruptly, in an erupting national and international crisis, as big as anything since 1948.
Nationalist leaders strut around the world stage. They stock up their nuclear and conventional arsenals and jostle for geopolitical advantage.
Torture is endorsed. Journalists are threatened or imprisoned. Scientific findings on climate change are denied. Intellectuals and experts are ridiculed. Ignorance and dogma are celebrated. Truth is swamped by lies. Legislation protecting workers and the poor is undone. Minorities are attacked and made scapegoats. Racism is given licence. People suffer discrimination on the basis of their religious or other beliefs. Democratic systems are damaged. Judges and lawyers are treated as traitors. The rule of law is undermined.
In this dangerous new world, it matters less whether that railway is nationalised or whether water distribution is in public ownership. Forms of ownership are always secondary to the actual provision and distribution of vital goods and services. But when our rights and liberties can no longer be taken for granted, questions over forms of ownership move even further down the ranking of priorities.
The ubiquitous, trivialising idea that the Left is defined in terms of public provision, and Right as private provision, is historically recent and a gross reversal of their original meanings. It is also a polarisation of lesser relevance in this world of rising authoritarian nationalism.
Our fundamental rights, our liberty, and the rule of law are now increasingly threatened. Their defence becomes the great struggle of our time.
This lesson is hardest for Americans and Britons, who were spared domestically from the jackboots of twentieth-century despotism. Struggles for British and American national liberty are beyond living memory. We have grown fat and lazy on the fruits of the liberal order. We have taken for granted its institutions and underestimated their fragility. We must repair our vigilance.
The liberal opportunity
For 100 years, for the reasons given above, liberalism has been marginalised. Now is its opportunity – indeed its urgent necessity.
Unlike our grandparents in the crisis-ridden 1930s, we have seen the socialist experiments of the twentieth century and counted their cost at 90 million lives. History and social science have more to teach us. If we wish to learn, we can know more about how markets work. We can understand the informational, organisational and other impediments to comprehensive national planning. We can appreciate why countervailing politico-economic power, based on a strong private sector, are necessary to buttress democracy and resist authoritarianism. The twentieth century has taught us these lessons.
The old Marxist mantra of bourgeoisie versus proletariat is also ungrounded in reality. Instead we have a highly fragmented working class, much of it enduringly aligned with authoritarianism and nationalism. Marxism relies on a quasi-religious and nonsensical belief that the working class – whatever it actually believes or strives for – carries our human destiny.
Class struggle has mattered, but it has never been the main motor of history. What have mattered more have been struggles for power, by individuals, dynasties, nations, religions or ideological movements.

The Storming of the Bastille in 1789
Liberalism was one of those movements. Based on the imperatives of equality and liberty, it matured in the Enlightenment.
Liberalism rose up in the English Civil War of the 1640s, in the American Revolution of the 1770s, and in the French Revolution of 1789, in titanic struggles against despotism and oppression.
Now, once again, liberalism is centre stage, as the enemy of authoritarian nationalism.
The liberal rainbow
Its allies are not those who pander to authoritarianism by eroding civil liberties, or do the spadework of the nationalist Right by making immigration (rather than assimilation) a foremost problem. The prime allies of liberalism are all those who defend liberty and human rights. But therein lies a concern, which must be discussed.
From the beginning, liberalism has harboured different views on the role of the state and of the degree of state intervention required in the economy and society. On the one hand there are liberals – sometimes called libertarians – who wish to minimise the role of the state.

Thomas Paine
John Maynard Keynes – another great liberal – argued that state regulation of financial markets and counter-cyclical expenditures are necessary to stabilise the capitalist system. Keynes showed that economic austerity is a flawed doctrine. Government deficits are best reduced by growth: budget cuts can contract the entire economy and make the problem worse.
There is a spectrum of views between individualist and social-democratic liberalism, but all liberals are united in their defence of individual liberty, human rights and political democracy. The diverse colouring of this rainbow does not diminish its united opposition to the dark intolerance and division that is exacerbated by authoritarian nationalism.
The struggle for liberty and equality has always been vital. But many twentieth-century radicals were diverted by the delusions of socialism. The renewed rise of authoritarianism has shown us again that liberalism is the vital political movement of the modern age.
28 January 2017
Minor edits: 29 January, 1, 16 May 2017
|
This book by G. M. Hodgson elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost
Published by University of Chicago Press in January 2018
|
Bibliography
Allett, John (1981) New Liberalism: The Political Economy of J. A. Hobson (Toronto: University of Toronto Press).
Beveridge, William (1944) Full Employment in a Free Society (London: Constable).
Clarke, Peter (1978) Liberals and Social Democrats (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press).
Claeys, Gregory (1989) Thomas Paine: Social and Political Thought (London and New York: Routledge).
Courtois, Stéphane, Werth, Nicolas, Panné, Jean-Louis, Packowski, Andrzej, Bartošek, and Margolin, Jean-Louis (1999) The Black Book of Communism: Crimes, Terror, Repression (Cambridge MA: Harvard University Press).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2015) Conceptualizing Capitalism: Institutions, Evolution, Future (Chicago: University of Chicago Press).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2017) Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, forthcoming).
Keane, John (1995) Tom Paine: A Political Life (London: Bloomsbury).
Keynes, John Maynard (1936) The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money (London: Macmillan).
McCloskey, Deirdre Nansen (2017) ‘Nationalism and Socialism Are Very Bad Ideas: But liberalism is a good one’, Reason.Com, February. http://reason.com/archives/2017/01/26/three-big-ideas
Monbiot, George (2016) ‘Neoliberalism – the ideology at the root of all our problems’, The Guardian, 15 April. https://www.theguardian.com/books/2016/apr/15/neoliberalism-ideology-problem-george-monbiot.
Townshend, Jules (1990) J. A. Hobson (Manchester: Manchester University Press).
Venugopal, Rajesh (2015) ‘Neoliberalism as a Concept’, Economy and Society, 44(2), pp. 165-87. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/03085147.2015.1013356.
Posted in Brexit, Common ownership, Democracy, Donald Trump, Immigration, Karl Marx, Labour Party, Left politics, Liberalism, Markets, Nationalization, Politics, Populism, Private enterprise, Right politics, Socialism
January 5th, 2017 by geoffhodgson1946

“Worth reading to show how Liberals have played their part in the development of much of Labour’s social and economic policies over the years” John Rogan
Geoffrey M. Hodgson
Labour did not win a majority in the 2017 general election. A future majority Labour government seems less likely than a progressive alliance of Labour with other parties.
But as Neal Lawson put it: “Labour’s tribalists, including its leader it seems, simply cannot stand the idea of working with others.” Furthermore, Britain’s unfair electoral system means that, even with 20 per cent of the vote in the new constituency boundaries, Labour could retain about 150 MPs, while the Liberal Democrats would be likely to get less than 50 MPs with the same share of the overall vote.
Labour’s tribalism and self-interest could transform it into a rump party of purists in permanent opposition, rather than as a serious engine of political power that can tackle the pressing problems of poverty, inequality, poor education, declining health services and global warming.
Labour has depended on Liberalism
My purpose here is to argue that such insularity is historically ungrounded. Furthermore, while Liberals too have their sins – from support of the First Word War to endorsement of Tory austerity in 2010-2015 – the very vitality and survival of the Labour Party has been largely due to Liberals and liberalism. Strange but true.
“Nonsense,” you might say: “Labour was built on the trade unions and the organised working class.” True. But what made strong trade unionism possible?

William Ewart Gladstone
Trade unions were made legal in the UK for the first time in 1871, under the Liberal Prime Minister William Ewart Gladstone. Gladstone also introduced the Representation of the People Act 1884, which extended the right to vote from roughly 28 per cent (in 1867) to about 60 per cent of adult males.
Liberals also introduced the Education Act of 1870, which established schooling for all children between the ages of 5 and 12 in England and Wales. (It was already instituted in Scotland.) This widened literacy and political awareness.
Liberalism in the nineteenth century made possible the widespread development of trade unionism and the election of working class members of parliament. Many of these reforms were prompted by the expansion of the industrial working class and fears of riot or revolution. The Lib-Lab dialectic has run both ways.
Gladstone was an individualistic Liberal, advocating low taxes and a minimal state. But from the origins of liberalism in the Enlightenment, there have co-existed welfarist, cooperative and redistributive strains within liberalism.

Thomas Paine
These include the proposals by Tom Paine (1737-1809) for welfare provision and redistributive wealth taxes. John Stuart Mill (1806-1883) supported taxes on unearned income, inheritance taxes, trade unions, worker cooperatives, participatory democracy, votes for women as well as men, and care for the natural environment. Thomas Henry Green (1836-1882) argued that the state should protect the social, political and economic environments in which individuals could freely develop. Liberalism has always fostered notions of social obligation beyond narrow self-interest.
As the male franchise was widened, Liberals recruited working-class candidates, including those financially maintained by trade unions. The first Lib-Lab candidate stood in the Southwark by-election of 1870. The Lib-Labs represented working class interests but remained within the Liberal Party.
But as socialist ideas became more widespread, some working-class leaders began to move away from the Liberals. The Independent Labour Party was formed in 1893 and it put up its own candidates in the 1895 general election. The ILP was involved in the formation of the Labour Representation Committee in 1900, which was renamed the Labour Party in 1906. This was the great schism between Labour and Liberalism.
Liberalism, solidarity and welfare
Gladstone’s resignation in 1894 was partly prompted by his opposition to the proposal by his Liberal chancellor Sir William Harcourt to introduce death duties – a substantial tax on property. These events dramatized the tension between individualist and redistributive-welfarist strands within liberalism. Even after Gladstone’s departure, the Liberal Party remained internally divided on these issues, and it suffered a cataclysmic defeat in the 1895 general election.
Liberals were also divided on the question of Irish home rule, imperialism and war. A faction of “Liberal Unionists” broke away to form their own party in 1886: they entered a coalition with the Tories in 1900 and later fused with them.
But this period also saw the rise of a “new” or “modern” liberalism in both Britain and the United States. It stressed the importance of economic equality, a welfare state and judicious state intervention in a market economy. A key British intellectual involved in this revival was John Atkinson Hobson (1858-1940).

John A Hobson
Frustrated by the Liberal Party divisions of the 1880s and 1890s, Hobson had been in favour of the formation of a new party, but by 1901 he was calling for an alliance between labour representatives such as Keir Hardie and “progressive” Liberals. But Hardie eventually came to the conclusion that his Independent Labour Party had “nothing in common” with the Liberals.
A revived Liberal Party won a huge election victory in 1906, and Hobson returned to working within its ranks. After the 1910 general election the Liberal Party did not have a majority and formed a coalition with 42 Labour Party MPs who had been elected. The Liberal Henry Campbell-Bannerman was Prime Minister until 1908, followed by Herbert Asquith, who was in power until 1916.
Aware of the need to retain and extend support among the working class, the 1906-1914 Liberal-led governments executed a series of major reforms and laid the foundations of the British welfare state. These reforms included the introduction of a state pension, compulsory health insurance, unemployment and sickness pay, an extension of free secondary education, and a reform of the House of Lords. As Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1908 to 1915, David Lloyd George was a key figure in the introduction of many of these reforms.
Liberal decline and Labour gain
Subsequently, the Liberal Party suffered a rapid decline. In his classic diagnosis, George Dangerfield put this down to the crises over Ireland, where the Liberals were unable to prevent violence and revolt, to the rise of the labour movement and industrial militancy, and to votes for women, over which the Liberal Party fatally hesitated. During the war, the Liberal government antagonised progressive support by introducing illiberal measures including conscription and restrictions on freedom of speech.

David Lloyd George
The Liberal Party split again in 1916, when a wing led by Lloyd George entered a coalition with the Conservatives. The presence of the new and vigorous Labour Party on the Left gave a new home to disenchanted Liberals. Hobson quit the Liberal party in 1916, later to dally with Labour. But he always advocated a mixed economy and insisted on the virtues of market competition and extensive private ownership.
The much-diminished Liberal group in Parliament propped up the minority Labour governments in 1924 and 1929.
The Liberal share of the vote slumped, falling as low as 10 per cent in 1931. In the interwar period, liberalism was ground down by the rising, opposed totalitarianisms of Communism and fascism. It had to wait to the 1970s to begin a long, slow and punctuated revival.
The Labour Party was built on the twin pillars of socialist ideology and strong trade unionism. It rose from 21 per cent of the vote in 1918 to 48 per cent of the vote in 1945.
But these pillars are inadequate. Trade unionism is important for the defence of worker’s rights and as a counterbalance to powerful corporate interests. But trade unionism does not a government build. It lacks the hegemonic capacity to unite diverse sectional interests in a fractured and class-divided society.
At the outset, Labour’s socialism offered no defence of a private sector or of private property. From 1918 to 1995, Labour’s Clause Four offered common but not private or mixed ownership.

Clement Attlee
In 1937, eight years before he became Prime Minister, Clement Attlee wrote of the “evils” of capitalism: their “cause is the private ownership of the means of life; the remedy is public ownership.” Attlee approvingly quoted the words of Bertrand Russell: “Socialism means the common ownership of land and capital together with a democratic form of government. … It involves the abolition of all unearned wealth and of all private control over the means of livelihood of the workers.”
It was possible to advance such views at the time, without much loss of popular appeal. The full horrors of Stalin’s Soviet Union were initially unappreciated and then masked by the Soviet alliance with Western powers in the Second World War. The unprecedented famines and other brutalities of Mao Zedong were yet to come.
Liberalism defined Labour in power
After 1945, the position of many leading Labour Party members began to shift. The realities of gaining and holding on to power – as a majority party for the first time – dramatized the political and practical unfeasibility of abolishing all private enterprise. Some nationalization was achieved, but a large private sector remained. Then the outbreak of the Cold War in 1948 impelled everyone to make a choice between capitalism and democracy on the one hand, and state ownership and totalitarianism on the other.
The twin pillars of trade unionism and Clause Four socialism could not, and never will, sustain Labour in power. Labour nationalized several industries, but hardly more than the Liberal Hobson had proposed as early as 1909.
The greatest achievement of the 1945-1951 Labour government was its massive development of the welfare state, upon the foundations laid down by the Liberals in 1906-1914. In this second round, Liberals still played a major role.
Beveridge, Keynes and social democracy

William Beveridge
William Beveridge (1879-1963) was originally close to the Fabians but, against the prevailing current, he moved toward the Liberals, and was briefly a Liberal MP from 1944-1945. His wartime Beveridge Report (1942) became the foundation Labour’s post-1945 welfare state.
Impelled by a strong vision of social justice, Beveridge proposed a system of universal national insurance, conferring benefits to people who were sick, unemployed, retired or widowed. He argued that this system would provide a minimum standard of living “below which no one should be allowed to fall”. His proposals were developed in conjunction with the plan for a National Health Service, as developed by the Ministry of Health.

John Maynard Keynes
Near-full employment was pivotal to his system of social welfare. He expanded on this in his 1944 book Full Employment in a Free Society. In developing this goal, Beveridge relied explicitly on the policy approach developed by another great Liberal – John Maynard Keynes. Keynes was instrumental in instating full employment a major policy goal. In his General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money he provided the theoretical underpinnings of this policy.
Much of the success of the 1945-51 Labour government depended on Liberal ideas. The bland mantra of common ownership provided neither a theoretical rationale nor a practical grounding for detailed policy.
When the Labour government tackled the problems of poverty, inequality and unrealised human potential within actually existing capitalism, they turned to Liberal thinkers such as Hobson, Keynes and Beveridge, who had grappled with the policy issues for years.
Insofar as Labour became a social-democratic rather than a genuinely socialist party, it has done so by borrowing ideas from liberals. (Socialism today is too-often taken to mean almost anything, but it was originally defined by Robert Owen as the abolition of private property.)
Labour after 1951
The graph of Labour’s share of the vote shows a long decline from its peak in 1951 to the disastrous result in 1983. The Labour governments of 1964-1970 and 1974-1979 had seen major reforms under the premiership of Harold Wilson. From 1974 to 1979 there was a pact between the Liberals in Parliament and the Labour Government.
But the Labour pillar of trade unionism begat the strike wave in the so-called 1978-1979 Winter of Discontent, and Labour’s Clause Four mantra still hung around its neck.
These enhanced the conditions for the victory of Margaret Thatcher in the 1979 general election. With an inadequately-developed alternative ideology sustaining a mixed economy, Labour fell back on its founding twin pillars and lurched the Left. The result was the disaster of 1983 and Labour’s lowest share of the vote since 1918.
When Neil Kinnock became Labour leader in 1983 he pulled the party back from the brink. It took a further 14 years for Labour to recover sufficiently to win a general election.
The coalition that never was
Until the day of polling in May 1997, when the scale of his majority became clear, Tony Blair considered a coalition with the Liberal Democrats after the election, and negotiated with Paddy Ashdown on that possibility. In his first speech to a Labour conference after his landslide election victory, Blair declared:
“my heroes aren’t just Ernie Bevin, Nye Bevan and Attlee. They are also Keynes, Beveridge, Lloyd George. Division among radicals almost one hundred years ago resulted in a 20th century dominated by Conservatives. I want the 21st century to be the century of the radicals.”

Tony Blair
Blair of course referred to the 1900 decision to set up a party in parliament independent of the Liberals, to represent working people. Blair’s election victory was impelled by shift toward liberalism and an explicit rejection of classical socialism. He tackled the twin pillars of trade unionism and common ownership, upon which Labour was founded.
The opportunity of another coalition emerged after Labour’s loss of an overall majority in 2010. But instead, the Liberal Democrats turned to the Tories and formed a coalition with them. One reason for this choice was that the Liberal Democrats under Nick Clegg had abandoned their Keynesian heritage and accepted a strategy of economic austerity. This mistake cost the Liberal Democrats dearly in the 2015 election.
When Labour suffered a second successive defeat in 2015 it moved again to the Left, ending in 2015 and 2016 with the election and re-election of a hard leftist with little experience in government and a preference for slogans over both theoretical argument and practical details.
Around sixty percent of the membership voted for Jeremy Corbyn on these occasions, showing that Labour had retained its 1918 roots. This has created the conditions for a similar return to Labour’s 1918 share of the vote.
Conclusion: history in reverse
The Labour Party was founded in an era of mass industrial trade unionism and increasing ideological support for socialism, as classically defined. Both of these forces have been gravely weakened and are in dramatic decline. Traditional trade unionism has not simply been undermined by the anti-union legislation by Conservative governments. Trade unions face vastly transformed workplaces with a much more fragmented workforce, often engaged in tasks that require detailed experience and specialist skills. To survive, their role must be transformed.
But the unions have been slow to adapt to this new reality and have declined in strength. Where some disruptive power has been retained – such as on some parts of the railway system – they hasten the demise of their jobs and their replacement by robots.
The ideological appeal of classical socialism has been fatally undermined by the practical experiments in Russia, China, North Korea, Cambodia, Cuba, Venezuela and elsewhere. These experiments have without exception undermined human rights and have led to an estimated total of 90 million deaths.

Jeremy Corbyn
From 1945 Labour was unable to rely on the twin pillars of trade unionism and socialism but it retained them nevertheless. Corbyn makes them central once again, but his anachronistic strategy is doomed to failure.
Labour’s problems are exacerbated by internal divisions over immigration, Brexit, defence and NATO (in a time of increasing international tension and insecurity). The Liberal Democrats alone speak for the 48 per cent that voted to remain in the European Union.
5 January 2017
Edited 6-8, 14 January, 1 July
|
My forthcoming book elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost
To be published by University of Chicago Press in November 2017
|
References
Allett, John (1981) New Liberalism: The Political Economy of J. A. Hobson (Toronto: University of Toronto Press).
Attlee, Clement R. (1937) The Labour Party in Perspective (London: Gollancz).
Beveridge, William (1944) Full Employment in a Free Society (London: Constable).
Clarke, Peter (1978) Liberals and Social Democrats (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press).
Dangerfield, George (1935) The Strange Death of Liberal England (London: Constable).
Harrop, Andrew (2017) ‘Stuck: How Labour is too weak to win, and too strong to die’, 3 January (London: Fabian Society). http://www.fabians.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Stuck-Fabian-Society-analysis-paper.pdf
Hobson, John A. (1909) The Crisis of Liberalism: New Issues of Democracy (London: King).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2017) Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, forthcoming).
Keynes, John Maynard (1936) The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money (London: Macmillan).
Lawson, Neil (2017) “Labour’s poll woes show why we need to do a deal with rival parties”, Labour List, 4 January. http://labourlist.org/2017/01/neal-lawson-labours-poll-woes-show-why-we-need-to-do-a-deal-with-rival-parties/
Townshend, Jules (1990) J. A. Hobson (Manchester: Manchester University Press).
Posted in Common ownership, Jeremy Corbyn, Labour Party, Left politics, Liberalism, Politics, Socialism, Tony Blair, Tony Blair
December 6th, 2016 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
Racist nationalism has returned from the fringes to mainstream politics. In 2016 it played a major role in the Brexit vote in the UK, in the election of Donald Trump in the US, in the presidential election in Austria, and in developments in many other countries.
Racism and other forms of discrimination, including by gender or belief, must be defeated. The Left has played a major role in countering racism, and it should be give due credit for that. But in some other respects the Left on this issue is weak and misguided.
Some things we cannot talk about – but we must
Some things have become difficult to discuss. I once tweeted the (obviously true) statement that “Islam is religion, not a race”. A fellow tweeter immediately assumed that I was some kind of bigot and responded “ugh!”
In this reactive climate it has become difficult to raise concerns about (say) Sharia law without being branded racist or right-wing. Discussion ends. But the fact that rightist bigots – such as Nigel Farage and Geert Wilders – go on about Sharia law does not mean that we cannot discuss it.
 Of course, Muslims and others suffer significant discrimination, in Britain and elsewhere. In recent months, Trump has been responsible for major anti-Muslim outbursts and has whipped up violent anti-Muslim sentiment in the US.
Of course, Muslims and others suffer significant discrimination, in Britain and elsewhere. In recent months, Trump has been responsible for major anti-Muslim outbursts and has whipped up violent anti-Muslim sentiment in the US.
We must defend the full human rights of everyone, including members of all faiths. But this does not mean that we must refrain from criticising religious doctrines.
On the contrary, our failure to discuss these issues has favoured conservatives over reformers within these religions, has allowed religious extremism to ferment, and has repeatedly played into the hands of the reactionary and extremist Right.
I explain here where and how the Left has got things wrong in this area. I concentrate mostly on the moderate Left. The sins of many on the Far Left are much worse, including their support for fanatical, religious, “anti-Imperialist”, extremists in Palestine, Iran and elsewhere.
The election of Trump is a wake-up call. We need to find more effective ways to counter racism and other forms of discrimination. We need to find ways to make multi-religious and multi-ethnic communities more inclusive and cohesive.
Immigration – beyond the numbers game
The recent massive increases of immigration into Europe and elsewhere are a fact. But at least as far as the UK is concerned, it has been shown that the economic benefits of immigration are positive.
 But much of the political debate is about immigrant numbers. The Tories ignore the economic evidence and start a Dutch auction of targets, to stem numbers. A large part of the Labour Party, facing a seepage of its working class support to UKIP, moves in a similar direction.
But much of the political debate is about immigrant numbers. The Tories ignore the economic evidence and start a Dutch auction of targets, to stem numbers. A large part of the Labour Party, facing a seepage of its working class support to UKIP, moves in a similar direction.
Of course, mass immigration becomes a problem when there are not enough school places, health services are severely stretched, housing is limited and inadequate, and the transport infrastructure groans from decades of under-investment.
Labour is internally divided between those that want to restrict immigration, and the leadership around Jeremy Corbyn who propose no restrictions at all. With some notable exceptions, what is missing is a discussion prioritising assimilation.
The Casey Review

Louise Casey
The recently-published, government-commissioned report by Louise Casey suggests that “the tough questions on social integration are being ducked”. Casey and her team found evidence that black and minority ethnic groups are still suffering from discrimination and disadvantage and responses by government and others are inadequate. While she found some evidence of integration, in other areas the outcomes were different:
“In some council wards, as many as 85% of the population come from a single minority background, and most of these high minority concentrations are deprived Pakistani or Bangladeshi heritage communities.”
These concentrated enclaves are more difficult to assimilate and create particular problems for women:
“this sense of retreat and retrenchment can sometimes go hand in hand with deeply regressive religious and cultural practices, especially when it comes to women. These practices are preventing women from playing a full part in society, contrary to our common British values, institutions and indeed, in some cases, our laws. … I’ve met far too many women suffering the effects of misogyny and domestic abuse, women being subjugated by their husbands and extended families. Often, the victims are foreign-born brides brought to Britain via arranged marriages. They have poor English, little education, low confidence, and are reliant on their husbands for their income and immigration status. They don’t know about their rights, or how to access support, and struggle to prepare their children effectively for school.”
Casey argued that fears of being labelled “racist” have prevented society from challenging sexist, misogynistic and patriarchal behaviour in some minority communities. Her report cites claims that some Sharia councils had supported the values of extremists, condoned wife-beating, ignored marital rape and allowed forced marriages.
Her report concluded with a rallying cry:
“The problem has not been a lack of knowledge but a failure of collective, consistent and persistent will to do something about it or give it the priority it deserves at both a national and local level.”
But to “do something about it” requires a clearer understanding of the problems involved and what kind of policies are needed to deal with them. Some people have criticised Casey’s empirical claims and more research is clearly required.
Multiculturalism
As several authors have pointed out, multiculturalism is an ambiguous concept. In one sense, at least, it is unobjectionable. All civilisations have drawn and benefitted from cultural variety. Western countries today benefit enormously from the influx of ideas, skills, fashions, cuisines and experiences that successive waves of immigration have brought. This has been true for millennia. It is no less true today.
Institutions are the stuff of society: institutions are systems of social rules. Some rules – concerning dress and fashion for example – can change profoundly without social collapse.
Other institutions – particularly in law and politics – are the outcomes of centuries of experience, deliberation and experimentation. We cannot put these in a culture-mixing food blender without tearing apart the fabric of society and wrecking social cohesion and solidarity.
Much discourse about multiculturalism ignores these differences in types of rules and institutions. Everything is placed under the vague and overly-capacious category of “culture”, assuming everything can be mixed at will. This soup-making, food-blender approach is dangerous and misconceived.
Cultural relativism
Some parts of the Left have embraced normative cultural relativism. This is the view that one person’s morality is as good as any other. It is said that there is no “objective” or “correct” morality. No overriding importance is given to democracy or to the United Nations Declaration of Universal Human Rights. Other cultures have different codes and priorities: let them be.
According to this view, asking people from other cultures to adopt our over-arching laws and values is seen as a manifestation of “oppression” or “Western imperialism”. We have to be very careful not to jump to the conclusion that Western moral values are superior. But that does not mean that we should reach no judgmental conclusion at all.

Germaine Greer
For example, in her 1999 book The Whole Woman, the self-declared “Marxist” and iconic feminist Germaine Greer asked us to refrain from criticising female genital mutilation, on the grounds that it would impose our cultural values on others.
In his excellent book What’s Left? Nick Cohen gives some further examples of highly misguided cultural relativism, including attempts by feminists and leftists to defend the Indian practice of burning widows alive after the deaths of their husbands.
Analytically, this kind of cultural relativism has major flaws. First, it falls down in dealing with changing attitudes through time in one country. A cultural relativist, time travelling back to 1800, could raise no objection to slavery, or to the lack of women’s rights. If one morality is as good as any other, then there can be no moral force for change.
Second, it is internally inconsistent. Cultural relativism denies that our values are valid or suitable for other cultures. Why should this normative claim (that we should not impose our normative values on other cultures) be adopted by others in different cultures? By the logic of cultural relativism, thinkers in other cultures are not obliged to be cultural relativists. The whole argument is self-defeating.
Third, cultural relativism degrades the role of morality, by treating it as a matter of individual preference. The whole point about morality is that it transcends individual preferences. Moral claims (be they right or wrong) are universal. Humans have developed systems of morality to provide us with rules that help social cohesion while simultaneously protecting individual rights and liberties.
Reticence to act – condemnation of action
As well as the benefits of cultural enrichment, mass immigration has also brought problems of assimilation. In the UK there are large communities where many people do not speak English, or remain ignorant of prevailing laws and values that have evolved over centuries to keep our society together and to protect our interests.
Many of these immigrants had limited experience of any Western-style democracy and had an inadequate appreciation of universal human rights. Many came from rural areas in undeveloped countries, where the state was weak and social and business interactions were governed by custom and religion, based on ties of loyalty to family and clan.

Ann Cryer
Faced with this issue, many progressive politicians have adopted a stance of ultra-tolerance and inaction. Consider the question of language. Should immigrants be obliged to learn the language of their new country, so that they can understand its culture and its laws? Some other countries take this on board.
But such an assimilationist policy in the UK was highly controversial as late as 2001. In that year, the Labour MP Ann Cryer bravely argued that many Muslims were held back economically and educationally by language difficulties. The problem was especially severe among Muslim women.
But she was faced with criticism and scorn from the Left. Shahid Malik, then a senior member of the Commission for Racial Equality and of the Labour Party National Executive Committee, and subsequently a Labour MP and government minister, responded to Cryer: “Her arguments are sinister and they have no basis in fact … she is doing the work of the extreme right wing.”
Promoting faith schools
Schooling must be central to any viable integration programme. Young people need to learn about the struggles for democracy, independence, rights and human emancipation, throughout the world. They should be free to discuss and evaluate all these things.
Such a broad education is less likely in a school that is linked to one particular religion. Instead it would be more viable in secular schools with pupils from multiple religions, classes and cultures. Broad-based secular education is even more vital in multi-cultural and multi-faith societies.
 After coming to power in 1997, Labour Prime Minister Tony Blair promoted a programme of expansion of faith schools. But a 2001 report commissioned by Bradford City Council concluded that its communities were becoming increasingly isolated along racial, cultural and religious lines, and that faith-segregated schools were fuelling the divisions.
After coming to power in 1997, Labour Prime Minister Tony Blair promoted a programme of expansion of faith schools. But a 2001 report commissioned by Bradford City Council concluded that its communities were becoming increasingly isolated along racial, cultural and religious lines, and that faith-segregated schools were fuelling the divisions.
In 2001 there were riots in Bradford, which spread to other northern cities. Yet in the same year the Labour Government proposed a large increase in the number of state schools run by religious organizations.
By 2002 there was a major public row, with accusations that some pupils were being taught creationism in and that homosexual acts are against God’s law. Campaigners for women’s rights expressed concern that conservative religious teachers were instructing young girls that women should take a secondary role in society.
Despite his previous opposition to Blair, in 2016 the Labour Leader Jeremy Corbyn expressed his support for faith schools. No major UK political party has dared to come out against them. They are being vigorously promoted by the current Conservative government.
Faith schools have hindered assimilation

David Bell
David Bell warned in a January 2005 speech to the Hansard Society – when he was Chief Inspector of Schools – that a traditional Islamic education did not equip Muslim children for living in modern Britain. He said: “I worry that many young people are being educated in faith-based schools, with little appreciation of their wider responsibilities and obligations to British society.” He continued:
“We must not allow our recognition of diversity to become apathy in the face of any challenge to our coherence as a nation … I would go further and say that an awareness of our common heritage as British citizens, equal under the law, should enable us to assert with confidence that we are intolerant of intolerance, illiberalism and attitudes and values that demean the place of certain sections of our community, be they women or people living in non-traditional relationships.”

Trevor Phillips
His comments were condemned as “irresponsible” and “derogatory” by some senior Muslims, but supported by Trevor Phillips, then chair of the Commission for Racial Equality.
In another lecture Bell said: “We can choose … whether we want to bring our diversity together in a single rainbow or whether we allow our differences to fester into separate cultures and separate communities.”
Phillips came to the conclusion that increasing self-segregation of British communities along ethnic and religious lines was a major threat to national integration and to Enlightenment values. Young people were being brought up with insufficient awareness of these values, in closed communities where extremism could fester.

David Miliband
Ken Livingstone, then Mayor of London, attacked Phillips for “pandering to the right”. During a televised discussion, the prominent Labour Minister David Miliband shook his head and described Phillips’s remarks about community segregation as “fatuous”.
Since then, Phillips’s concerns about social segregation in British communities have been vindicated by several experts, while other evidence indicates a small amount of progress. Even the most optimistic reading of the evidence suggests a serious and enduring problem.
On faith schools, the Casey report noted their role in institutionalising segregation:
“The Government had attempted to alter the segregation of pupils in faith schools by introducing admissions criteria for new faith-based Free Schools. But these did not seem to be having an impact on the diversity of minority faith schools … [their] admission policies do seem to play a role in reinforcing ethnic concentrations.”
But Casey did not take the final step. She wrote: “ending state support for all faith schools would be disproportionate”. But how serious do the problems have to become before it becomes proportionate?
Rather than relying on failed palliatives, state-funded faith schools should be phased out. Taxpayers should not subsidise religion: religion and the state should part company.
A recent poll found that an overwhelming majority of the British public opposed religious discrimination in faith school admissions. Making all faith schools non-discriminatory in terms of religion would be a big positive step.
Fostering extremism
Ed Husain was born and educated in Britain, where he obtained a Master’s Degree. He was drawn toward extreme versions of Islam and was persuaded that Western democracies are irredeemably corrupt and must be replaced by a theocracies based on Islamic law.
 After several years he renounced his former extremism, but retained his Islamic faith. In an interview he revealed the segregated life of his upbringing:
After several years he renounced his former extremism, but retained his Islamic faith. In an interview he revealed the segregated life of his upbringing:
“The result of 25 years of multiculturalism has not been multicultural communities. It has been mono-cultural communities. Islamic communities are segregated. Many Muslims want to live apart from mainstream British society; official government policy has helped them do so. I grew up without any white friends. My school was almost entirely Muslim. I had almost no direct experience of ‘British life’ or ‘British institutions’.” (Quoted in Cohen 2007, p. 378.)
British policy-makers have welcomed diversity. But they have defined needs and rights via the ethnic categories into which people were placed, using those divisions to shape public policy. The result has been a more fragmented society, which has nurtured extremism.
In the name of multi-culturalism, Britain has become a more divided society, where inclusive, universal, Enlightenment values are often side-lined or unknown. These communal enclaves, found in France and Belgium as well as Britain, have become hothouses for violent extremism.
Hassan Butt was born in Luton in England in 1980. In 2000 he travelled to Pakistan and worked for the Taliban and other jihadists against the West. Subsequently he renounced his anti-Western views.
Butt explained that “Islamic theology, unlike Christian theology, does not allow for the separation of the state and religion … [they] are considered to be one and the same.” Consequently, since there no righteous Islamic state is deemed to exist, the extremists have “declared war on the whole world”.
 Some on the Far Left disowned Butt for betraying the struggle against “Western imperialism”. He was also criticized by one member of the “Stop the War” movement, who is a leading supporter of the Muslim Brotherhood, for his “call to change the face of Islam” (Cohen 2007, pp. 371-2).
Some on the Far Left disowned Butt for betraying the struggle against “Western imperialism”. He was also criticized by one member of the “Stop the War” movement, who is a leading supporter of the Muslim Brotherhood, for his “call to change the face of Islam” (Cohen 2007, pp. 371-2).
Butt’s response was clear: “I believe that the issue of terrorism can be easily demystified if Muslims and non-Muslims start openly to discuss the ideas that fuel terrorism.” However, many on the Left, as well as the Right, are not helping this process.
British values?
Successive British Prime Ministers have reacted to the threat of Islamist extremism by calling for “British values”. After claims that some schools in Birmingham were promoting Islamist extremism, in 2014 the Conservative Prime Minister David Cameron outlined plans to put the promotion of “British values” at the heart of the national curriculum for schools. This is now official policy:
“Schools should promote the fundamental British values of democracy, the rule of law, individual liberty, and mutual respect and tolerance of those with different faiths and beliefs.”
 But the official government document outlining this policy mentions respect and tolerance for other races but fails to mention discrimination against women or gays. It rightly mentions the freedom to “choose and hold” any faith, but not the freedom to exit a religion without sanction. It mentions “individual liberty” only once, and fails to uphold freedom of non-violent expression, including when it may cause offence.
But the official government document outlining this policy mentions respect and tolerance for other races but fails to mention discrimination against women or gays. It rightly mentions the freedom to “choose and hold” any faith, but not the freedom to exit a religion without sanction. It mentions “individual liberty” only once, and fails to uphold freedom of non-violent expression, including when it may cause offence.
Are these omissions an accident, or are they designed not to offend a particular religious minority?
 Another problem here is not the values as such, but their nationalistic description as “British”. Democracy was not invented in Britain: Ancient Athens and Viking Iceland have much earlier precursors. The US and France have much earlier claims to the values of liberty and religious tolerance. Britain legally discriminated against Protestant nonconformists and Catholics until the nineteenth century, and it still bars any Catholic from becoming its sovereign.
Another problem here is not the values as such, but their nationalistic description as “British”. Democracy was not invented in Britain: Ancient Athens and Viking Iceland have much earlier precursors. The US and France have much earlier claims to the values of liberty and religious tolerance. Britain legally discriminated against Protestant nonconformists and Catholics until the nineteenth century, and it still bars any Catholic from becoming its sovereign.
Apart from being misleading and inaccurate, the label of “British values” would hardly be effective in preventing a young Muslim from being radicalised. On the contrary, the label can help bolster the misperception that Britain and the rest of the West are at war against Islam. This nationalistic labelling readily allows the distortion that “British values” are being promoted by the UK authorities in a global effort to counter Islam.
It would be more accurate and effective to label values such as democracy, the rule of law, individual liberty, and freedom of worship as “universal values” or “Enlightenment values”. They are not simply values that British residents and citizens should adopt. Other countries should promote these values too.
Islamophobia?
Polly Toynbee is a leading progressive, and vigilantly anti-racist, British journalist. Yet in 2004 she was proclaimed by the Islamic Human Rights Commission as the winner of their “Most Islamophobic Media Personality” award.

Polly Toynbee
In her words, she received this ridiculous appellation because she “had challenged the legitimacy of the idea of Islamophobia and warned of the danger to free speech of trying to make criticism of a religion a crime akin to racism.” She rightly noted that the “occasional note of reason from moderate Islamic groups is so weak it hardly makes itself heard”. She highlighted the difficulties involved in starting a serious dialogue on this issue.
The failure to distinguish racism from criticism of religion sadly remains widespread. Many on the Left have done excellent work since the 1970s in campaigning against racism, fascism and discrimination. But the frequent confusion of criticism of religion with racism has diverted their efforts.
It must be repeated that concerns about Islam as a belief system are not equivalent to bigotry toward Muslims. Racism and persecution of Muslims are serious problems and should be vigilantly opposed. But the option to criticise Islam, or any other belief system, is an important right, and it should be protected.
The term “Islamophobia” is partly to blame. Despite widespread usage, it is rarely defined and there is no consensus on its definition.
Does it literally mean fear of Islam? Or criticism of Islam? Or hatred of Islam? Or persecution of Muslims? Its intended meaning can range from scholarly criticism of Islamic doctrines to racist acts against ethnic groups who are Muslim. These are obviously very different. Yet they are all lumped together under the same label.
“Anti-Muslim prejudice” or “anti-Muslim discrimination” would be much better terms. They accurately describe this very real and sadly widespread problem.
Criticism of religion can be enlightening – indeed a part of Enlightenment (and British) values, from Voltaire to Bertrand Russell. We should also be free to criticise Sharia law, as we are free to criticise other laws.

Justin Welby
As Archbishop of Canterbury Justin Welby pointed out recently, there also needs to be a discussion about the doctrinal links between religion and extremism:
“This requires a move away from the argument that has become increasingly popular, which is to say that ISIS is nothing to do with Islam, or that Christian militia in the Central African Republic are nothing to do with Christianity, or Hindu nationalist persecution of Christians in South India is nothing to do with Hinduism.”
Extreme and draconian statements can be found in the Old Testament of the Bible as well as in the Qur’an. Believing that they are obeying the word of God, these texts have spurred violent religious extremists, as we are all sadly aware.
Nevertheless, many modern Christians, Jews and Muslims have accepted the power of state law over religious law. They obey the laws of their country. They do not kill homosexuals (Leviticus 20:13), or slay apostates (Deuteronomy 13:6-10), or stone to death a bride who is not a virgin (Deuteronomy 22:20-21), or rape non-Muslim women (Qur’an 23:1-6, 70:22-30), or make war on unbelievers (Qur’an 8:12, 9:5, 9:73, 9:123).
We must help this vital transition from regressive religious law, toward a recognition of modern secular law and democracy. But we do not do so by pretending it is not needed, or refusing to discuss it, or branding those that discuss it as “Islamophobic”.
Signs of hope
On a more positive note, the authors of the 2007 Policy Exchange Report argued for a change of approach. The government and others “should stop emphasising difference and engage with Muslims as citizens”.
Policies of “group rights or representation” for specific Islamic communities are likely to alienate other sections of the Muslim population further. These well-informed remarks went against much of the then-current local and national government policy.
The authors continued: “The exaggeration of Islamophobia does not make Muslims feel protected but instead reinforces feelings of victimisation and alienation.” They also called for “a broader intellectual debate in order to challenge the crude anti-Western, anti-British ideas that dominate cultural and intellectual life. This means allowing free speech and debate, even when it causes offence to some minority groups.”
We need to be honest. Extremist religions of all kinds can threaten liberal, democratic and Enlightenment values. Christianity in particular has been violently repressive and brutal. Some religious sects today are fanatical and intolerant.
These issues need to be openly discussed, in a civilised manner. They should not be swept under the carpet by those on the Regressive Left who act as if they do not understand the difference between race and religion, or would shut down critical discussion of a religion because it might be wrongly construed by others as an attack on a minority, or by other politicians of any stripe who are simply too scared to take the issue on.
In an immensely positive development, the “Muslim Reform Movement” was launched in 2015. In their inaugural statement they defended freedom of speech, gender equality, a secular state and the UN Declaration of Universal Human Rights. They noted explicitly that freedom of speech included the right to criticize Islam: “Ideas do not have rights. Human beings have rights.”
By contrast, the blanket and ill-defined leftist rhetoric of “Islamophobia” does not help those Muslims who are struggling to reform and modernise their religion. Instead, the more conservative leaders of Muslim communities protect their regressive and reactionary views behind its smokescreen. Modernising Muslims are thus impaired by an unwitting coalition of leftists and Muslim conservatives.
Responsibility lies on both sides. In a climate of open discussion, we all need to be vigilant against acts of hatred or violence against Muslims and other minorities.
Initiatives to preserve liberal values in a multi-faith and multi-ethnic world should be welcomed. In addition, the Left needs to re-establish its links with the Enlightenment and its project to separate church from state. Within any society, freedom of worship should be protected, as well as the freedom to criticise religion.
Inward-looking, unreforming, dogmatic religion is a major barrier to assimilation. The Left needs to learn that lesson, and to encourage open discussion of the issues involved.

6 December 2016
Edited 7th and 10th December 2016, with thanks to Andrew Ross. Further edit, 23 January 2017.
|
My forthcoming book elaborates on some of the political issues raised in this blog:
Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost
To be published by University of Chicago Press in November 2017
|
References
Accord Coalition (2016) ‘Public overwhelmingly opposes religious discrimination in faith school admissions’, Accord, 2 November. http://accordcoalition.org.uk/2016/11/02/public-overwhelmingly-opposes-religious-discrimination-in-faith-school-admissions/
Asthana, Anushka and Nazia Parveen (2016) ‘Call for action to tackle growing ethnic segregation across UK’, The Gaurdian, 1 November. https://www.theguardian.com/society/2016/nov/01/call-for-action-to-tackle-growing-ethnic-segregation-across-uk
Asthana, Anushka and Peter Walker (2016) ‘Casey review raises alarm over social integration in the UK’, The Guardian, 5 December. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2016/dec/04/social-integration-louise-casey-uk-report-condemns-failings
BBC News (2001) ‘MP calls for English tests for immigrants’, 17 July. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/1436867.stm
Bell, David (2005) ‘Full Text of David Bell’s Speech’, The Guardian, 17 January. http://www.theguardian.com/education/2005/jan/17/faithschools.schools
Board of Deputies of British Jews (2016) ‘Board of Deputies statement on meeting with Leader of the Opposition Jeremy Corbyn’, 9 February. https://www.bod.org.uk/board-of-deputies-statement-on-meeting-with-leader-of-the-opposition-jeremy-corbyn/
Butt, Hassan (2007) ‘My plea to fellow Muslims: You must renounce terror’, The Observer, 1 July. http://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2007/jul/01/comment.religion1
Casey, Louise (2016) ‘The tough questions on social integration are being ducked’, The Observer, 4 December. https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2016/dec/04/tough-questions-social-integration-laws-values-every-person-britain
Cohen, Nick (2007) What’s Left? How the Left Lost its Way (London and New York: Harper).
Department of Education (2014) Promoting Fundamental British Values as Part of SMSC in Schools (London: Department of Education). https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/380595/SMSC_Guidance_Maintained_Schools.pdf
Department for Communities and Local Government (2016) The Casey Review: A review into opportunity and integration (London: Department for Communities and Local Government). https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/574565/The_Casey_Review.pdf
Dobson, Roger (2014) ‘British Muslims face Worst Job Discrimination of any Minority Group, According to Research’, The Independent, 30 November. http://www.independent.co.uk/news/uk/home-news/british-muslims-face-worst-job-discrimination-of-any-minority-group-9893211.html
Gillard, Derek (2007) Never Mind the Evidence: Blair’s Obsession with Faith Schools www.educationengland.org.uk/articles/26blairfaith.html
Greer, Germaine (1999) The Whole Woman (New York: Doubleday).
Hodgson, Geoffrey M. (2017) Wrong Turnings: How the Left Got Lost (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, forthcoming).
Husain, Ed (2007) The Islamist: Why I Joined Radical Islam in Britain, What I Saw Inside, and Why I Left (London Allan Lane).
Hussain, Dilly (2015) ‘How “British Values” are used as a Smoke Screen for Anti-Muslim Government Policies’, Stop the War Coalition, 15 June. Formerly http://www.stopwar.org.uk/news/how-british-values-are-used-as-a-smokescreen-for-anti-muslim-government-policies. Now unavailable.
Kinnock, Stephen (2016) ‘How to build an inclusive and patriotic view of Britishness’, Labour List, 2 December. https://labourlist.org/2016/12/kinnock-how-to-build-an-inclusive-patriotic-and-confident-view-of-britishness/
Malik, Kenan (2005) ‘The Islamophobia Myth’, Prospect, February. http://www.kenanmalik.com/essays/prospect_islamophobia.html
Mirza, Munira, Senthilkumaran, Abi and Ja’far, Zein (2007) Living apart Together: British Muslims and the Paradox of Multiculturalism (London: Policy Exchange), https://policyexchange.org.uk/publication/living-apart-together-british-muslims-and-the-paradox-of-multiculturalism
Mortimer, Caroline (2016) ‘Justin Welby: It’s time to stop saying Isis has ‘nothing to do with Islam’”, The Independent, 19 November. http://www.independent.co.uk/news/people/isis-nothing-to-do-with-islam-justin-welby-archbishop-canterbury-religion-a7427096.html
National Secular Society (2015c) ‘Muslim Reform Movement Embraces Secularism and Universal Human Rights’, National Secular Society, 8 December. http://www.secularism.org.uk/news/2015/12/muslim-reform-movement-embraces-secularism-and-universal-human-rights
Portes, Jonathan (2012) ‘Inching towards integration?, National Institute of Economic and Social Research, 5 March. http://www.niesr.ac.uk/blog/inching-towards-integration#.WEglE01vicx
Sides, John (2015) ‘New research shows that French Muslims experience extraordinary discrimination in the job market’, The Washington Post, 23 November. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/monkey-cage/wp/2015/11/23/new-research-shows-that-french-muslims-experience-extraordinary-discrimination-in-the-job-market/
Toynbee, Polly (2004) ‘We Must be Free to Criticise without Being Called Racist’, The Guardian, 18 August. http://www.theguardian.com/world/2004/aug/18/religion.politics
Travis, Alan (2016) ‘Mass EU migration into Britain is actually good news for UK economy’, The Guardian, 18 February. https://www.theguardian.com/uk-news/2016/feb/18/mass-eu-migration-into-britain-is-actually-good-news-for-uk-economy
White, Michael (2015) ‘Trevor Phillips says the Unsayable about Race and Multiculturalism’, The Guardian, 16 March 2015. http://www.theguardian.com/uk-news/2015/mar/16/trevor-phillips-race-multiculturalism-blog
Posted in Assimilation, Christianity, Democracy, Donald Trump, Immigration, Islam, Judaism, Labour Party, Left politics, Liberalism, Populism, Religion, Right politics
September 16th, 2016 by geoffhodgson1946

Geoffrey M. Hodgson
There are several different kinds of populism, emanating from both the left and right. But they have in common a view that some powerful minority group are clearly to blame for the ills suffered by a majority. As Julian Baggini put it, in his excellent article on Corbyn’s populism:
‘Populism is … a way of doing politics that has three key features. First, it has a disdain for elites and experts of all kinds, especially political ones. Second, it supposes that the purpose of politics is simply to put into action the will of the people, who are seen as homogenous and united in their goals. Third, it proposes straightforward, simple solutions to what are in fact complex problems.’
Rather than enter into a discussion over political problems and details, populists accuse those who fail to support them as collaborators of the exploiting elite. They believe that the elite is the main obstacle to progress, and solutions will appear once the elite is removed. They are suspicious of experts and dissenters. They are typically vague about their own objectives: their primary aim is to unite the bulk of the population behind a leader, against the elite.
The Great Crash of 2008 undermined confidence in existing elites. For this and other reasons, populism is now on the rise, in both Europe and the USA.
Populism on the Right
The campaign by UKIP to quit the European Union was populism incarnate. Its leader, Nigel Farage, complained frequently that the elites have gained too much power over hard-working ordinary people. Furthermore, elites at the national level had allegedly handed over power to unaccountable rulers in Europe, who have allowed mass immigration and robbed the UK of its sovereignty.
Because of his focus on a nationalist solution, and his identification of foreigners as a primary problem, Farage is an example of a right populist. By championing ‘ordinary British people’ against the establishment, and relying more on sentiment than on reasoned argument or expert advice, he is populist to the core.
 After his success in the Brexit referendum, Farage flew across the Atlantic to show his support for Donald Trump. At his August 2016 speech at a Donald Trump rally in Mississippi, Farage celebrated that Britain ‘chose not to be ruled by unelected old men in Brussels’. He drew parallels between the US and Britain, saying ordinary people everywhere had been ‘let down by government’. He was greeted by rapturous applause.
After his success in the Brexit referendum, Farage flew across the Atlantic to show his support for Donald Trump. At his August 2016 speech at a Donald Trump rally in Mississippi, Farage celebrated that Britain ‘chose not to be ruled by unelected old men in Brussels’. He drew parallels between the US and Britain, saying ordinary people everywhere had been ‘let down by government’. He was greeted by rapturous applause.
Trump’s rhetoric has much in common with that of Farage. Both blame immigrants for the problems in the country. Trump adds his rabid hostility to Muslims.
Corbynism as Left Populism
There are important differences between populists on the left and right. Left populists place less emphasis on the role of immigrants or foreigners: they are more inclusionary. Left populists also tend to favour greater state involvement in the economy. But elements of right populism can find their way into left movements, and vice versa.
 Jeremy Corbyn is very different from Nigel Farage and Donald Trump. Corbyn is neither a racist nor a misogynist (although he has shared political platforms with homophobes and anti-Semites). But Corbynism as a movement has strong populist features.
Jeremy Corbyn is very different from Nigel Farage and Donald Trump. Corbyn is neither a racist nor a misogynist (although he has shared political platforms with homophobes and anti-Semites). But Corbynism as a movement has strong populist features.
Other prominent examples of left populist movements include Syriza in Greece, Podemos in Spain and the ‘socialist’ regime established by the late President Hugo Chávez in Venezuela.
Labour has always been more pragmatic than ideological. Although Corbyn has some Marxist theoreticians close to him, including within his Momentum Praetorian Guard, he has relied much more on populist sentiment rather than Marxist theory.
The recent growth of left populism has been triggered by the crisis within social democracy, the disastrous invasion of Iraq in 2003, increasing economic inequality within leading economies, unaffordable housing, cuts in the welfare state and high rates of unemployment, especially among the young.
Corbynism vaguely promotes ‘socialism’, but there is no apparent agreement on what this means. There is a general suspicion of private enterprise, as well as a justified concern about the excessive power of some large corporations. When difficulties appear, public ownership is typically seen as the simple and obvious cure.
Like all populists, Corbyn rails against the elite. For him it is the rich minority and the large corporations. Like Farage, he identifies an elite that is bolstered by powerful friends abroad. But for Corbyn the most important foreign allies of the despised British elite are in Washington DC. With its anti-West foreign policy, Corbynism is Marxism-Leninism in populist clothing.
Corbynism Undermines Parliamentary Democracy
To public ownership is added the populist Corbynista slogans of ‘democratic control’ or ‘democratic management’ of enterprises. Without any detailed explanation of how this would work, it nevertheless reassures the left-populist followers that they, and not the elite, will somehow be in control. This left-populist slogan of ‘democratic control’ is seen as the obvious and straightforward way to ‘put into action the will of the people’.

Some extension of worker and community participation is desirable. But it cannot be a substitute for managerial discretion and leadership. Corbyn’s ultra-democracy is infeasible. When it threatens parliamentary democracy it is dangerous.
The Corbynistas want to shift power away from Parliament. They want MPs to follow ‘the will of the people’, which means, in practice, the implementation in Parliament of the resolutions of their local constituency parties. Inadequate heed is taken of the diverse views and interests of the electorate, and the need for expert deliberation and debate to make policy feasible and effective.
Instead of careful, empirically-grounded debate among diverse viewpoints, aimed at developing viable policies to deal with complex economic and political problems, Corbynistas are suspicious of dissent from their official line.
Any defence of markets or private ownership is worrying for them. It challenges their ‘obvious’, ‘democratic’ and simplistic solutions, and therefore must be opposed. Such dissent is branded ‘Blairite’ or ‘red Tory’ or ‘neoliberal’.
Instead of pluralism and extended debate, Corbynism treats the party resolution as the correct line, which all are instructed to follow. There is little appreciation of the complexity of modern politico-economic systems, and the consequent fallibility of all decision making.
Parliamentary institutions have evolved to deal with real-world complexities. They provide some mechanisms to challenge and scrutinise legislation. By moving from representative to delegate democracy, Corbynism would corrode the basic institutions of parliamentary democracy.
Any leader of any political party committed to working through parliament would resign when 80 per cent of his or her parliamentary representatives passed a vote of no confidence in his or her leadership. When this happened, Corbyn did not resign: his primary focus is not on parliament but on the populist ‘mass movement’ outside.
Totalitarian Dangers of Populism – The Example of Venezuela
The record of both left and right populism in power is abysmal. There is an important example of left populism in power, and it is close to Corbyn’s heart.
He has always had a romantic soft spot for Latin American revolutionaries. He wrote in 2011: ‘What the Cubans and … Che Guevara were preaching in the 1960s has an even greater resonance today’. This suggests that armed insurrection is appropriate, even in those Latin American countries that have become democracies.

Jeremy Corbyn and Hugo Chávez
In 1998, the Marxist politician Hugo Chávez was elected as President of Venezuela. Using the high oil revenues during 1999-2007, his government expanded access to food, housing, healthcare, and education, especially for the poor and the indigenous minorities.
Chávez nationalized key industries and created participatory Communal Councils. His ‘Chavista’ populism emphasised the ‘will of the people’, against the rich elite and their perceived allies in the United States.
Chávez created new ‘democratic’ institutions at the base to bolster his power. In 1999, the new Constitutional Assembly, filled with elected supporters of Chávez, drafted a new constitution that made censorship easier and granted the executive branch of government more power. The Constitutional Assembly extended the presidential term. It abolished the two houses of Congress. It also granted Chávez the power to legislate on citizen rights, to promote military officers and to oversee economic and financial matters.
In 2002 Chávez was briefly deposed in a coup, which may have had support from foreign agencies such as the CIA. The hostility of the US government to his regime was no secret. But Chávez was restored to power by the army and popular mobilisations.
Chávez seized control of the courts and the electoral authority, and suppressed much of the opposition media. He removed political checks and balances, seeing them as obstacles to his socialist revolution.

Hugo Chávez
Accordingly, the device of populist democracy was used to push the country in the direction of dictatorship. The high pre-Crash oil revenues were used to address some basic needs and to buy the support of the people. These supporters were then persuaded to approve increases in presidential powers, to protect the ‘socialist revolution’ against its enemies.
Chávez failed to diversify the economy and reduce its reliance on oil. He antagonised private investors. The economy was not robust enough to withstand the post-2008 oil price collapse. His government had become one of the most corrupt in the world. Serious shortages of food and medicine emerged. Chávez died of cancer in 2013 and was replaced as President by Nicolás Maduro.
But Corbyn’s enthusiasm for the regime was undiminished. As late as 2015, when Venezuela was in ever-deepening crisis, he remarked:
‘we celebrate, and it is a cause for celebration, the achievements of Venezuela, in jobs, in housing, in health, in education, but above all its role in the whole world … we recognise what they have achieved.’

Food Shortages in Venezuela
These gave him powers to intervene more heavily in companies and in the currency markets. Arbitrary detentions of dissidents became more common.
In July 2016 he used his executive powers to decree that citizens could be forced to work in the country’s fields for 60-day periods, which may be extended ‘if circumstances merit.’
Starvation became rife. In August 2016 a gang of hungry Venezuelans broke into a zoo and butchered a horse for its meat.
Populism in general, and the left populisms of Chávez, Maduro and Corbyn in particular, are profound threats to any enduring and viable democracy. Using Chávez as a prime example. Kurt Weyland wrote:
‘Determined and politically compelled to boost their personal predominance, populist leaders strive to weaken constitutional checks and balances and to subordinate independent agencies to their will. They undermine institutional protections against the abuse of power and seek political hegemony. Correspondingly, populist leaders treat opponents not as adversaries in a fair and equal competition, but as profound threats. Branding rivals “enemies of the people,” they seek all means to defeat and marginalize them. Turning politics into a struggle of “us against them,” populists undermine pluralism and bend or trample institutional safeguards.’
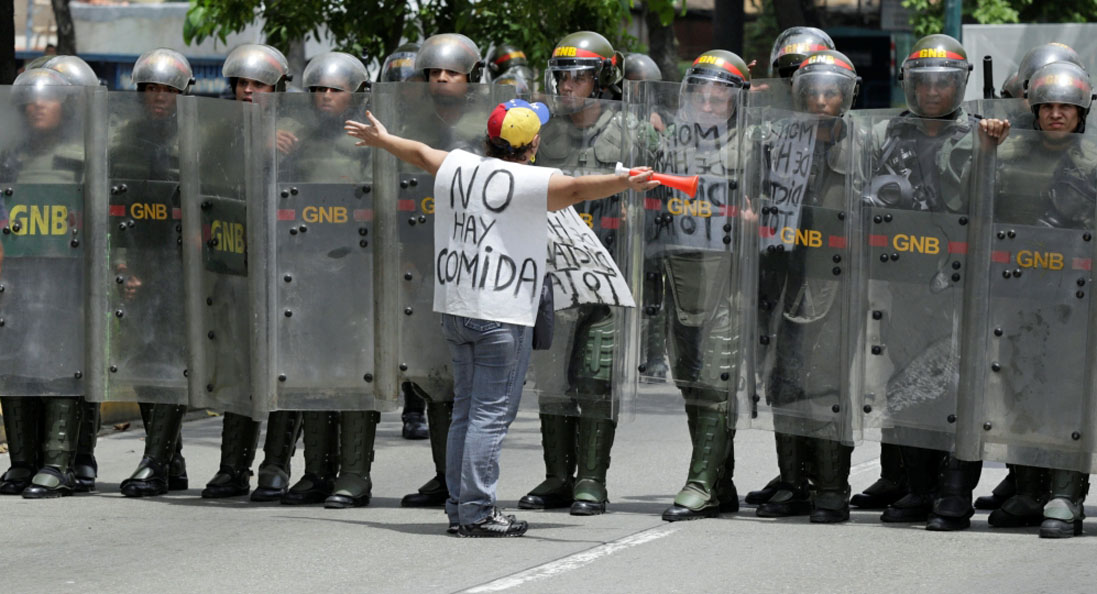

“There’s no food”
The tragic example of Venezuela is a warning to us all. Like Corbyn, Chávez started with a fairly modest economic programme, closer to social democracy than Marxist orthodoxy. But to bolster his power, Chávez extended state control. Maduro further undermined freedom of speech and put opponents in jail.
Because of a populist mistrust of liberal, pluralist institutions, Venezuela is lurching toward despotism. Currently it retains some semblance of democracy, but press freedom is limited and critical journalists are jailed. Since 2004, ‘defamation’ of the government, including ‘disrespect for the authorities’, has been a criminal offence.
Supporters of Chávez and Maduro blame the hostility of the US for Venezuela’s distress, just as it was blamed for economic problems in Cuba after its 1959 revolution. US belligerence made things worse. But the major cause of economic stagnation in both places is the hobbling of the private sector, and the unchecked concentration of excessive political, legal and economic power in the hands of the overbearing state.
Populism must be Defeated
Although it is unlikely that either UKIP or Corbyn’s Labour will ever win power, they can do serious damage to public debate and the functioning of a parliamentary democracy. In particular, by neutering Labour as a parliamentary force, the UK is deprived of an effective opposition to the Tory government.
 Consider the example of the EU referendum in June 2016. After the result, Corbyn took it for granted that Britain should leave the EU and immediately trigger Brexit, irrespective of the outcome of Britain’s negotiations on the terms of leaving. Like his fellow-populist Farage, Corbyn accepted that ‘the people had spoken’. For him, the expression of popular will was the end of the matter.
Consider the example of the EU referendum in June 2016. After the result, Corbyn took it for granted that Britain should leave the EU and immediately trigger Brexit, irrespective of the outcome of Britain’s negotiations on the terms of leaving. Like his fellow-populist Farage, Corbyn accepted that ‘the people had spoken’. For him, the expression of popular will was the end of the matter.
After the June 2016 vote to leave the EU, Britain is probably in its worse political crisis since the Second World War. It faces years of political and economic uncertainty, with no obvious resolution. In these circumstances, popular frustration and deprivation can feed populism. Left populism has its own dangers, and we know from history that left populists can shift to the right. In turn, right populism can feed fascism.
All populisms, including Corbynism, pose a serious threat to representative democracy. As Baggini put it:
‘Our tradition of representative democracy rests on a rejection of all three pillars of populism. It accepts that a well-run society needs specialists and full-time politicians whose judgments often carry more weight than those of voters who put them into power. It accepts that the “will of the people” is diverse and contradictory, and that the job of politics is to balance competing demands, not simply to obey them. It follows that there are few, if any, easy solutions and that anyone who promises them is a charlatan. Making the case for representative democracy therefore means telling the electorate it doesn’t always know best, a truism that populism has turned into an elitist heresy.’
Populists do not understand that political checks and balances, safeguarded by countervailing politico-economic power, are necessary to help protect democracy and liberty. With confidence in their ‘obvious’ solutions to complex problems, they treat criticism with disdain and close down reasonable discussion. All must ‘unite behind the leader’ who is revered for saving the masses from the enemy elite.
For these reasons Corbynism must be treated as a dangerous ideological threat to a liberal democracy, and not as an infantile, reversible outburst of ultra-leftism.
No-one has a feasible strategy to turn Labour back to its previous form. History offers no clear example of the internal undoing of populist fanaticism. It has always been defeated from outside. Labour is now irretrievable: there is no way of reversing the populist entrenchment within.
Corbyn’s Labour is a danger for the British political system as the Tories are for its economy and for its social fabric. Corbynism is a threat to liberal, pluralist democracy.
We need to build a progressive opposition to both Toryism and Corbynism. We need to defend liberal, pluralist democracy from the populisms of left and right. Building an alternative will take a generation, but we must start now.
16 September 2016
Minor edits: 17,18, 22 September 2016
Major edit: 18 June 2017

Bibliography
Bagehot (2016) ‘Why a “True Labour” splinter party could succeed where the SDP failed’, The Economist, 12 April. http://www.economist.com/blogs/bagehot/2016/08/labour-pains.
Baggini, Julian (2016) ‘Jeremy Corbyn is a great populist. But that’s no good for our democracy’, The Guardian, 30 July. https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2016/jul/25/jeremy-corbyn-populist-democracy-mps.
Borger, Julian (2016) ‘Venezuela’s worsening economic crisis’, The Guardian, 22 June. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2016/jun/22/venezuela-economic-crisis-guardian-briefing
Canning, Paul (2016) ‘Venezuela: The Left’s giant forgetting’. http://paulocanning.blogspot.co.uk/2016/09/venezuela-lefts-giant-forgetting.html
Corbyn, Jeremy (2011) ‘Foreword, to John A. Hobson, Imperialism: A Study’, facsimile reprint of 1902 edition (Nottingham: Spokesman).
Cunliffe, Rachel (2016) ‘Corbyn looks the other way as Venezuela self-destructs’, 18 January, http://capx.co/corbyn-looks-the-other-way-as-venezuela-self-destructs/.
Lawson, Neal (2016) ‘Social democracy without social democrats: how can the left recover?’ New Statesman. 12 May. http://www.newstatesman.com/politics/staggers/2016/05/social-democracy-without-social-democrats-how-can-left-recover.
Telesur (2015) ‘British MP Jeremy Corbyn speaks out for Venezuela’, 6 June. http://www.telesurtv.net/english/news/British-MP-Jeremy-Corbyn-Speaks-Out-For-Venezuela-20150605-0033.html.
Weyland, Kurt (2013) ‘The threat from the populist left’, Journal of Democracy, 24(3), pp. 18-32.
Wikipedia (2016) ‘Populism’. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Populism.
Posted in Democracy, Jeremy Corbyn, Labour Party, Left politics, Liberalism, Populism, Socialism, Uncategorized, Venezuela


 I was at the LSE student occupation in 1967 and one of the Grosvenor Square demonstrations in 1968. In that year I copied Bertrand Russell and tore up my Labour Party membership card in protest against US aggression in Vietnam.
I was at the LSE student occupation in 1967 and one of the Grosvenor Square demonstrations in 1968. In that year I copied Bertrand Russell and tore up my Labour Party membership card in protest against US aggression in Vietnam.








 I am a radical liberal. I believe in social solidarity with the less-privileged, as well as in individual rights. As Charles Kennedy showed when he was leader, the Liberal Democrats can succeed when they take principled, radical positions on justice, equality and war.
I am a radical liberal. I believe in social solidarity with the less-privileged, as well as in individual rights. As Charles Kennedy showed when he was leader, the Liberal Democrats can succeed when they take principled, radical positions on justice, equality and war.


 Sometimes, as in his Critique of the Gotha Programme of 1875, Marx referred to the “lower” and “higher phases” of communism, instead of socialism.
Sometimes, as in his Critique of the Gotha Programme of 1875, Marx referred to the “lower” and “higher phases” of communism, instead of socialism. 






 With the Brexit vote in 2016, Britain has entered its most dangerous political crisis since the Second World War. The country is governed by an inept Conservative Party that is tearing up the UK constitution and concentrating unprecedented power in the hands of its duplicitous ministers.
With the Brexit vote in 2016, Britain has entered its most dangerous political crisis since the Second World War. The country is governed by an inept Conservative Party that is tearing up the UK constitution and concentrating unprecedented power in the hands of its duplicitous ministers.







 As late as 1973 Robinson opposed “market socialism” and advocated a centrally-planned economy. She wrote of the “success of the Chinese economy in reducing the appeal of the money motive”. After extolling the virtues of Mao’s system, she reported that “Chinese patriotism and socialist ideology are pulling together”.
As late as 1973 Robinson opposed “market socialism” and advocated a centrally-planned economy. She wrote of the “success of the Chinese economy in reducing the appeal of the money motive”. After extolling the virtues of Mao’s system, she reported that “Chinese patriotism and socialist ideology are pulling together”. In 1964 Robinson visited Communist North Korea and extolled the “Korean miracle” in its economy. She attributed its claimed success to public ownership and central planning.
In 1964 Robinson visited Communist North Korea and extolled the “Korean miracle” in its economy. She attributed its claimed success to public ownership and central planning.



 Other countries have turned in the same direction, including the United States under Donald Trump and Russia under Vladimir Putin. Previously, both Soviet-style and fascist economies have embraced economic nationalism. China has continued along this road, even after its acceptance of private enterprise and a market economy.
Other countries have turned in the same direction, including the United States under Donald Trump and Russia under Vladimir Putin. Previously, both Soviet-style and fascist economies have embraced economic nationalism. China has continued along this road, even after its acceptance of private enterprise and a market economy.

 With his 1995 changes to Clause Four of the Labour Party Constitution, Blair brought in an explicit commitment to a dynamic private sector. Labour stood for an economy where “the enterprise of the market and the rigour of competition are joined with the forces of partnership and co-operation”. Corbyn has returned to the spirit of Labour pre-1995 constitution, even if he has not yet changed the wording.
With his 1995 changes to Clause Four of the Labour Party Constitution, Blair brought in an explicit commitment to a dynamic private sector. Labour stood for an economy where “the enterprise of the market and the rigour of competition are joined with the forces of partnership and co-operation”. Corbyn has returned to the spirit of Labour pre-1995 constitution, even if he has not yet changed the wording.



 I had written a book entitled The Democratic Economy where I argued that socialists should support a permanent private sector in the economy. The book was published by Penguin in 1984. Another influential work at the time was Alec Nove’s Economics of Feasible Socialism, which also argued for a substantial role for markets.
I had written a book entitled The Democratic Economy where I argued that socialists should support a permanent private sector in the economy. The book was published by Penguin in 1984. Another influential work at the time was Alec Nove’s Economics of Feasible Socialism, which also argued for a substantial role for markets. There was a commitment to “political pluralism” and to “economic pluralism” involving “a variety of forms of common ownership … and the toleration of a small private sector including self-employed workers and other private firms.” The economy must be dominated by mechanisms of “democratic planning … but also accommodating a market mechanism in some areas.”
There was a commitment to “political pluralism” and to “economic pluralism” involving “a variety of forms of common ownership … and the toleration of a small private sector including self-employed workers and other private firms.” The economy must be dominated by mechanisms of “democratic planning … but also accommodating a market mechanism in some areas.”
 But while old ideas within Labour had survived, the structure of the party and its electoral base had changed enormously in the period from 1983 to 2015. Kinnock had relied on the moderating force of the trade unions, to fight the hard left and move the party toward electability. But by 2015 the unions had been gravely weakened and several had moved toward the hard left.
But while old ideas within Labour had survived, the structure of the party and its electoral base had changed enormously in the period from 1983 to 2015. Kinnock had relied on the moderating force of the trade unions, to fight the hard left and move the party toward electability. But by 2015 the unions had been gravely weakened and several had moved toward the hard left.
 But Blair still wanted to cooperate with the Liberal Democrats on several issues, including on electoral reform. He insisted that the two parties were natural allies, and they should not have gone their separate ways a hundred years earlier. In his first speech to a Labour conference after his landslide election victory,
But Blair still wanted to cooperate with the Liberal Democrats on several issues, including on electoral reform. He insisted that the two parties were natural allies, and they should not have gone their separate ways a hundred years earlier. In his first speech to a Labour conference after his landslide election victory,  While leading figures in his Cabinet such as Robin Cook, Mo Mowlam, Clare Short and Peter Mandelson supported electoral reform, Blair faced the implacable opposition of Chancellor Gordon Brown, Deputy Prime Minister and Secretary of State John Prescott, Home Secretary Jack Straw, numerous trade union leaders and an energetic campaign against proportional representation from Labour’s ranks.
While leading figures in his Cabinet such as Robin Cook, Mo Mowlam, Clare Short and Peter Mandelson supported electoral reform, Blair faced the implacable opposition of Chancellor Gordon Brown, Deputy Prime Minister and Secretary of State John Prescott, Home Secretary Jack Straw, numerous trade union leaders and an energetic campaign against proportional representation from Labour’s ranks. I can speak with a little authority here, because this was once my own major objection to proportional representation (PR). As loyal and active Labour party members, Peter Hain and I published a booklet in 1982 entitled Proportional Misrepresentation?
I can speak with a little authority here, because this was once my own major objection to proportional representation (PR). As loyal and active Labour party members, Peter Hain and I published a booklet in 1982 entitled Proportional Misrepresentation?  The Jenkins Commission reported in September 1998 and suggested the alternative vote top-up (AV+) system. Blair immediately faced intense opposition, from within his own Cabinet, from a large number of Labour MPs, from a large section of the Labour Party in the country, and from several trade unions.
The Jenkins Commission reported in September 1998 and suggested the alternative vote top-up (AV+) system. Blair immediately faced intense opposition, from within his own Cabinet, from a large number of Labour MPs, from a large section of the Labour Party in the country, and from several trade unions.
 But if a more proportional system had been in place in 2010, then a coalition between Labour and the Liberal Democrats would have had something like 366 seats, which would have been a clear overall majority. The Tories could have been kept out of power.
But if a more proportional system had been in place in 2010, then a coalition between Labour and the Liberal Democrats would have had something like 366 seats, which would have been a clear overall majority. The Tories could have been kept out of power. But a tiny consolation of this dismal entrapment is the time it gives us to debate the best system, which would offer something closer to proportionality, and would have a chance of convincing the electorate.
But a tiny consolation of this dismal entrapment is the time it gives us to debate the best system, which would offer something closer to proportionality, and would have a chance of convincing the electorate.










 Of course, Muslims and others suffer significant discrimination, in
Of course, Muslims and others suffer significant discrimination, in  But much of the political debate is about immigrant numbers. The Tories ignore the economic evidence and start a Dutch auction of targets, to stem numbers. A large part of the Labour Party, facing a seepage of its working class support to UKIP, moves in a similar direction.
But much of the political debate is about immigrant numbers. The Tories ignore the economic evidence and start a Dutch auction of targets, to stem numbers. A large part of the Labour Party, facing a seepage of its working class support to UKIP, moves in a similar direction.


 After coming to power in 1997, Labour Prime Minister
After coming to power in 1997, Labour Prime Minister 


 After several years he renounced his former extremism, but retained his Islamic faith. In an interview he revealed the segregated life of his upbringing:
After several years he renounced his former extremism, but retained his Islamic faith. In an interview he revealed the segregated life of his upbringing: Some on the Far Left disowned Butt for betraying the struggle against “Western imperialism”. He was also criticized by one member of the “Stop the War” movement, who is a leading supporter of the Muslim Brotherhood, for his “call to change the face of Islam” (Cohen 2007, pp. 371-2).
Some on the Far Left disowned Butt for betraying the struggle against “Western imperialism”. He was also criticized by one member of the “Stop the War” movement, who is a leading supporter of the Muslim Brotherhood, for his “call to change the face of Islam” (Cohen 2007, pp. 371-2). But the official government document outlining this policy mentions respect and tolerance for other races but fails to mention discrimination against women or gays. It rightly mentions the freedom to “choose and hold” any faith, but not the freedom to exit a religion without sanction. It mentions “individual liberty” only once, and fails to uphold freedom of non-violent expression, including when it may cause offence.
But the official government document outlining this policy mentions respect and tolerance for other races but fails to mention discrimination against women or gays. It rightly mentions the freedom to “choose and hold” any faith, but not the freedom to exit a religion without sanction. It mentions “individual liberty” only once, and fails to uphold freedom of non-violent expression, including when it may cause offence. Another problem here is not the values as such, but their nationalistic description as “British”. Democracy was not invented in Britain: Ancient Athens and Viking Iceland have much earlier precursors. The US and France have much earlier claims to the values of liberty and religious tolerance. Britain legally discriminated against Protestant nonconformists and Catholics until the nineteenth century, and it still bars any Catholic from becoming its sovereign.
Another problem here is not the values as such, but their nationalistic description as “British”. Democracy was not invented in Britain: Ancient Athens and Viking Iceland have much earlier precursors. The US and France have much earlier claims to the values of liberty and religious tolerance. Britain legally discriminated against Protestant nonconformists and Catholics until the nineteenth century, and it still bars any Catholic from becoming its sovereign.



 After his success in the Brexit referendum, Farage flew across the Atlantic to show his support for Donald Trump. At his August 2016 speech at a Donald Trump rally in Mississippi, Farage celebrated that Britain ‘chose not to be ruled by unelected old men in Brussels’. He drew parallels between the US and Britain, saying ordinary people everywhere had been ‘let down by government’. He was greeted by rapturous applause.
After his success in the Brexit referendum, Farage flew across the Atlantic to show his support for Donald Trump. At his August 2016 speech at a Donald Trump rally in Mississippi, Farage celebrated that Britain ‘chose not to be ruled by unelected old men in Brussels’. He drew parallels between the US and Britain, saying ordinary people everywhere had been ‘let down by government’. He was greeted by rapturous applause. Jeremy Corbyn is very different from Nigel Farage and Donald Trump. Corbyn is neither a racist nor a misogynist (
Jeremy Corbyn is very different from Nigel Farage and Donald Trump. Corbyn is neither a racist nor a misogynist (


